Zichao Wei
On the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Generalization in Neural Networks
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Why do neural networks fail to generalize addition from 16-digit to 32-digit numbers, while a child who learns the rule can apply it to arbitrarily long sequences? We argue that this failure is not an engineering problem but a violation of physical postulates. Drawing inspiration from physics, we identify three constraints that any generalizing system must satisfy: (1) Locality -- information propagates at finite speed; (2) Symmetry -- the laws of computation are invariant across space and time; (3) Stability -- the system converges to discrete attractors that resist noise accumulation. From these postulates, we derive -- rather than design -- the Spatiotemporal Evolution with Attractor Dynamics (SEAD) architecture: a neural cellular automaton where local convolutional rules are iterated until convergence. Experiments on three tasks validate our theory: (1) Parity -- demonstrating perfect length generalization via light-cone propagation; (2) Addition -- achieving scale-invariant inference from L=16 to L=1 million with 100% accuracy, exhibiting input-adaptive computation; (3) Rule 110 -- learning a Turing-complete cellular automaton without trajectory divergence. Our results suggest that the gap between statistical learning and logical reasoning can be bridged -- not by scaling parameters, but by respecting the physics of computation.
Autoregressive, Yet Revisable: In Decoding Revision for Secure Code Generation
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) based code generation is predominantly formulated as a strictly monotonic process, appending tokens linearly to an immutable prefix. This formulation contrasts to the cognitive process of programming, which is inherently interleaved with forward generation and on-the-fly revision. While prior works attempt to introduce revision via post-hoc agents or external static tools, they either suffer from high latency or fail to leverage the model's intrinsic semantic reasoning. In this paper, we propose Stream of Revision, a paradigm shift that elevates code generation from a monotonic stream to a dynamic, self-correcting trajectory by leveraging model's intrinsic capabilities. We introduce specific action tokens that enable the model to seamlessly backtrack and edit its own history within a single forward pass. By internalizing the revision loop, our framework Stream of Revision allows the model to activate its latent capabilities just-in-time without external dependencies. Empirical results on secure code generation show that Stream of Revision significantly reduces vulnerabilities with minimal inference overhead.
Using eye tracking to investigate what native Chinese speakers notice about linguistic landscape images
Dec 16, 2023Abstract:Linguistic landscape is an important field in sociolinguistic research. Eye tracking technology is a common technology in psychological research. There are few cases of using eye movement to study linguistic landscape. This paper uses eye tracking technology to study the actual fixation of the linguistic landscape and finds that in the two dimensions of fixation time and fixation times, the fixation of native Chinese speakers to the linguistic landscape is higher than that of the general landscape. This paper argues that this phenomenon is due to the higher information density of linguistic landscapes. At the same time, the article also discusses other possible reasons for this phenomenon.
An Extensive Study on Adversarial Attack against Pre-trained Models of Code
Nov 23, 2023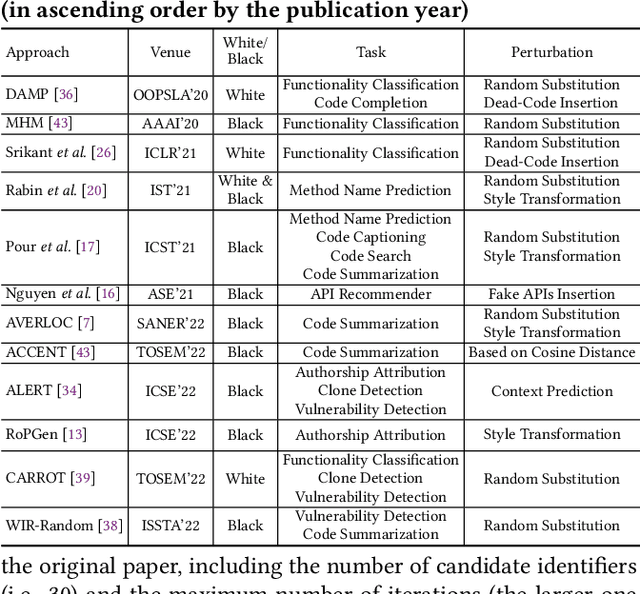
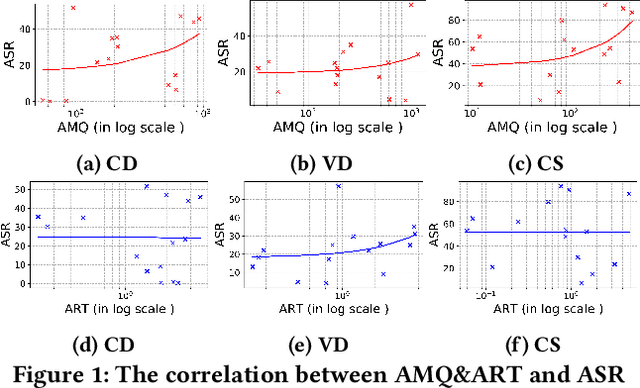
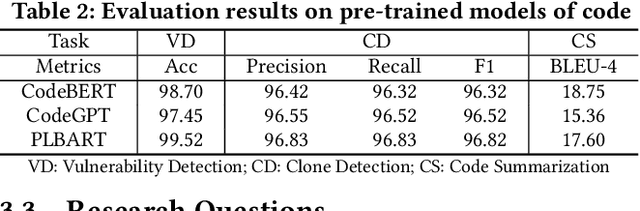
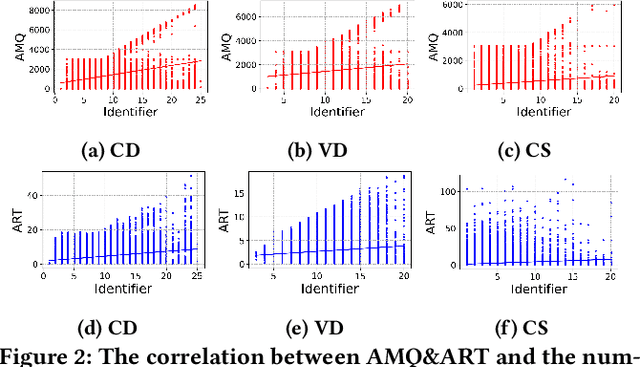
Abstract:Transformer-based pre-trained models of code (PTMC) have been widely utilized and have achieved state-of-the-art performance in many mission-critical applications. However, they can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks through identifier substitution or coding style transformation, which can significantly degrade accuracy and may further incur security concerns. Although several approaches have been proposed to generate adversarial examples for PTMC, the effectiveness and efficiency of such approaches, especially on different code intelligence tasks, has not been well understood. To bridge this gap, this study systematically analyzes five state-of-the-art adversarial attack approaches from three perspectives: effectiveness, efficiency, and the quality of generated examples. The results show that none of the five approaches balances all these perspectives. Particularly, approaches with a high attack success rate tend to be time-consuming; the adversarial code they generate often lack naturalness, and vice versa. To address this limitation, we explore the impact of perturbing identifiers under different contexts and find that identifier substitution within for and if statements is the most effective. Based on these findings, we propose a new approach that prioritizes different types of statements for various tasks and further utilizes beam search to generate adversarial examples. Evaluation results show that it outperforms the state-of-the-art ALERT in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency while preserving the naturalness of the generated adversarial examples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge