A Convex-Combinatorial Model for Planar Caging
Paper and Code
Sep 17, 2018
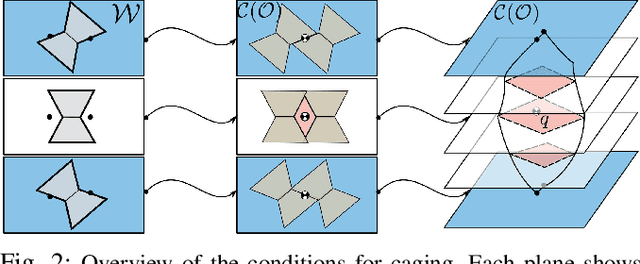
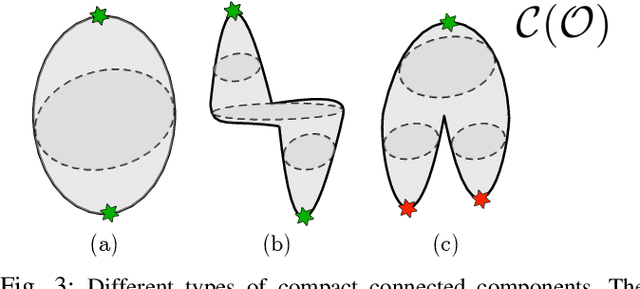
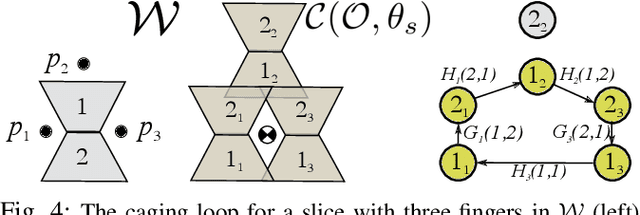
Caging is a promising tool which allows a robot to manipulate an object without directly reasoning about the contact dynamics involved. Furthermore, caging also provides useful guarantees in terms of robustness to uncertainty, and often serves as a way-point to a grasp. Unfortunately, previous work on caging is often based on computational geometry or discrete topology tools, causing restriction on gripper geometry, and difficulty on integration into larger manipulation frameworks. In this paper, we develop a convex-combinatorial model to characterize caging from an optimization perspective. More specifically, we study the configuration space of the object, where the fingers act as obstacles that enclose the configuration of the object. The convex-combinatorial nature of this approach provides guarantees on optimality, convergence and scalability, and its optimization nature makes it adaptable for further applications on robot manipulation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge