A Model-Based Derivative-Free Approach to Black-Box Adversarial Examples: BOBYQA
Paper and Code
Feb 24, 2020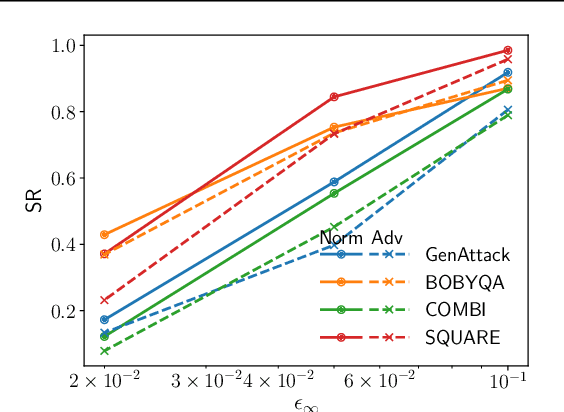
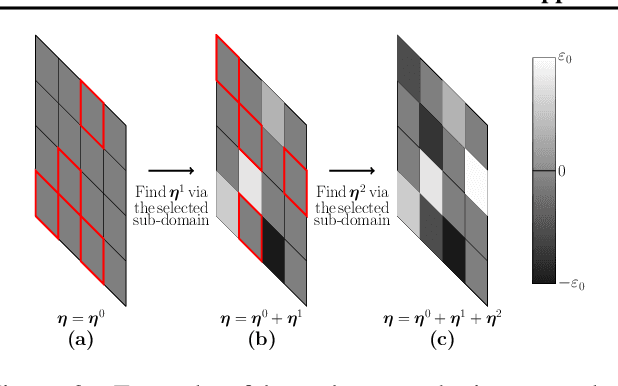
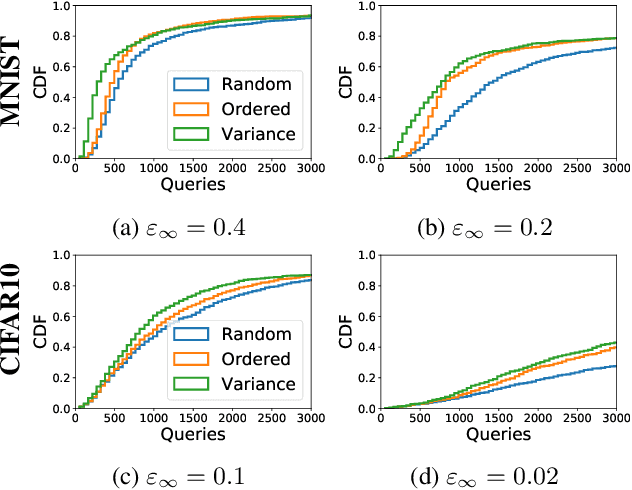
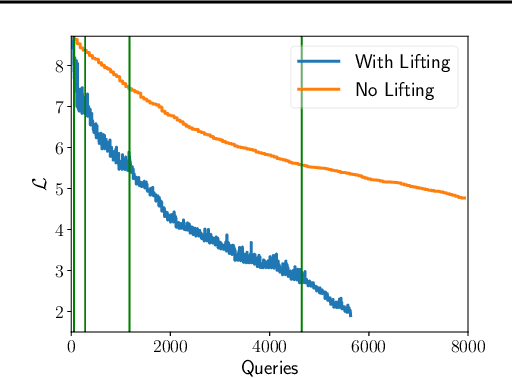
We demonstrate that model-based derivative free optimisation algorithms can generate adversarial targeted misclassification of deep networks using fewer network queries than non-model-based methods. Specifically, we consider the black-box setting, and show that the number of networks queries is less impacted by making the task more challenging either through reducing the allowed $\ell^{\infty}$ perturbation energy or training the network with defences against adversarial misclassification. We illustrate this by contrasting the BOBYQA algorithm with the state-of-the-art model-free adversarial targeted misclassification approaches based on genetic, combinatorial, and direct-search algorithms. We observe that for high $\ell^{\infty}$ energy perturbations on networks, the aforementioned simpler model-free methods require the fewest queries. In contrast, the proposed BOBYQA based method achieves state-of-the-art results when the perturbation energy decreases, or if the network is trained against adversarial perturbations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge