Zulqarnain Bin Ashraf
Dual-Diode Unified SWIPT for High Data Rates with Adaptive Detection
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Due to their low-complexity and energy-efficiency, unified simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (U-SWIPT) receivers are especially suitable for low-power Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Towards accurately modeling practical operating conditions, in this study, we provide a unified transient framework for a dual-diode U-SWIPT that jointly accounts for diode nonlinearity and capacitor-induced memory effects. The proposed model accurately describes the inherent time dependence of the rectifier, highlighting its fundamental impact on both energy harvesting (EH) and information decoding (ID) processes. Based on the provided memory-aware model, we design a low-complexity adaptive detector that learns the nonlinear state transition dynamics and performs decision-directed detection with linear complexity. The proposed detection scheme approaches maximum likelihood sequence detection (MLSD) performance in memory-dominated regimes, while avoiding the exponential search required by classical sequence detection. Overall, these results demonstrate that properly exploiting rectifier memory provides a better tradeoff between data rate and reliability for U-SWIPT receivers.
Integrated SWIPT Receiver with Memory Effects: Circuit Analysis and Information Detection
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Wireless power transfer has been proposed as a key technology for the foreseen machine type networks. A main challenge in the research community lies in acquiring a simple yet accurate model to capture the energy harvesting performance. In this work, we focus on a half-wave rectifier and based on circuit analysis we provide the actual output of the circuit which accounts for the memory introduced by the capacitor. The provided expressions are also validated through circuit simulations on ADS. Then, the half-wave rectifier is used as an integrated simultaneous wireless information and power transfer receiver where the circuit's output is used for decoding information based on amplitude modulation. We investigate the bit error rate performance based on two detection schemes: (i) symbol-by-symbol maximum likelihood (ML); and (ii) ML sequence detection (MLSD). We show that the symbol period is critical due to the intersymbol interference induced by circuit. Our results reveal that MLSD is necessary towards improving the error probability and achieving higher data rates.
Performance Analysis of 6G Multiuser Massive MIMO-OFDM THz Wireless Systems with Hybrid Beamforming under Intercarrier Interference
Jan 22, 2024Abstract:6G networks are expected to provide more diverse capabilities than their predecessors and are likely to support applications beyond current mobile applications, such as virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR), AI, and the Internet of Things (IoT). In contrast to typical multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, THz MIMO precoding cannot be conducted totally at baseband using digital precoders due to the restricted number of signal mixers and analog-to-digital converters that can be supported due to their cost and power consumption. In this thesis, we analyzed the performance of multiuser massive MIMO-OFDM THz wireless systems with hybrid beamforming. Carrier frequency offset (CFO) is one of the most well-known disturbances for OFDM. For practicality, we accounted for CFO, which results in Intercarrier Interference. Incorporating the combined impact of molecular absorption, high sparsity, and multi-path fading, we analyzed a three-dimensional wideband THz channel and the carrier frequency offset in multi-carrier systems. With this model, we first presented a two-stage wideband hybrid beamforming technique comprising Riemannian manifolds optimization for analog beamforming and then a zero-forcing (ZF) approach for digital beamforming. We adjusted the objective function to reduce complexity, and instead of maximizing the bit rate, we determined parameters by minimizing interference. Numerical results demonstrate the significance of considering ICI for practical implementation for the THz system. We demonstrated how our change in problem formulation minimizes latency without compromising results. We also evaluated spectral efficiency by varying the number of RF chains and antennas. The spectral efficiency grows as the number of RF chains and antennas increases, but the spectral efficiency of antennas declines when the number of users increases.
A CNN-LSTM-based Fusion Separation Deep Neural Network for 6G Ultra-Massive MIMO Hybrid Beamforming
Sep 26, 2022
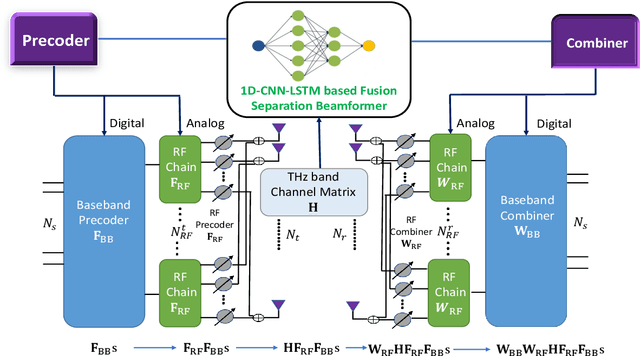
Abstract:In the sixth-generation (6G) cellular networks, hybrid beamforming would be a real-time optimization problem that is becoming progressively more challenging. Although numerical computation-based iterative methods such as the minimal mean square error (MMSE) and the alternative manifold-optimization (Alt-Min) can already attain near-optimal performance, their computational cost renders them unsuitable for real-time applications. However, recent studies have demonstrated that machine learning techniques like deep neural networks (DNN) can learn the mapping done by those algorithms between channel state information (CSI) and near-optimal resource allocation, and then approximate this mapping in near real-time. In light of this, we investigate various DNN architectures for beamforming challenges in the terahertz (THz) band for ultra-massive multiple-input multiple-output (UM-MIMO) and explore their contextual mathematical modeling. Specifically, we design a sophisticated 1D convolutional neural network and long short-term memory (1D CNN-LSTM) based fusion-separation scheme, which can approach the performance of the Alt-Min algorithm in terms of spectral efficiency (SE) and, at the same time, use significantly less computational effort. Simulation results indicate that the proposed system can attain almost the same level of SE as that of the numerical iterative algorithms, while incurring a substantial reduction in computational cost. Our DNN-based approach also exhibits exceptional adaptability to diverse network setups and high scalability. Although the current model only addresses the fully connected hybrid architecture, our approach can also be expanded to address a variety of other network topologies. INDEX TERMS 6G, CNN, Hybrid Beamforming, LSTM, UM-MIMO
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge