Zhongxiang Zhao
Tricolore: Multi-Behavior User Profiling for Enhanced Candidate Generation in Recommender Systems
May 04, 2025
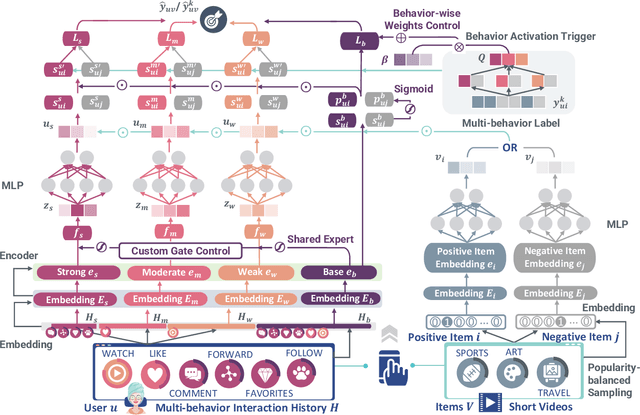
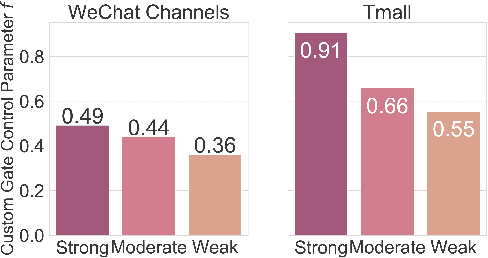
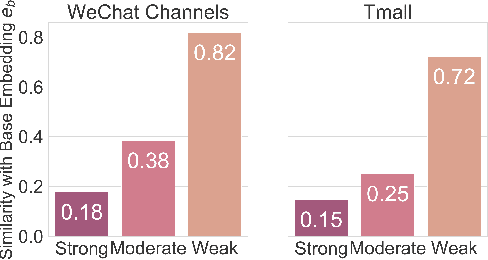
Abstract:Online platforms aggregate extensive user feedback across diverse behaviors, providing a rich source for enhancing user engagement. Traditional recommender systems, however, typically optimize for a single target behavior and represent user preferences with a single vector, limiting their ability to handle multiple important behaviors or optimization objectives. This conventional approach also struggles to capture the full spectrum of user interests, resulting in a narrow item pool during candidate generation. To address these limitations, we present Tricolore, a versatile multi-vector learning framework that uncovers connections between different behavior types for more robust candidate generation. Tricolore's adaptive multi-task structure is also customizable to specific platform needs. To manage the variability in sparsity across behavior types, we incorporate a behavior-wise multi-view fusion module that dynamically enhances learning. Moreover, a popularity-balanced strategy ensures the recommendation list balances accuracy with item popularity, fostering diversity and improving overall performance. Extensive experiments on public datasets demonstrate Tricolore's effectiveness across various recommendation scenarios, from short video platforms to e-commerce. By leveraging a shared base embedding strategy, Tricolore also significantly improves the performance for cold-start users. The source code is publicly available at: https://github.com/abnering/Tricolore.
Topic-Enhanced Memory Networks for Personalised Point-of-Interest Recommendation
May 19, 2019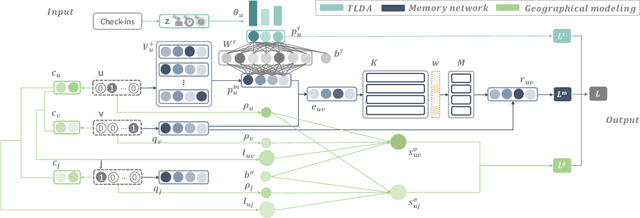
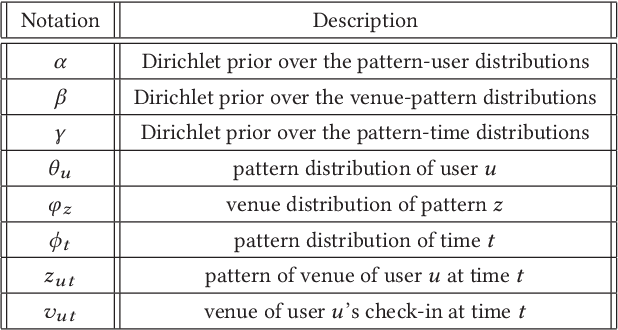
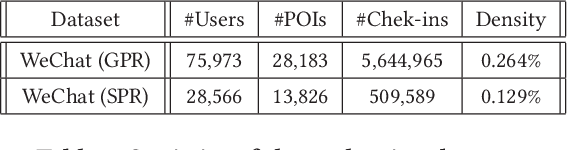
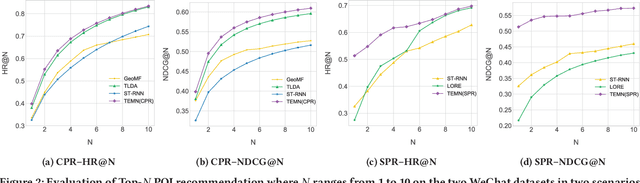
Abstract:Point-of-Interest (POI) recommender systems play a vital role in people's lives by recommending unexplored POIs to users and have drawn extensive attention from both academia and industry. Despite their value, however, they still suffer from the challenges of capturing complicated user preferences and fine-grained user-POI relationship for spatio-temporal sensitive POI recommendation. Existing recommendation algorithms, including both shallow and deep approaches, usually embed the visiting records of a user into a single latent vector to model user preferences: this has limited power of representation and interpretability. In this paper, we propose a novel topic-enhanced memory network (TEMN), a deep architecture to integrate the topic model and memory network capitalising on the strengths of both the global structure of latent patterns and local neighbourhood-based features in a nonlinear fashion. We further incorporate a geographical module to exploit user-specific spatial preference and POI-specific spatial influence to enhance recommendations. The proposed unified hybrid model is widely applicable to various POI recommendation scenarios. Extensive experiments on real-world WeChat datasets demonstrate its effectiveness (improvement ratio of 3.25% and 29.95% for context-aware and sequential recommendation, respectively). Also, qualitative analysis of the attention weights and topic modeling provides insight into the model's recommendation process and results.
Discovering Latent Patterns of Urban Cultural Interactions in WeChat for Modern City Planning
Jun 14, 2018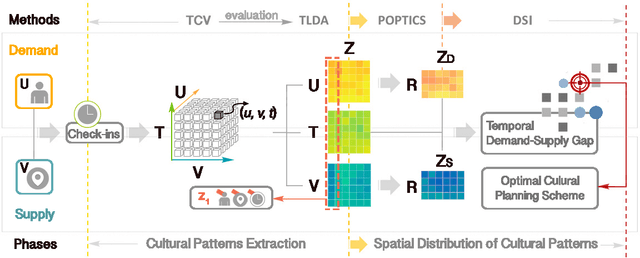
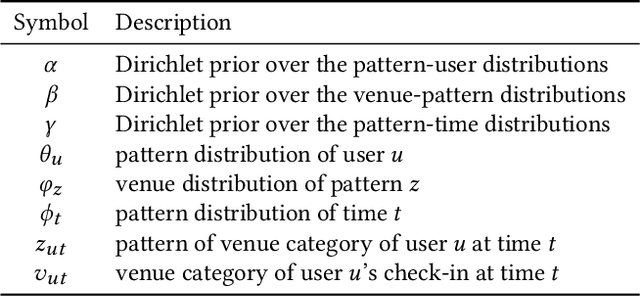
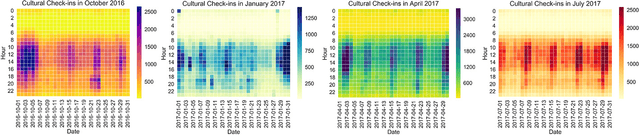
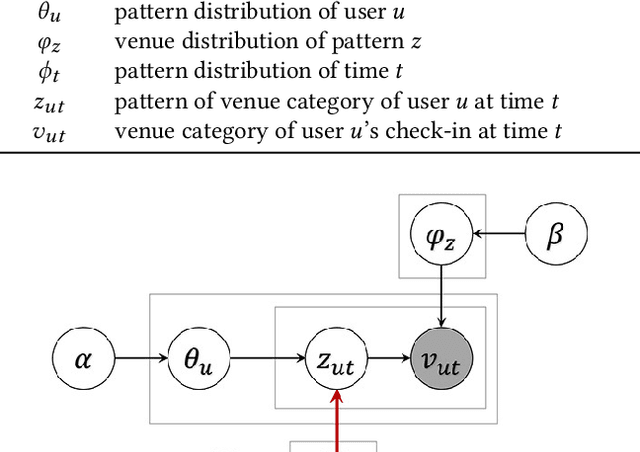
Abstract:Cultural activity is an inherent aspect of urban life and the success of a modern city is largely determined by its capacity to offer generous cultural entertainment to its citizens. To this end, the optimal allocation of cultural establishments and related resources across urban regions becomes of vital importance, as it can reduce financial costs in terms of planning and improve quality of life in the city, more generally. In this paper, we make use of a large longitudinal dataset of user location check-ins from the online social network WeChat to develop a data-driven framework for cultural planning in the city of Beijing. We exploit rich spatio-temporal representations on user activity at cultural venues and use a novel extended version of the traditional latent Dirichlet allocation model that incorporates temporal information to identify latent patterns of urban cultural interactions. Using the characteristic typologies of mobile user cultural activities emitted by the model, we determine the levels of demand for different types of cultural resources across urban areas. We then compare those with the corresponding levels of supply as driven by the presence and spatial reach of cultural venues in local areas to obtain high resolution maps that indicate urban regions with lack of cultural resources, and thus give suggestions for further urban cultural planning and investment optimisation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge