A-ACT: Action Anticipation through Cycle Transformations
Paper and Code
Apr 02, 2022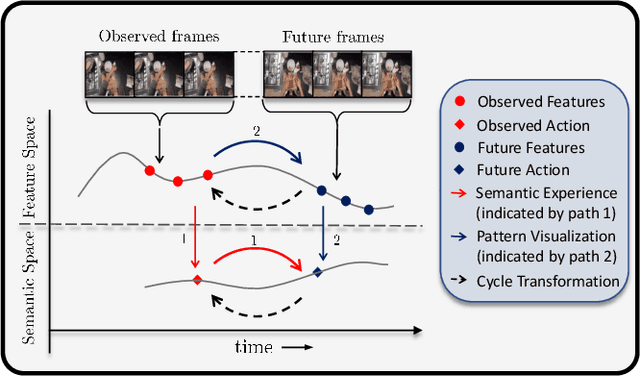
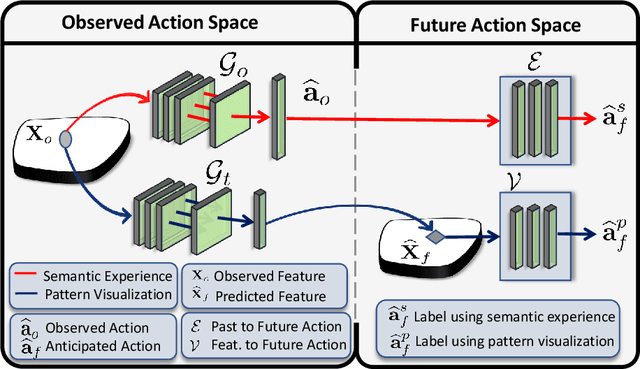
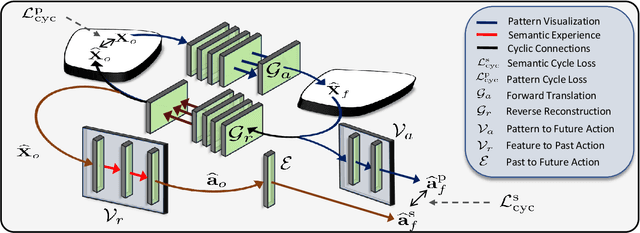
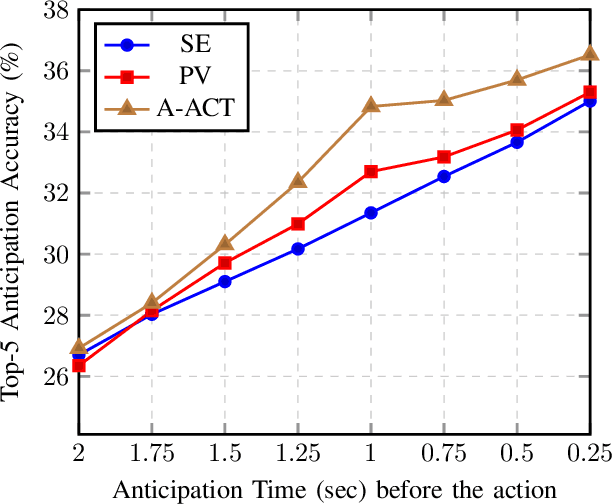
While action anticipation has garnered a lot of research interest recently, most of the works focus on anticipating future action directly through observed visual cues only. In this work, we take a step back to analyze how the human capability to anticipate the future can be transferred to machine learning algorithms. To incorporate this ability in intelligent systems a question worth pondering upon is how exactly do we anticipate? Is it by anticipating future actions from past experiences? Or is it by simulating possible scenarios based on cues from the present? A recent study on human psychology explains that, in anticipating an occurrence, the human brain counts on both systems. In this work, we study the impact of each system for the task of action anticipation and introduce a paradigm to integrate them in a learning framework. We believe that intelligent systems designed by leveraging the psychological anticipation models will do a more nuanced job at the task of human action prediction. Furthermore, we introduce cyclic transformation in the temporal dimension in feature and semantic label space to instill the human ability of reasoning of past actions based on the predicted future. Experiments on Epic-Kitchen, Breakfast, and 50Salads dataset demonstrate that the action anticipation model learned using a combination of the two systems along with the cycle transformation performs favorably against various state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge