Zhenshuo Zhang
Efficient Estimation of Kernel Surrogate Models for Task Attribution
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Modern AI agents such as large language models are trained on diverse tasks -- translation, code generation, mathematical reasoning, and text prediction -- simultaneously. A key question is to quantify how each individual training task influences performance on a target task, a problem we refer to as task attribution. The direct approach, leave-one-out retraining, measures the effect of removing each task, but is computationally infeasible at scale. An alternative approach that builds surrogate models to predict a target task's performance for any subset of training tasks has emerged in recent literature. Prior work focuses on linear surrogate models, which capture first-order relationships, but miss nonlinear interactions such as synergy, antagonism, or XOR-type effects. In this paper, we first consider a unified task weighting framework for analyzing task attribution methods, and show a new connection between linear surrogate models and influence functions through a second-order analysis. Then, we introduce kernel surrogate models, which more effectively represent second-order task interactions. To efficiently learn the kernel surrogate, we develop a gradient-based estimation procedure that leverages a first-order approximation of pretrained models; empirically, this yields accurate estimates with less than $2\%$ relative error without repeated retraining. Experiments across multiple domains -- including math reasoning in transformers, in-context learning, and multi-objective reinforcement learning -- demonstrate the effectiveness of kernel surrogate models. They achieve a $25\%$ higher correlation with the leave-one-out ground truth than linear surrogates and influence-function baselines. When used for downstream task selection, kernel surrogate models yield a $40\%$ improvement in demonstration selection for in-context learning and multi-objective reinforcement learning benchmarks.
One-Sided Matrix Completion from Ultra-Sparse Samples
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Matrix completion is a classical problem that has received recurring interest across a wide range of fields. In this paper, we revisit this problem in an ultra-sparse sampling regime, where each entry of an unknown, $n\times d$ matrix $M$ (with $n \ge d$) is observed independently with probability $p = C / d$, for a fixed integer $C \ge 2$. This setting is motivated by applications involving large, sparse panel datasets, where the number of rows far exceeds the number of columns. When each row contains only $C$ entries -- fewer than the rank of $M$ -- accurate imputation of $M$ is impossible. Instead, we estimate the row span of $M$ or the averaged second-moment matrix $T = M^{\top} M / n$. The empirical second-moment matrix computed from observed entries exhibits non-random and sparse missingness. We propose an unbiased estimator that normalizes each nonzero entry of the second moment by its observed frequency, followed by gradient descent to impute the missing entries of $T$. The normalization divides a weighted sum of $n$ binomial random variables by the total number of ones. We show that the estimator is unbiased for any $p$ and enjoys low variance. When the row vectors of $M$ are drawn uniformly from a rank-$r$ factor model satisfying an incoherence condition, we prove that if $n \ge O({d r^5 ε^{-2} C^{-2} \log d})$, any local minimum of the gradient-descent objective is approximately global and recovers $T$ with error at most $ε^2$. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world data validate our approach. On three MovieLens datasets, our algorithm reduces bias by $88\%$ relative to baseline estimators. We also empirically validate the linear sampling complexity of $n$ relative to $d$ on synthetic data. On an Amazon reviews dataset with sparsity $10^{-7}$, our method reduces the recovery error of $T$ by $59\%$ and $M$ by $38\%$ compared to baseline methods.
* 41 pages
Scalable Multi-Objective and Meta Reinforcement Learning via Gradient Estimation
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:We study the problem of efficiently estimating policies that simultaneously optimize multiple objectives in reinforcement learning (RL). Given $n$ objectives (or tasks), we seek the optimal partition of these objectives into $k \ll n$ groups, where each group comprises related objectives that can be trained together. This problem arises in applications such as robotics, control, and preference optimization in language models, where learning a single policy for all $n$ objectives is suboptimal as $n$ grows. We introduce a two-stage procedure -- meta-training followed by fine-tuning -- to address this problem. We first learn a meta-policy for all objectives using multitask learning. Then, we adapt the meta-policy to multiple randomly sampled subsets of objectives. The adaptation step leverages a first-order approximation property of well-trained policy networks, which is empirically verified to be accurate within a $2\%$ error margin across various RL environments. The resulting algorithm, PolicyGradEx, efficiently estimates an aggregate task-affinity score matrix given a policy evaluation algorithm. Based on the estimated affinity score matrix, we cluster the $n$ objectives into $k$ groups by maximizing the intra-cluster affinity scores. Experiments on three robotic control and the Meta-World benchmarks demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by $16\%$ on average, while delivering up to $26\times$ faster speedup relative to performing full training to obtain the clusters. Ablation studies validate each component of our approach. For instance, compared with random grouping and gradient-similarity-based grouping, our loss-based clustering yields an improvement of $19\%$. Finally, we analyze the generalization error of policy networks by measuring the Hessian trace of the loss surface, which gives non-vacuous measures relative to the observed generalization errors.
Hybrid DQN-TD3 Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Navigation in Dynamic Environments
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a hierarchical path-planning and control framework that combines a high-level Deep Q-Network (DQN) for discrete sub-goal selection with a low-level Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (TD3) controller for continuous actuation. The high-level module selects behaviors and sub-goals; the low-level module executes smooth velocity commands. We design a practical reward shaping scheme (direction, distance, obstacle avoidance, action smoothness, collision penalty, time penalty, and progress), together with a LiDAR-based safety gate that prevents unsafe motions. The system is implemented in ROS + Gazebo (TurtleBot3) and evaluated with PathBench metrics, including success rate, collision rate, path efficiency, and re-planning efficiency, in dynamic and partially observable environments. Experiments show improved success rate and sample efficiency over single-algorithm baselines (DQN or TD3 alone) and rule-based planners, with better generalization to unseen obstacle configurations and reduced abrupt control changes. Code and evaluation scripts are available at the project repository.
Linear-Time Demonstration Selection for In-Context Learning via Gradient Estimation
Aug 27, 2025
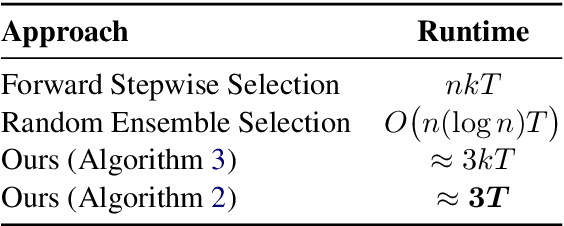
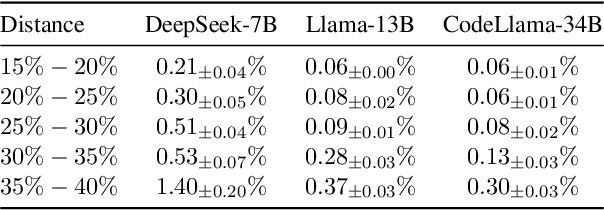

Abstract:This paper introduces an algorithm to select demonstration examples for in-context learning of a query set. Given a set of $n$ examples, how can we quickly select $k$ out of $n$ to best serve as the conditioning for downstream inference? This problem has broad applications in prompt tuning and chain-of-thought reasoning. Since model weights remain fixed during in-context learning, previous work has sought to design methods based on the similarity of token embeddings. This work proposes a new approach based on gradients of the output taken in the input embedding space. Our approach estimates model outputs through a first-order approximation using the gradients. Then, we apply this estimation to multiple randomly sampled subsets. Finally, we aggregate the sampled subset outcomes to form an influence score for each demonstration, and select $k$ most relevant examples. This procedure only requires pre-computing model outputs and gradients once, resulting in a linear-time algorithm relative to model and training set sizes. Extensive experiments across various models and datasets validate the efficiency of our approach. We show that the gradient estimation procedure yields approximations of full inference with less than $\mathbf{1}\%$ error across six datasets. This allows us to scale up subset selection that would otherwise run full inference by up to $\mathbf{37.7}\times$ on models with up to $34$ billion parameters, and outperform existing selection methods based on input embeddings by $\mathbf{11}\%$ on average.
GraphControl: Adding Conditional Control to Universal Graph Pre-trained Models for Graph Domain Transfer Learning
Oct 12, 2023


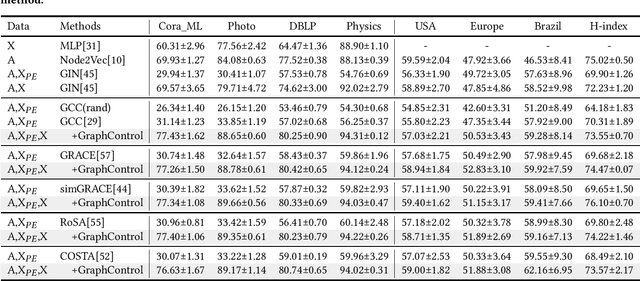
Abstract:Graph-structured data is ubiquitous in the world which models complex relationships between objects, enabling various Web applications. Daily influxes of unlabeled graph data on the Web offer immense potential for these applications. Graph self-supervised algorithms have achieved significant success in acquiring generic knowledge from abundant unlabeled graph data. These pre-trained models can be applied to various downstream Web applications, saving training time and improving downstream (target) performance. However, different graphs, even across seemingly similar domains, can differ significantly in terms of attribute semantics, posing difficulties, if not infeasibility, for transferring the pre-trained models to downstream tasks. Concretely speaking, for example, the additional task-specific node information in downstream tasks (specificity) is usually deliberately omitted so that the pre-trained representation (transferability) can be leveraged. The trade-off as such is termed as "transferability-specificity dilemma" in this work. To address this challenge, we introduce an innovative deployment module coined as GraphControl, motivated by ControlNet, to realize better graph domain transfer learning. Specifically, by leveraging universal structural pre-trained models and GraphControl, we align the input space across various graphs and incorporate unique characteristics of target data as conditional inputs. These conditions will be progressively integrated into the model during fine-tuning or prompt tuning through ControlNet, facilitating personalized deployment. Extensive experiments show that our method significantly enhances the adaptability of pre-trained models on target attributed datasets, achieving 1.4-3x performance gain. Furthermore, it outperforms training-from-scratch methods on target data with a comparable margin and exhibits faster convergence.
MARIO: Model Agnostic Recipe for Improving OOD Generalization of Graph Contrastive Learning
Aug 02, 2023



Abstract:In this work, we investigate the problem of out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization for unsupervised learning methods on graph data. This scenario is particularly challenging because graph neural networks (GNNs) have been shown to be sensitive to distributional shifts, even when labels are available. To address this challenge, we propose a \underline{M}odel-\underline{A}gnostic \underline{R}ecipe for \underline{I}mproving \underline{O}OD generalizability of unsupervised graph contrastive learning methods, which we refer to as MARIO. MARIO introduces two principles aimed at developing distributional-shift-robust graph contrastive methods to overcome the limitations of existing frameworks: (i) Information Bottleneck (IB) principle for achieving generalizable representations and (ii) Invariant principle that incorporates adversarial data augmentation to obtain invariant representations. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that investigates the OOD generalization problem of graph contrastive learning, with a specific focus on node-level tasks. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the OOD test set, while maintaining comparable performance on the in-distribution test set when compared to existing approaches. The source code for our method can be found at: https://github.com/ZhuYun97/MARIO
Structure-Aware Group Discrimination with Adaptive-View Graph Encoder: A Fast Graph Contrastive Learning Framework
Mar 09, 2023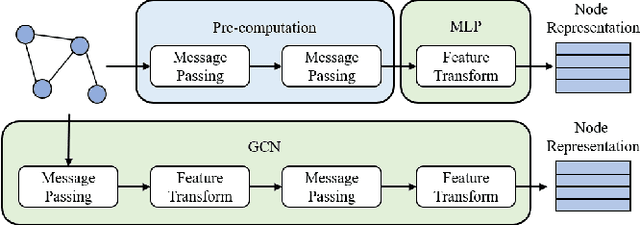
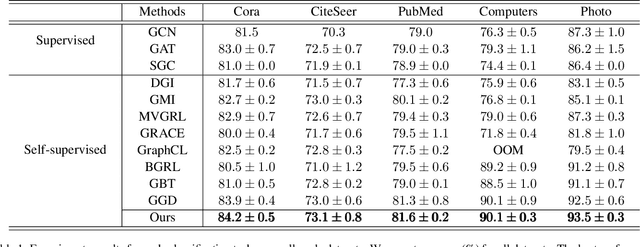
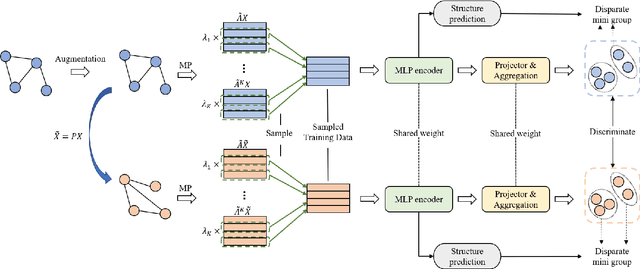
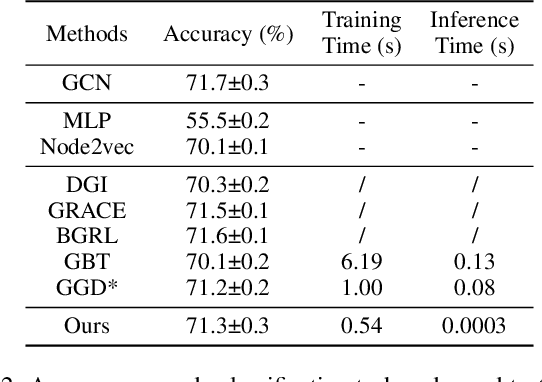
Abstract:Albeit having gained significant progress lately, large-scale graph representation learning remains expensive to train and deploy for two main reasons: (i) the repetitive computation of multi-hop message passing and non-linearity in graph neural networks (GNNs); (ii) the computational cost of complex pairwise contrastive learning loss. Two main contributions are made in this paper targeting this twofold challenge: we first propose an adaptive-view graph neural encoder (AVGE) with a limited number of message passing to accelerate the forward pass computation, and then we propose a structure-aware group discrimination (SAGD) loss in our framework which avoids inefficient pairwise loss computing in most common GCL and improves the performance of the simple group discrimination. By the framework proposed, we manage to bring down the training and inference cost on various large-scale datasets by a significant margin (250x faster inference time) without loss of the downstream-task performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge