A Few More Examples May Be Worth Billions of Parameters
Paper and Code
Oct 08, 2021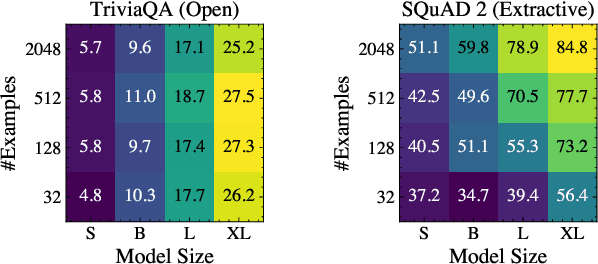
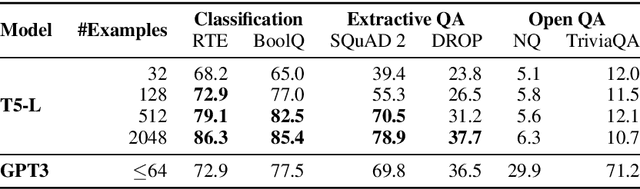
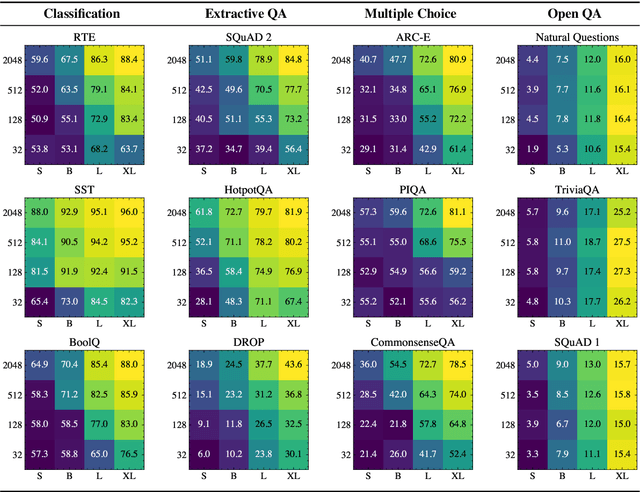
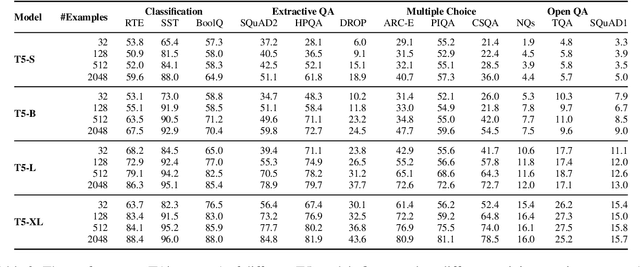
We investigate the dynamics of increasing the number of model parameters versus the number of labeled examples across a wide variety of tasks. Our exploration reveals that while scaling parameters consistently yields performance improvements, the contribution of additional examples highly depends on the task's format. Specifically, in open question answering tasks, enlarging the training set does not improve performance. In contrast, classification, extractive question answering, and multiple choice tasks benefit so much from additional examples that collecting a few hundred examples is often "worth" billions of parameters. We hypothesize that unlike open question answering, which involves recalling specific information, solving strategies for tasks with a more restricted output space transfer across examples, and can therefore be learned with small amounts of labeled data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge