A Computational Model of the Short-Cut Rule for 2D Shape Decomposition
Paper and Code
Sep 07, 2014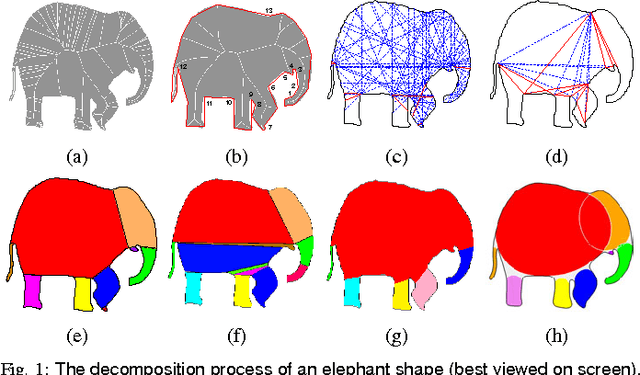
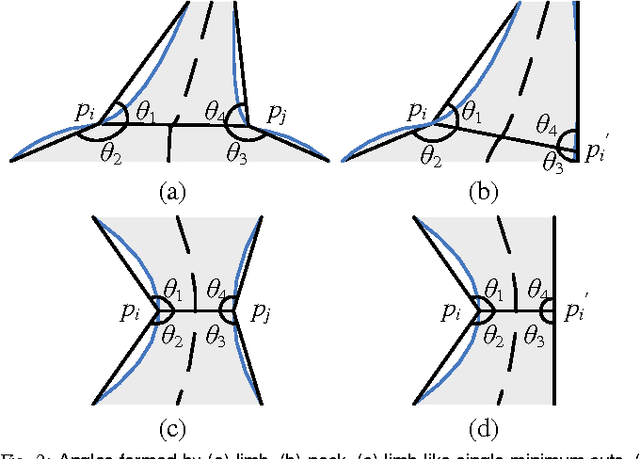
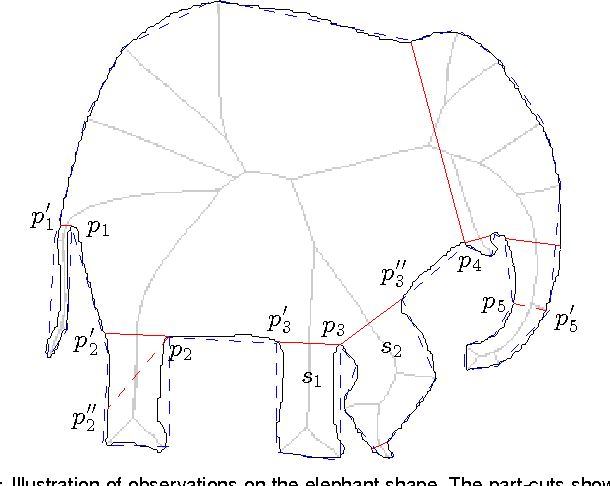
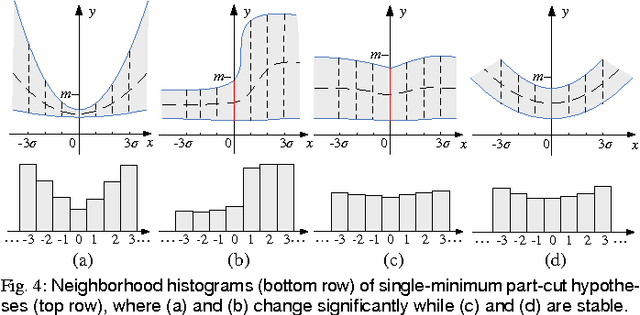
We propose a new 2D shape decomposition method based on the short-cut rule. The short-cut rule originates from cognition research, and states that the human visual system prefers to partition an object into parts using the shortest possible cuts. We propose and implement a computational model for the short-cut rule and apply it to the problem of shape decomposition. The model we proposed generates a set of cut hypotheses passing through the points on the silhouette which represent the negative minima of curvature. We then show that most part-cut hypotheses can be eliminated by analysis of local properties of each. Finally, the remaining hypotheses are evaluated in ascending length order, which guarantees that of any pair of conflicting cuts only the shortest will be accepted. We demonstrate that, compared with state-of-the-art shape decomposition methods, the proposed approach achieves decomposition results which better correspond to human intuition as revealed in psychological experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge