2CoBel : An Efficient Belief Function Extension for Two-dimensional Continuous Spaces
Paper and Code
Mar 23, 2018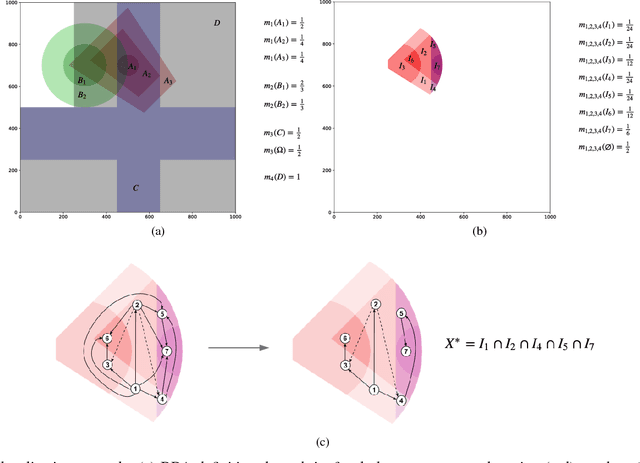
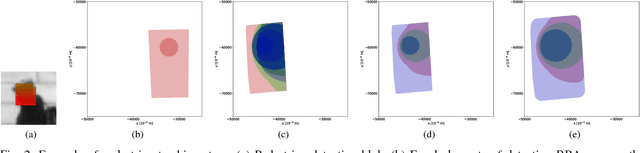
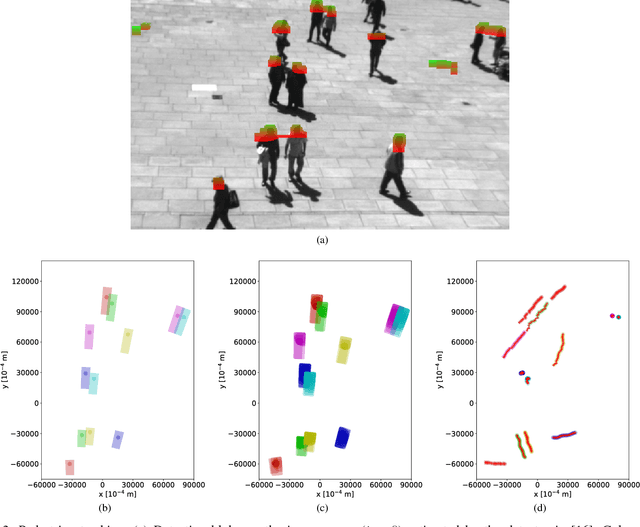
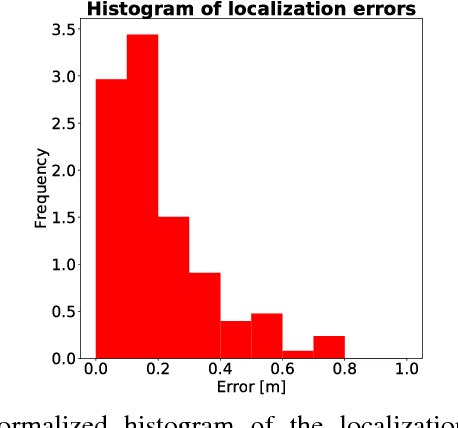
This paper introduces an innovative approach for handling 2D compound hypotheses within the Belief Function Theory framework. We propose a polygon-based generic rep- resentation which relies on polygon clipping operators. This approach allows us to account in the computational cost for the precision of the representation independently of the cardinality of the discernment frame. For the BBA combination and decision making, we propose efficient algorithms which rely on hashes for fast lookup, and on a topological ordering of the focal elements within a directed acyclic graph encoding their interconnections. Additionally, an implementation of the functionalities proposed in this paper is provided as an open source library. Experimental results on a pedestrian localization problem are reported. The experiments show that the solution is accurate and that it fully benefits from the scalability of the 2D search space granularity provided by our representation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge