Zvonko Kostanjčar
Robot See, Robot Do: Imitation Reward for Noisy Financial Environments
Nov 13, 2024



Abstract:The sequential nature of decision-making in financial asset trading aligns naturally with the reinforcement learning (RL) framework, making RL a common approach in this domain. However, the low signal-to-noise ratio in financial markets results in noisy estimates of environment components, including the reward function, which hinders effective policy learning by RL agents. Given the critical importance of reward function design in RL problems, this paper introduces a novel and more robust reward function by leveraging imitation learning, where a trend labeling algorithm acts as an expert. We integrate imitation (expert's) feedback with reinforcement (agent's) feedback in a model-free RL algorithm, effectively embedding the imitation learning problem within the RL paradigm to handle the stochasticity of reward signals. Empirical results demonstrate that this novel approach improves financial performance metrics compared to traditional benchmarks and RL agents trained solely using reinforcement feedback.
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robust Goal-Based Wealth Management
Jul 25, 2023Abstract:Goal-based investing is an approach to wealth management that prioritizes achieving specific financial goals. It is naturally formulated as a sequential decision-making problem as it requires choosing the appropriate investment until a goal is achieved. Consequently, reinforcement learning, a machine learning technique appropriate for sequential decision-making, offers a promising path for optimizing these investment strategies. In this paper, a novel approach for robust goal-based wealth management based on deep reinforcement learning is proposed. The experimental results indicate its superiority over several goal-based wealth management benchmarks on both simulated and historical market data.
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Market Making Under a Hawkes Process-Based Limit Order Book Model
Jul 20, 2022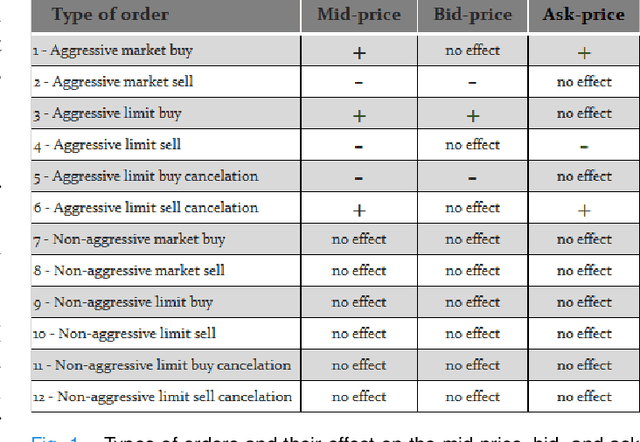
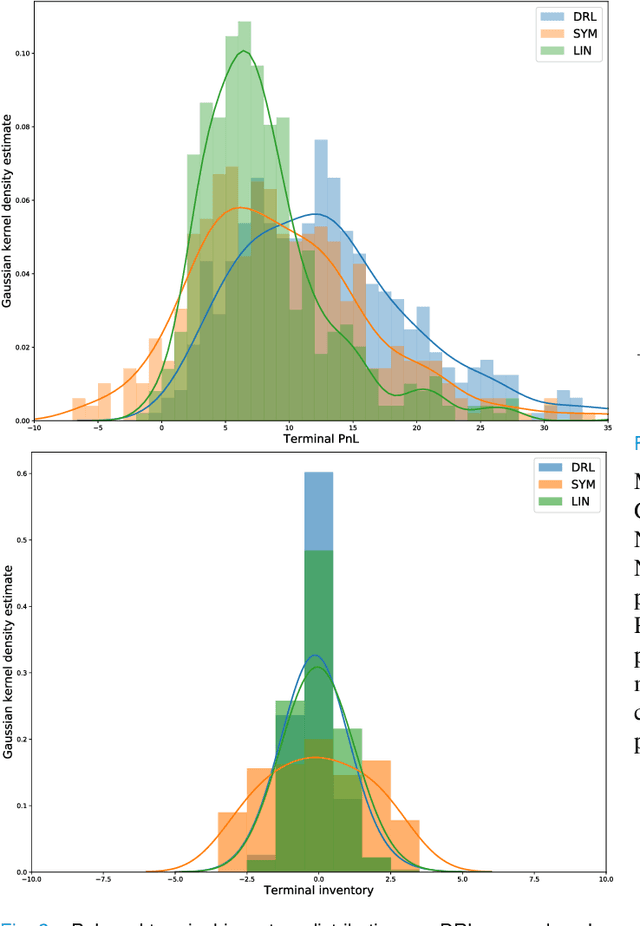
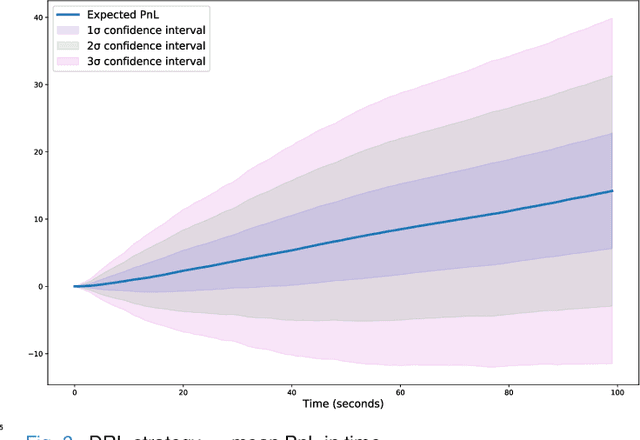
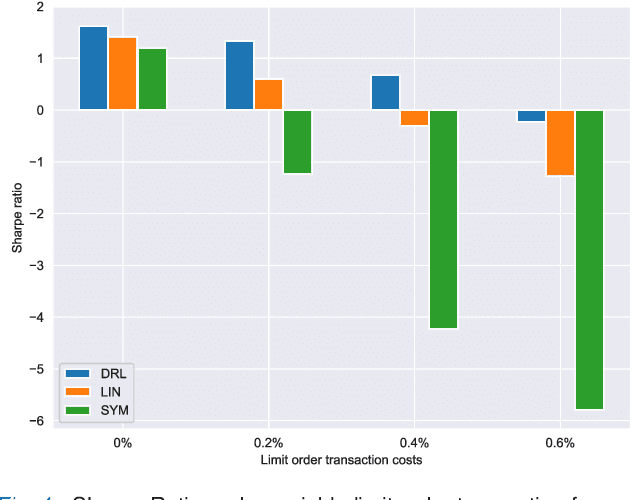
Abstract:The stochastic control problem of optimal market making is among the central problems in quantitative finance. In this paper, a deep reinforcement learning-based controller is trained on a weakly consistent, multivariate Hawkes process-based limit order book simulator to obtain market making controls. The proposed approach leverages the advantages of Monte Carlo backtesting and contributes to the line of research on market making under weakly consistent limit order book models. The ensuing deep reinforcement learning controller is compared to multiple market making benchmarks, with the results indicating its superior performance with respect to various risk-reward metrics, even under significant transaction costs.
* 6 pages, 4 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge