A General Arbitration Model for Robust Human-Robot Shared Control with Multi-Source Uncertainty Modeling
Paper and Code
Mar 11, 2020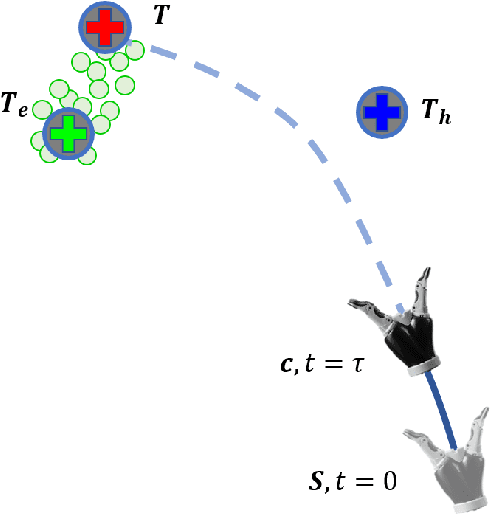
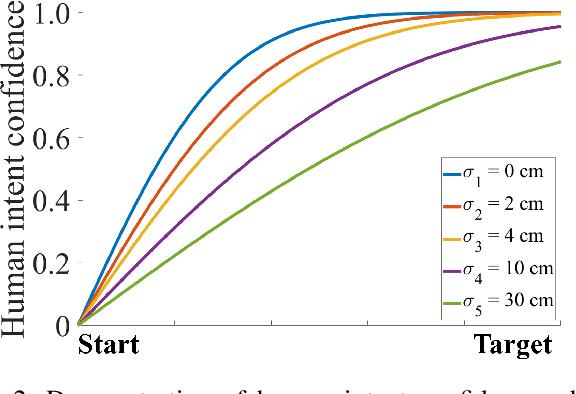

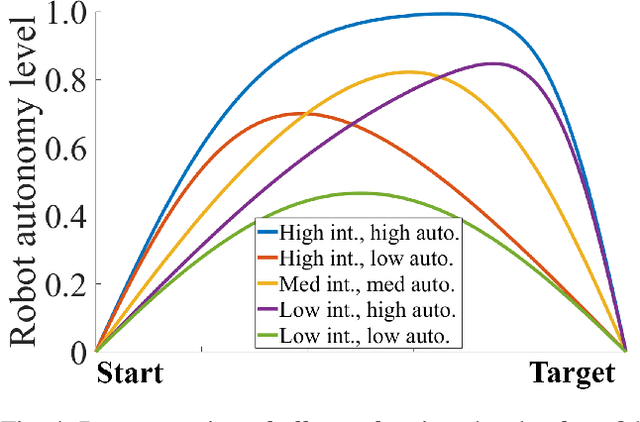
Shared control in teleoperation leverages both human and robot's strengths and has demonstrated great advantages of reducing the difficulties in teleoperating a robot and increasing the task performance. One fundamental question in shared control is how to effectively allocate the control power to the human and robot. Researchers have been subjectively defining the arbitrate policies following conflicting principles, which resulted in great inconsistency in the policies. We attribute this inconsistency to the inconsiderateness of the multi-resource uncertainty in the human-robot system. To fill the gap, we developed a multi-source uncertainty model that was applicable to various types of uncertainty in real world, and then a general arbitration model was developed to comprehensively fuse the uncertainty and regulate the arbitration weight assigned to the robotic agent. Beside traditional macro performance metrics, we introduced objective and quantitative metrics of robotic helpfulness and friendliness that evaluated the assistive robot's cooperation at micro and macro levels. Results from simulations and experiments showed the new arbitration model was more effective and friendly over the existing policies and was robust to coping with multi-source uncertainty. With this new arbitration model, we expect the increased adoption of human-robot shared control in practical and complex teleoperation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge