A Gap-Based Framework for Chinese Word Segmentation via Very Deep Convolutional Networks
Paper and Code
Dec 27, 2017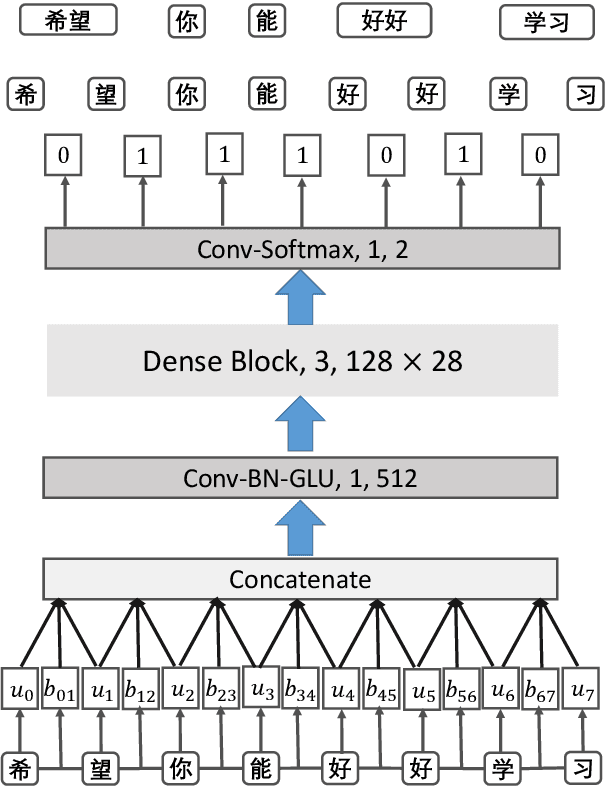
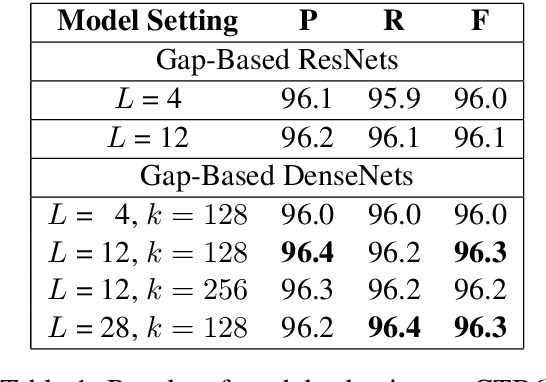
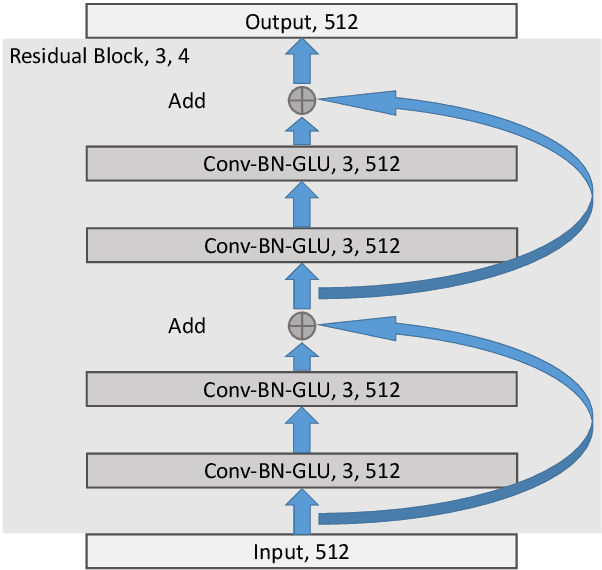
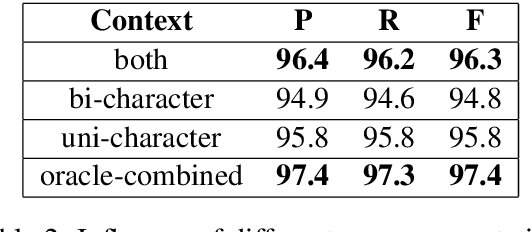
Most previous approaches to Chinese word segmentation can be roughly classified into character-based and word-based methods. The former regards this task as a sequence-labeling problem, while the latter directly segments character sequence into words. However, if we consider segmenting a given sentence, the most intuitive idea is to predict whether to segment for each gap between two consecutive characters, which in comparison makes previous approaches seem too complex. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a gap-based framework to implement this intuitive idea. Moreover, very deep convolutional neural networks, namely, ResNets and DenseNets, are exploited in our experiments. Results show that our approach outperforms the best character-based and word-based methods on 5 benchmarks, without any further post-processing module (e.g. Conditional Random Fields) nor beam search.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge