A Clinical Dataset for the Evaluation of Motion Planners in Medical Applications
Paper and Code
Oct 19, 2022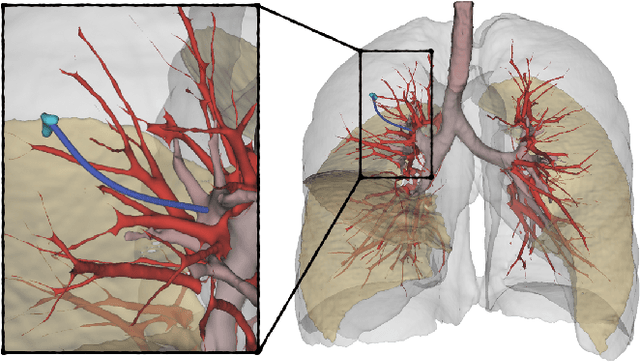
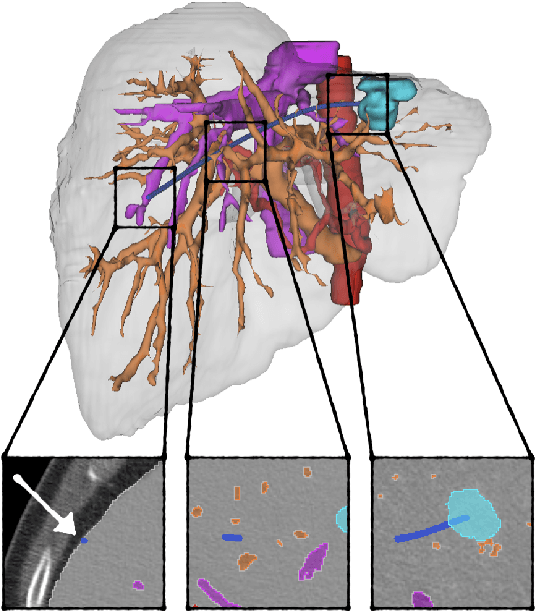
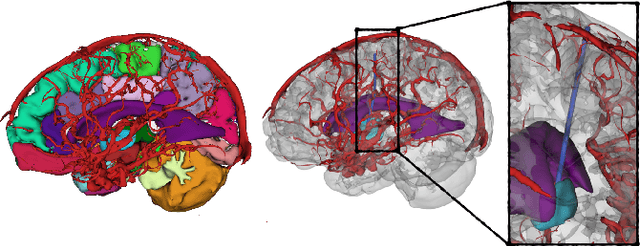
The prospect of using autonomous robots to enhance the capabilities of physicians and enable novel procedures has led to considerable efforts in developing medical robots and incorporating autonomous capabilities. Motion planning is a core component for any such system working in an environment that demands near perfect levels of safety, reliability, and precision. Despite the extensive and promising work that has gone into developing motion planners for medical robots, a standardized and clinically-meaningful way to compare existing algorithms and evaluate novel planners and robots is not well established. We present the Medical Motion Planning Dataset (Med-MPD), a publicly-available dataset of real clinical scenarios in various organs for the purpose of evaluating motion planners for minimally-invasive medical robots. Our goal is that this dataset serve as a first step towards creating a larger robust medical motion planning benchmark framework, advance research into medical motion planners, and lift some of the burden of generating medical evaluation data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge