Zhaolin Xiao
A learning-based view extrapolation method for axial super-resolution
Mar 11, 2021
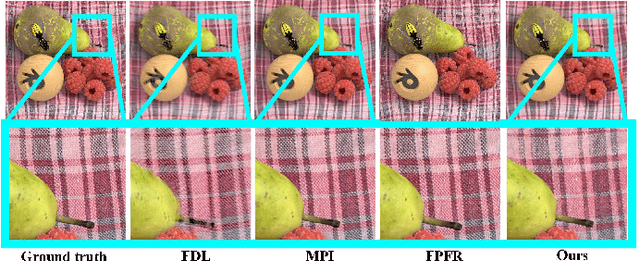


Abstract:Axial light field resolution refers to the ability to distinguish features at different depths by refocusing. The axial refocusing precision corresponds to the minimum distance in the axial direction between two distinguishable refocusing planes. High refocusing precision can be essential for some light field applications like microscopy. In this paper, we propose a learning-based method to extrapolate novel views from axial volumes of sheared epipolar plane images (EPIs). As extended numerical aperture (NA) in classical imaging, the extrapolated light field gives re-focused images with a shallower depth of field (DOF), leading to more accurate refocusing results. Most importantly, the proposed approach does not need accurate depth estimation. Experimental results with both synthetic and real light fields show that the method not only works well for light fields with small baselines as those captured by plenoptic cameras (especially for the plenoptic 1.0 cameras), but also applies to light fields with larger baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge