Zhigong Song
RoboMatch: A Mobile-Manipulation Teleoperation Platform with Auto-Matching Network Architecture for Long-Horizon Manipulation
Sep 10, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents RoboMatch, a novel unified teleoperation platform for mobile manipulation with an auto-matching network architecture, designed to tackle long-horizon tasks in dynamic environments. Our system enhances teleoperation performance, data collection efficiency, task accuracy, and operational stability. The core of RoboMatch is a cockpit-style control interface that enables synchronous operation of the mobile base and dual arms, significantly improving control precision and data collection. Moreover, we introduce the Proprioceptive-Visual Enhanced Diffusion Policy (PVE-DP), which leverages Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) for multi-scale visual feature extraction and integrates high-precision IMUs at the end-effector to enrich proprioceptive feedback, substantially boosting fine manipulation performance. Furthermore, we propose an Auto-Matching Network (AMN) architecture that decomposes long-horizon tasks into logical sequences and dynamically assigns lightweight pre-trained models for distributed inference. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach improves data collection efficiency by over 20%, increases task success rates by 20-30% with PVE-DP, and enhances long-horizon inference performance by approximately 40% with AMN, offering a robust solution for complex manipulation tasks.
Efficient Bi-manipulation using RGBD Multi-model Fusion based on Attention Mechanism
Apr 27, 2024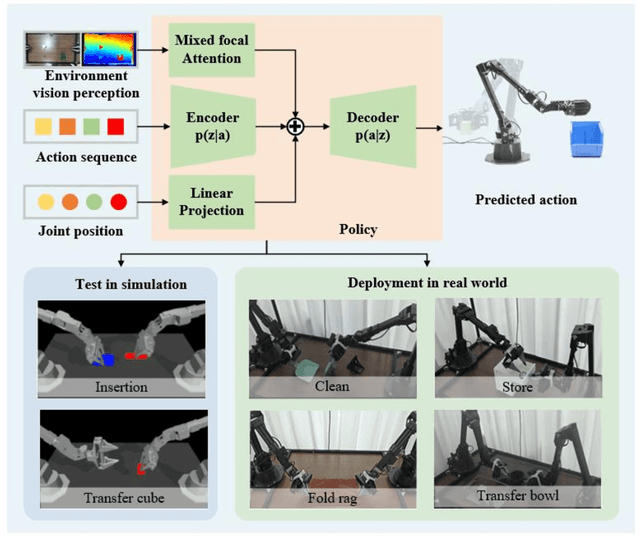
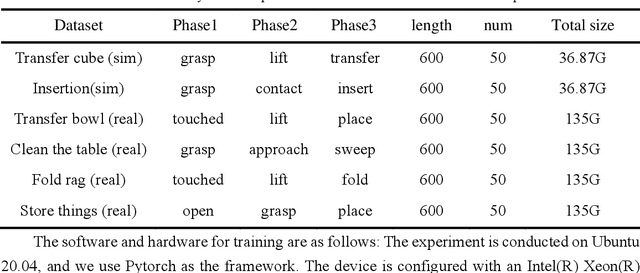
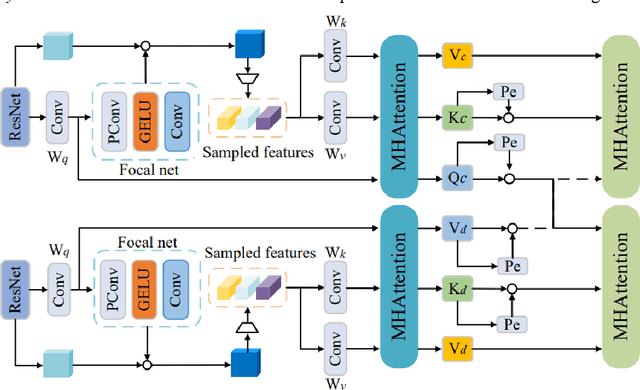
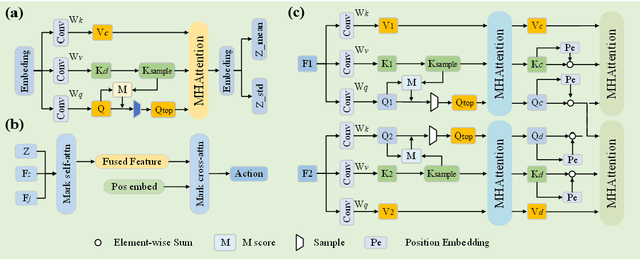
Abstract:Dual-arm robots have great application prospects in intelligent manufacturing due to their human-like structure when deployed with advanced intelligence algorithm. However, the previous visuomotor policy suffers from perception deficiencies in environments where features of images are impaired by the various conditions, such as abnormal lighting, occlusion and shadow etc. The Focal CVAE framework is proposed for RGB-D multi-modal data fusion to address this challenge. In this study, a mixed focal attention module is designed for the fusion of RGB images containing color features and depth images containing 3D shape and structure information. This module highlights the prominent local features and focuses on the relevance of RGB and depth via cross-attention. A saliency attention module is proposed to improve its computational efficiency, which is applied in the encoder and the decoder of the framework. We illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method via extensive simulation and experiments. It's shown that the performances of bi-manipulation are all significantly improved in the four real-world tasks with lower computational cost. Besides, the robustness is validated through experiments under different scenarios where there is a perception deficiency problem, demonstrating the feasibility of the method.
Fractal Gripper: Adaptive manipulator with mode switching
Feb 25, 2024

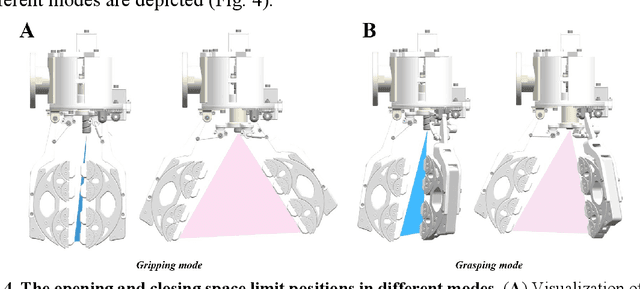
Abstract:Although the multi-jointed underactuated manipulator is highly dexterous, its grasping capacity does not match that of the parallel jaw gripper. This work introduces a fractal gripper to enhance the grasping capacity of multi-joint underactuated manipulators, preserving their passive clamping features. We describe in detail the working principle and manufacturing process of the fractal gripper. This work, inspired by the 'Fractal Vise' structure, resulted in the invention of a fractal gripper with mode switching capabilities. The fractal gripper inherits the inherent adaptive properties of the fractal structure and realizes the self-resetting function by integrating spring into the original design, thereby enhancing the efficiency of object grasping tasks. The fractal gripper prevents object damage by distributing pressure evenly and applying it at multiple points through its fractal structure during closure. Objects of various shapes are effectively grasped by the fractal gripper, which ensures a safe and secure grasp. The superior performance was provided by the force distribution characteristics of the fractal gripper. By applying the flexible polymer PDMS, which possesses superior elasticity, to the fractal structure's wrapping surface, potential scratching during grasping is effectively prevented, thus protecting the object's geometric surface. Grab experiments with objects of diverse shapes and sizes confirm fractal gripper multi-scale adaptability and superior grasping stability.
A Generative Machine Learning Model for Material Microstructure 3D Reconstruction and Performance Evaluation
Feb 24, 2024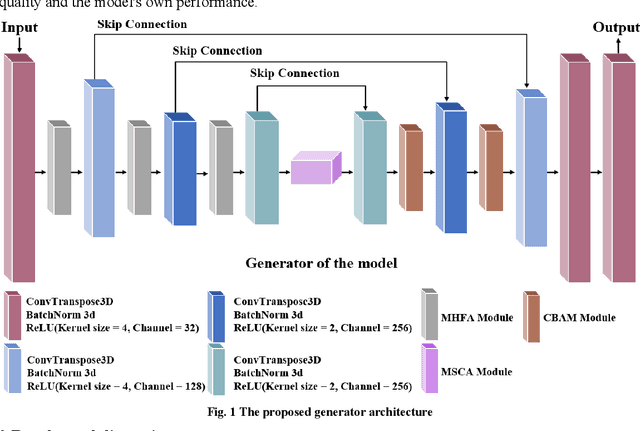

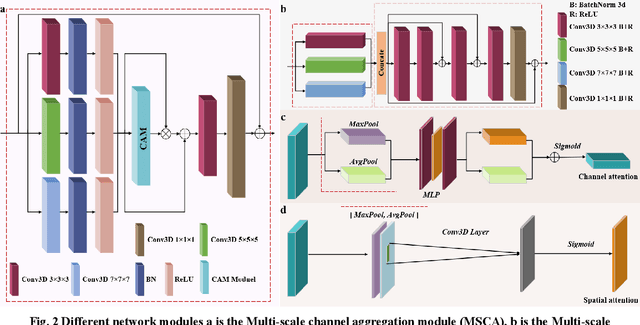

Abstract:The reconstruction of 3D microstructures from 2D slices is considered to hold significant value in predicting the spatial structure and physical properties of materials.The dimensional extension from 2D to 3D is viewed as a highly challenging inverse problem from the current technological perspective.Recently,methods based on generative adversarial networks have garnered widespread attention.However,they are still hampered by numerous limitations,including oversimplified models,a requirement for a substantial number of training samples,and difficulties in achieving model convergence during training.In light of this,a novel generative model that integrates the multiscale properties of U-net with and the generative capabilities of GAN has been proposed.Based on this,the innovative construction of a multi-scale channel aggregation module,a multi-scale hierarchical feature aggregation module and a convolutional block attention mechanism can better capture the properties of the material microstructure and extract the image information.The model's accuracy is further improved by combining the image regularization loss with the Wasserstein distance loss.In addition,this study utilizes the anisotropy index to accurately distinguish the nature of the image,which can clearly determine the isotropy and anisotropy of the image.It is also the first time that the generation quality of material samples from different domains is evaluated and the performance of the model itself is compared.The experimental results demonstrate that the present model not only shows a very high similarity between the generated 3D structures and real samples but is also highly consistent with real data in terms of statistical data analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge