A Deep Genetic Programming based Methodology for Art Media Classification Robust to Adversarial Perturbations
Paper and Code
Oct 03, 2020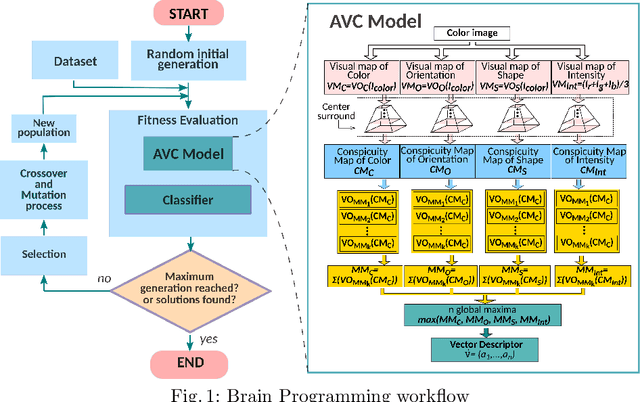
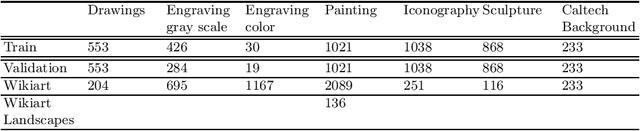
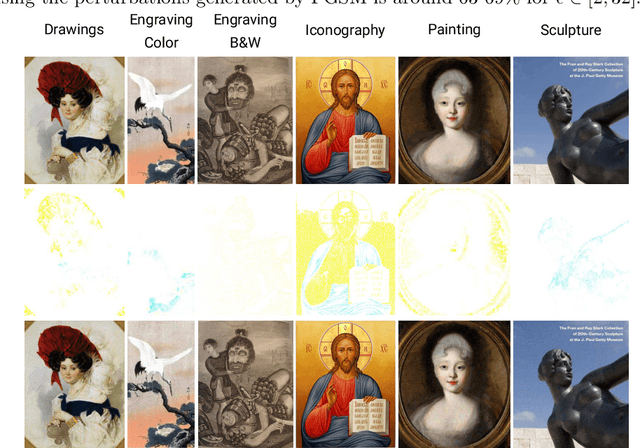
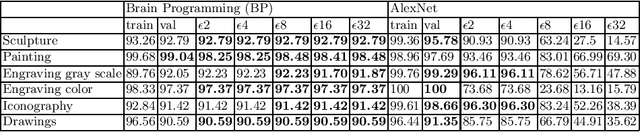
Art Media Classification problem is a current research area that has attracted attention due to the complex extraction and analysis of features of high-value art pieces. The perception of the attributes can not be subjective, as humans sometimes follow a biased interpretation of artworks while ensuring automated observation's trustworthiness. Machine Learning has outperformed many areas through its learning process of artificial feature extraction from images instead of designing handcrafted feature detectors. However, a major concern related to its reliability has brought attention because, with small perturbations made intentionally in the input image (adversarial attack), its prediction can be completely changed. In this manner, we foresee two ways of approaching the situation: (1) solve the problem of adversarial attacks in current neural networks methodologies, or (2) propose a different approach that can challenge deep learning without the effects of adversarial attacks. The first one has not been solved yet, and adversarial attacks have become even more complex to defend. Therefore, this work presents a Deep Genetic Programming method, called Brain Programming, that competes with deep learning and studies the transferability of adversarial attacks using two artworks databases made by art experts. The results show that the Brain Programming method preserves its performance in comparison with AlexNet, making it robust to these perturbations and competing to the performance of Deep Learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge