Zhou He
FDA Jamming Against Airborne Phased-MIMO Radar-Part II: Jamming STAP Performance Analysis
Aug 06, 2024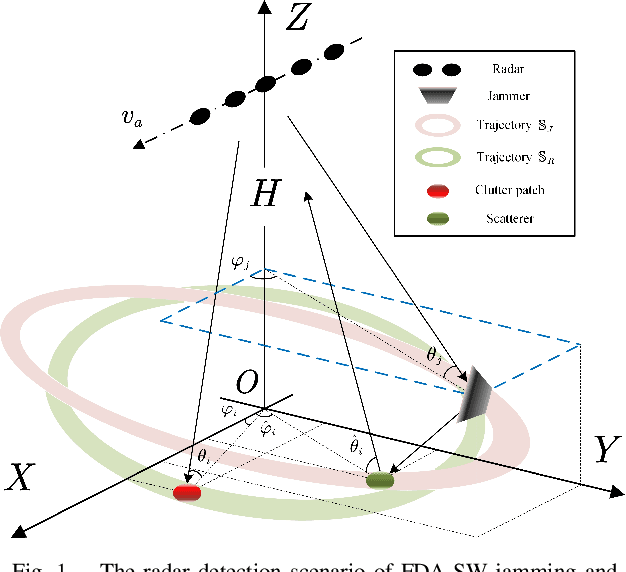
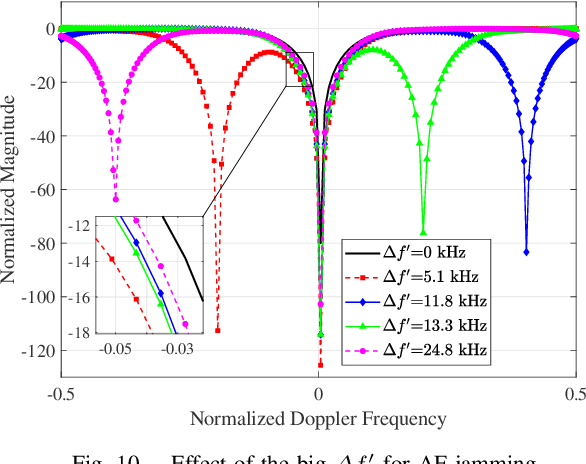
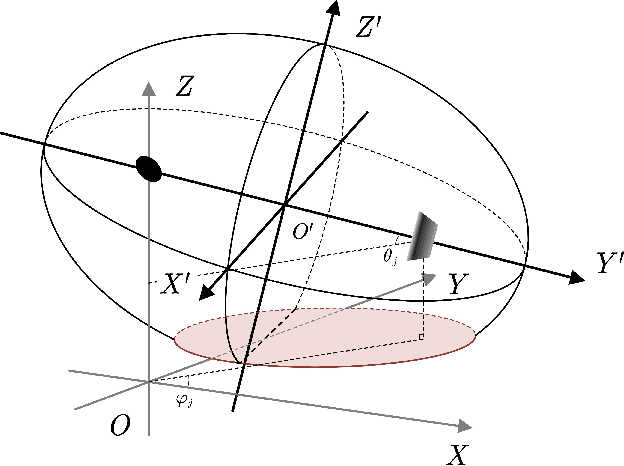
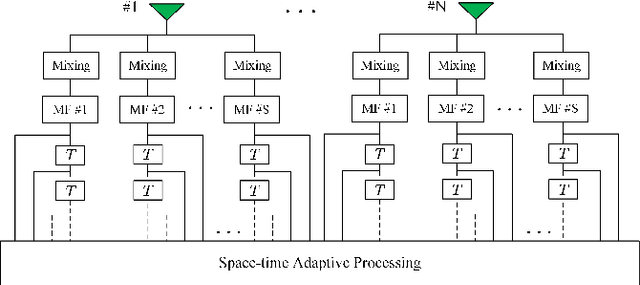
Abstract:The first part of this series introduced the effectiveness of frequency diverse array (FDA) jamming through direct wave propagation in countering airborne phased multiple-input multiple-output (Phased-MIMO) radar. This part focuses on the effectiveness of FDA scattered wave (FDA-SW) jamming on the space-time adaptive processing (STAP) for airborne phased-MIMO radar. Distinguished from the clutter signals, the ground equidistant scatterers of FDA-SW jamming constitute an elliptical ring, whose trajectory equations are mathematically derived to further determine the spatial frequency and Doppler frequency. For the phased-MIMO radar with different transmitting partitions, the effects of jamming frequency offset of FDA-SW on the clutter rank and STAP performance are discussed. Theoretical analysis provides the variation interval of clutter rank and the relationship between the jamming frequency offset and the improvement factor (IF) notch of phased-MIMO-STAP. Importantly, the requirements of jamming frequency offset for both two-part applications are discussed in this part. Numerical results verify these mathematical findings and validate the effectiveness of the proposed FDA jamming in countering the phased-MIMO radar.
3D Deep Affine-Invariant Shape Learning for Brain MR Image Segmentation
Sep 17, 2019



Abstract:Recent advancements in medical image segmentation techniques have achieved compelling results. However, most of the widely used approaches do not take into account any prior knowledge about the shape of the biomedical structures being segmented. More recently, some works have presented approaches to incorporate shape information. However, many of them are indeed introducing more parameters to the segmentation network to learn the general features, which any segmentation network is able learn, instead of specifically shape features. In this paper, we present a novel approach that seamlessly integrates the shape information into the segmentation network. Experiments on human brain MRI segmentation demonstrate that our approach can achieve a lower Hausdorff distance and higher Dice coefficient than the state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge