Zhuoxin Chen
Survey of Data-driven Newsvendor: Unified Analysis and Spectrum of Achievable Regrets
Sep 05, 2024
Abstract:In the Newsvendor problem, the goal is to guess the number that will be drawn from some distribution, with asymmetric consequences for guessing too high vs. too low. In the data-driven version, the distribution is unknown, and one must work with samples from the distribution. Data-driven Newsvendor has been studied under many variants: additive vs. multiplicative regret, high probability vs. expectation bounds, and different distribution classes. This paper studies all combinations of these variants, filling in many gaps in the literature and simplifying many proofs. In particular, we provide a unified analysis based on the notion of clustered distributions, which in conjunction with our new lower bounds, shows that the entire spectrum of regrets between $1/\sqrt{n}$ and $1/n$ can be possible.
Decoupled Federated Learning on Long-Tailed and Non-IID data with Feature Statistics
Mar 13, 2024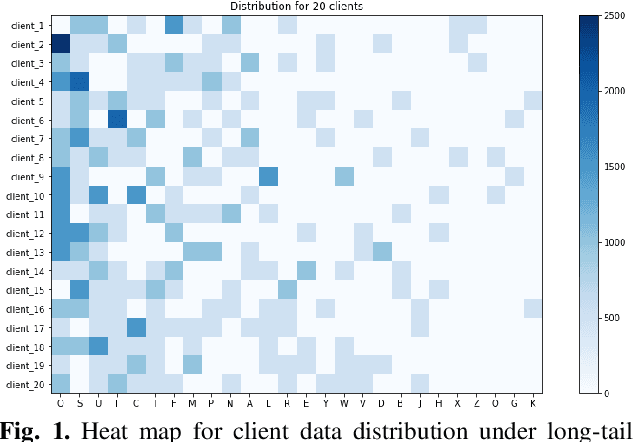
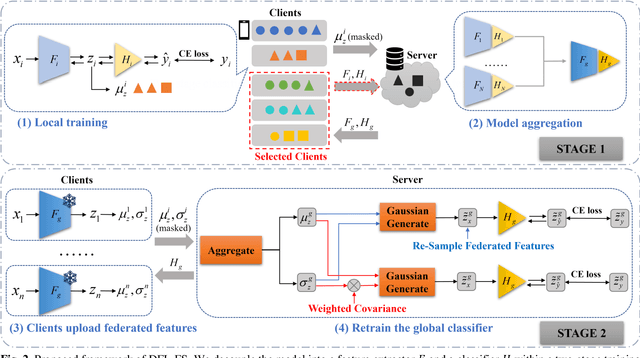
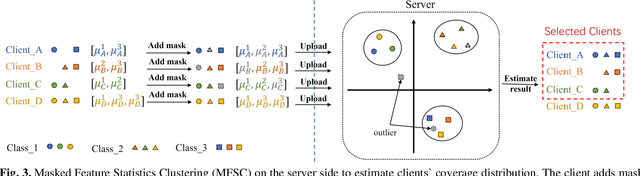
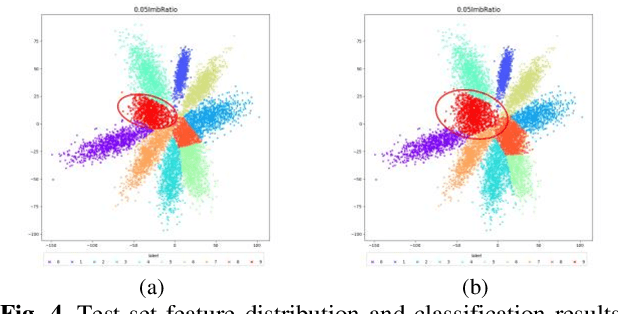
Abstract:Federated learning is designed to enhance data security and privacy, but faces challenges when dealing with heterogeneous data in long-tailed and non-IID distributions. This paper explores an overlooked scenario where tail classes are sparsely distributed over a few clients, causing the models trained with these classes to have a lower probability of being selected during client aggregation, leading to slower convergence rates and poorer model performance. To address this issue, we propose a two-stage Decoupled Federated learning framework using Feature Statistics (DFL-FS). In the first stage, the server estimates the client's class coverage distributions through masked local feature statistics clustering to select models for aggregation to accelerate convergence and enhance feature learning without privacy leakage. In the second stage, DFL-FS employs federated feature regeneration based on global feature statistics and utilizes resampling and weighted covariance to calibrate the global classifier to enhance the model's adaptability to long-tailed data distributions. We conducted experiments on CIFAR10-LT and CIFAR100-LT datasets with various long-tailed rates. The results demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both accuracy and convergence rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge