Zhenwei Liu
Accelerating Matroid Optimization through Fast Imprecise Oracles
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Querying complex models for precise information (e.g. traffic models, database systems, large ML models) often entails intense computations and results in long response times. Thus, weaker models which give imprecise results quickly can be advantageous, provided inaccuracies can be resolved using few queries to a stronger model. In the fundamental problem of computing a maximum-weight basis of a matroid, a well-known generalization of many combinatorial optimization problems, algorithms have access to a clean oracle to query matroid information. We additionally equip algorithms with a fast but dirty oracle modelling an unknown, potentially different matroid. We design and analyze practical algorithms which only use few clean queries w.r.t. the quality of the dirty oracle, while maintaining robustness against arbitrarily poor dirty matroids, approaching the performance of classic algorithms for the given problem. Notably, we prove that our algorithms are, in many respects, best-possible. Further, we outline extensions to other matroid oracle types, non-free dirty oracles and other matroid problems.
Robotic Depowdering for Additive Manufacturing via Pose Tracking
Jul 09, 2022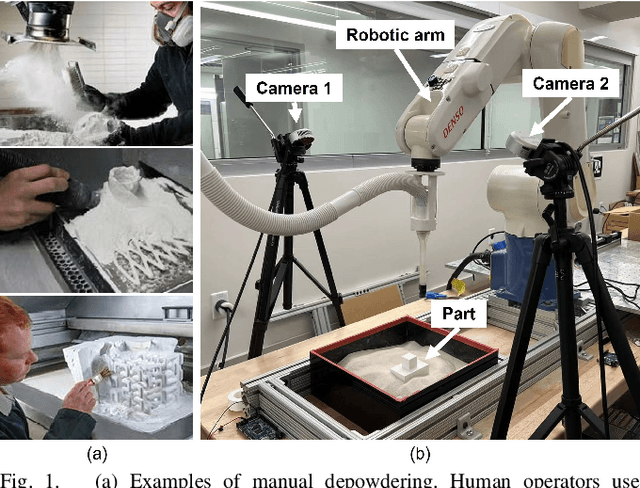
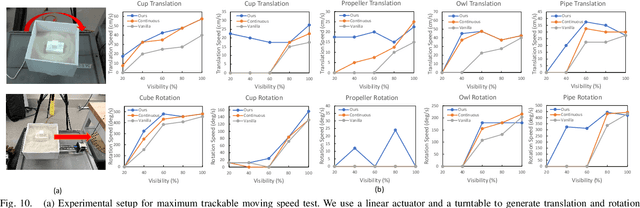
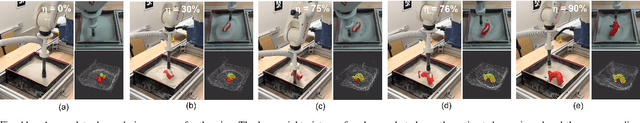

Abstract:With the rapid development of powder-based additive manufacturing, depowdering, a process of removing unfused powder that covers 3D-printed parts, has become a major bottleneck to further improve its productiveness. Traditional manual depowdering is extremely time-consuming and costly, and some prior automated systems either require pre-depowdering or lack adaptability to different 3D-printed parts. To solve these problems, we introduce a robotic system that automatically removes unfused powder from the surface of 3D-printed parts. The key component is a visual perception system, which consists of a pose-tracking module that tracks the 6D pose of powder-occluded parts in real-time, and a progress estimation module that estimates the depowdering completion percentage. The tracking module can be run efficiently on a laptop CPU at up to 60 FPS. Experiments show that our depowdering system can remove unfused powder from the surface of various 3D-printed parts without causing any damage. To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the first vision-based robotic depowdering systems that adapt to parts with various shapes without the need for pre-depowdering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge