A Method to Model Conditional Distributions with Normalizing Flows
Paper and Code
Nov 05, 2019
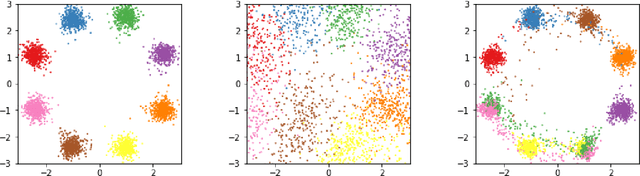


In this work, we investigate the use of normalizing flows to model conditional distributions. In particular, we use our proposed method to analyze inverse problems with invertible neural networks by maximizing the posterior likelihood. Our method uses only a single loss and is easy to train. This is an improvement on the previous method that solves similar inverse problems with invertible neural networks but which involves a combination of several loss terms with ad-hoc weighting. In addition, our method provides a natural framework to incorporate conditioning in normalizing flows, and therefore, we can train an invertible network to perform conditional generation. We analyze our method and perform a careful comparison with previous approaches. Simple experiments show the effectiveness of our method, and more comprehensive experimental evaluations are undergoing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge