A Causal Intervention Scheme for Semantic Segmentation of Quasi-periodic Cardiovascular Signals
Paper and Code
Sep 19, 2022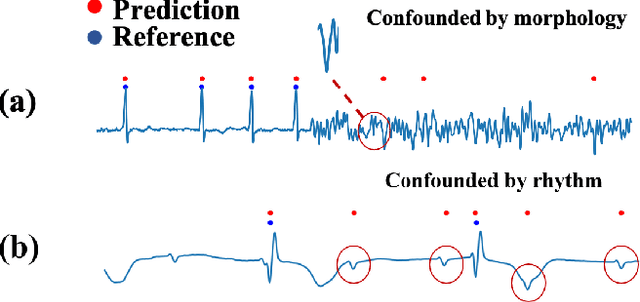
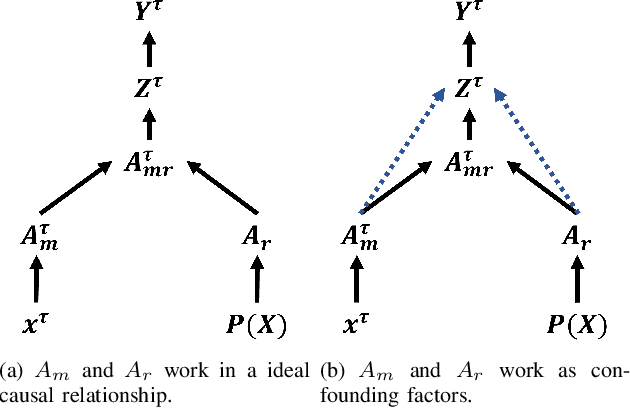
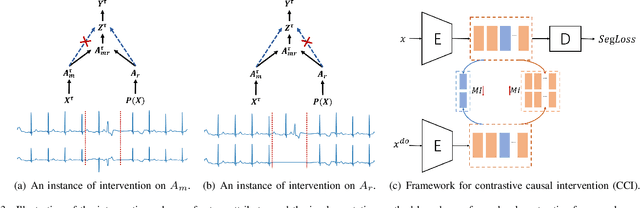
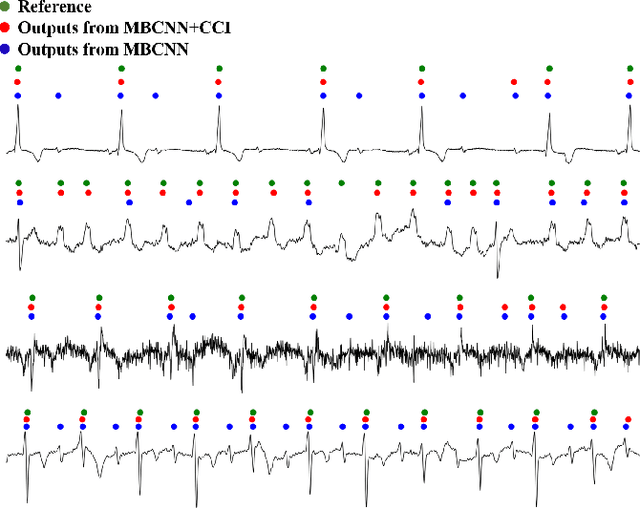
Precise segmentation is a vital first step to analyze semantic information of cardiac cycle and capture anomaly with cardiovascular signals. However, in the field of deep semantic segmentation, inference is often unilaterally confounded by the individual attribute of data. Towards cardiovascular signals, quasi-periodicity is the essential characteristic to be learned, regarded as the synthesize of the attributes of morphology (Am) and rhythm (Ar). Our key insight is to suppress the over-dependence on Am or Ar while the generation process of deep representations. To address this issue, we establish a structural causal model as the foundation to customize the intervention approaches on Am and Ar, respectively. In this paper, we propose contrastive causal intervention (CCI) to form a novel training paradigm under a frame-level contrastive framework. The intervention can eliminate the implicit statistical bias brought by the single attribute and lead to more objective representations. We conduct comprehensive experiments with the controlled condition for QRS location and heart sound segmentation. The final results indicate that our approach can evidently improve the performance by up to 0.41% for QRS location and 2.73% for heart sound segmentation. The efficiency of the proposed method is generalized to multiple databases and noisy signals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge