Ziyi Xi
AI-Generated Image Detection using a Cross-Attention Enhanced Dual-Stream Network
Jun 12, 2023

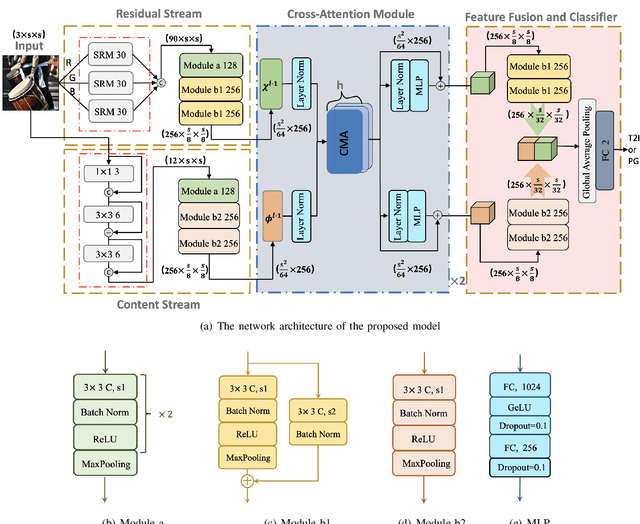

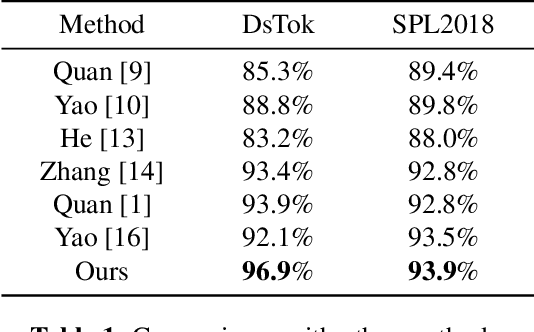
Abstract:With the rapid evolution of AI Generated Content (AIGC), forged images produced through this technology are inherently more deceptive and require less human intervention compared to traditional Computer-generated Graphics (CG). However, owing to the disparities between CG and AIGC, conventional CG detection methods tend to be inadequate in identifying AIGC-produced images. To address this issue, our research concentrates on the text-to-image generation process in AIGC. Initially, we first assemble two text-to-image databases utilizing two distinct AI systems, DALLE2 and DreamStudio. Aiming to holistically capture the inherent anomalies produced by AIGC, we develope a robust dual-stream network comprised of a residual stream and a content stream. The former employs the Spatial Rich Model (SRM) to meticulously extract various texture information from images, while the latter seeks to capture additional forged traces in low frequency, thereby extracting complementary information that the residual stream may overlook. To enhance the information exchange between these two streams, we incorporate a cross multi-head attention mechanism. Numerous comparative experiments are performed on both databases, and the results show that our detection method consistently outperforms traditional CG detection techniques across a range of image resolutions. Moreover, our method exhibits superior performance through a series of robustness tests and cross-database experiments. When applied to widely recognized traditional CG benchmarks such as SPL2018 and DsTok, our approach significantly exceeds the capabilities of other existing methods in the field of CG detection.
Dual Stream Computer-Generated Image Detection Network Based On Channel Joint And Softpool
Jul 07, 2022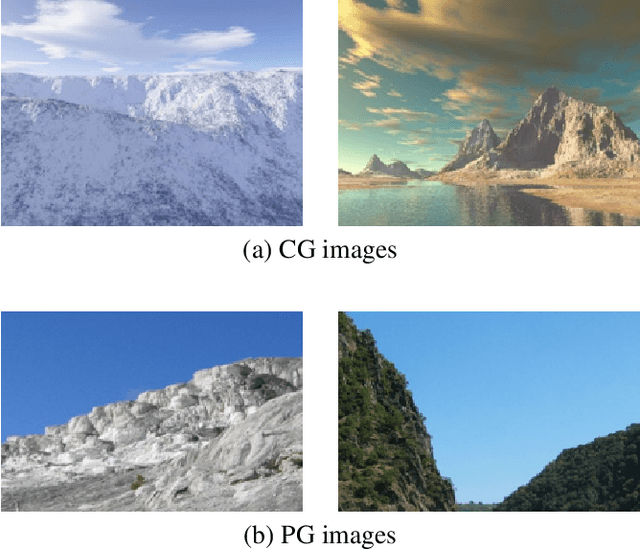
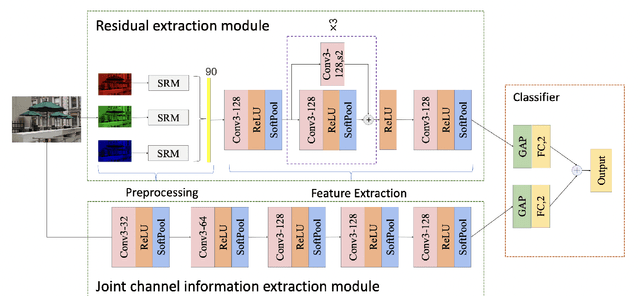
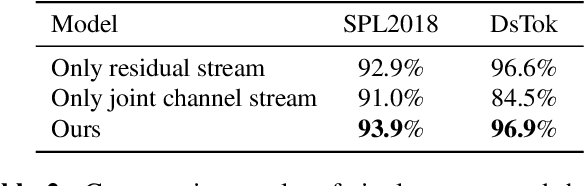
Abstract:With the development of computer graphics technology, the images synthesized by computer software become more and more closer to the photographs. While computer graphics technology brings us a grand visual feast in the field of games and movies, it may also be utilized by someone with bad intentions to guide public opinions and cause political crisis or social unrest. Therefore, how to distinguish the computer-generated graphics (CG) from the photographs (PG) has become an important topic in the field of digital image forensics. This paper proposes a dual stream convolutional neural network based on channel joint and softpool. The proposed network architecture includes a residual module for extracting image noise information and a joint channel information extraction module for capturing the shallow semantic information of image. In addition, we also design a residual structure to enhance feature extraction and reduce the loss of information in residual flow. The joint channel information extraction module can obtain the shallow semantic information of the input image which can be used as the information supplement block of the residual module. The whole network uses SoftPool to reduce the information loss of down-sampling for image. Finally, we fuse the two flows to get the classification results. Experiments on SPL2018 and DsTok show that the proposed method outperforms existing methods, especially on the DsTok dataset. For example, the performance of our model surpasses the state-of-the-art by a large margin of 3%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge