Zoltan Szlavik
Access to care: analysis of the geographical distribution of healthcare using Linked Open Data
Apr 11, 2022
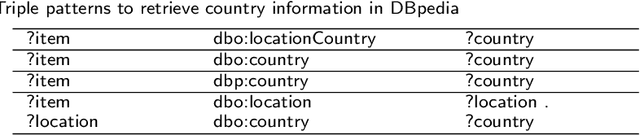
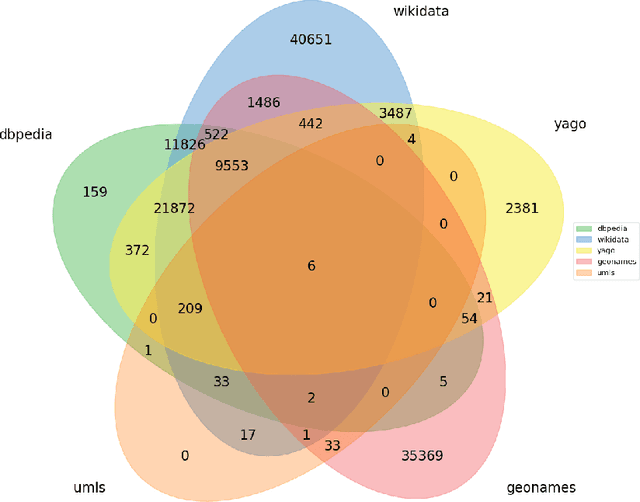
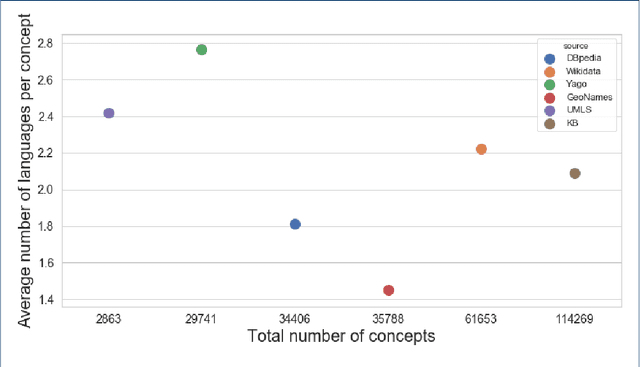
Abstract:Background: Access to medical care is strongly dependent on resource allocation, such as the geographical distribution of medical facilities. Nevertheless, this data is usually restricted to country official documentation, not available to the public. While some medical facilities' data is accessible as semantic resources on the Web, it is not consistent in its modeling and has yet to be integrated into a complete, open, and specialized repository. This work focuses on generating a comprehensive semantic dataset of medical facilities worldwide containing extensive information about such facilities' geo-location. Results: For this purpose, we collect, align, and link various open-source databases where medical facilities' information may be present. This work allows us to evaluate each data source along various dimensions, such as completeness, correctness, and interlinking with other sources, all critical aspects of current knowledge representation technologies. Conclusions: Our contributions directly benefit stakeholders in the biomedical and health domain (patients, healthcare professionals, companies, regulatory authorities, and researchers), who will now have a better overview of the access to and distribution of medical facilities.
Unfairness towards subjective opinions in Machine Learning
Nov 06, 2019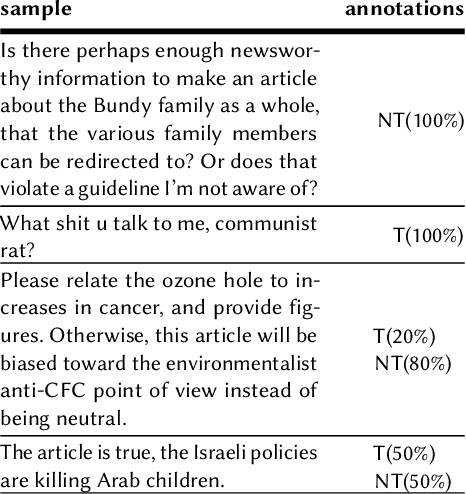
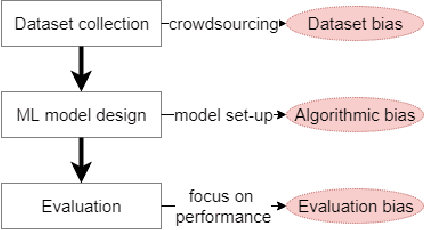
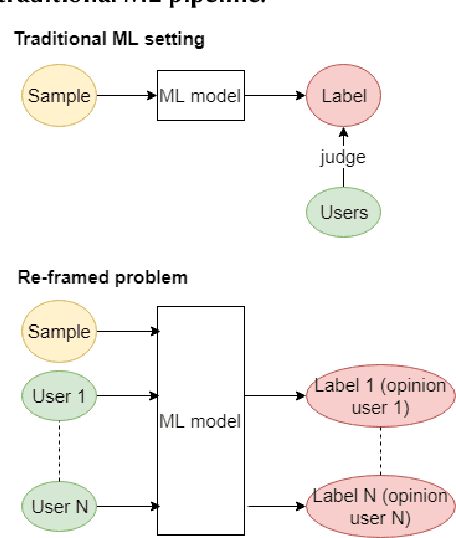
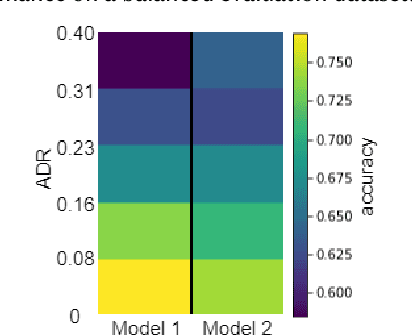
Abstract:Despite the high interest for Machine Learning (ML) in academia and industry, many issues related to the application of ML to real-life problems are yet to be addressed. Here we put forward one limitation which arises from a lack of adaptation of ML models and datasets to specific applications. We formalise a new notion of unfairness as exclusion of opinions. We propose ways to quantify this unfairness, and aid understanding its causes through visualisation. These insights into the functioning of ML-based systems hint at methods to mitigate unfairness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge