Zhao-Yang Liu
Gaussian Graph with Prototypical Contrastive Learning in E-Commerce Bundle Recommendation
Jul 25, 2023Abstract:Bundle recommendation aims to provide a bundle of items to satisfy the user preference on e-commerce platform. Existing successful solutions are based on the contrastive graph learning paradigm where graph neural networks (GNNs) are employed to learn representations from user-level and bundle-level graph views with a contrastive learning module to enhance the cooperative association between different views. Nevertheless, they ignore the uncertainty issue which has a significant impact in real bundle recommendation scenarios due to the lack of discriminative information caused by highly sparsity or diversity. We further suggest that their instancewise contrastive learning fails to distinguish the semantically similar negatives (i.e., sampling bias issue), resulting in performance degradation. In this paper, we propose a novel Gaussian Graph with Prototypical Contrastive Learning (GPCL) framework to overcome these challenges. In particular, GPCL embeds each user/bundle/item as a Gaussian distribution rather than a fixed vector. We further design a prototypical contrastive learning module to capture the contextual information and mitigate the sampling bias issue. Extensive experiments demonstrate that benefiting from the proposed components, we achieve new state-of-the-art performance compared to previous methods on several public datasets. Moreover, GPCL has been deployed on real-world e-commerce platform and achieved substantial improvements.
Cost-Effective Training of Deep CNNs with Active Model Adaptation
Jun 05, 2018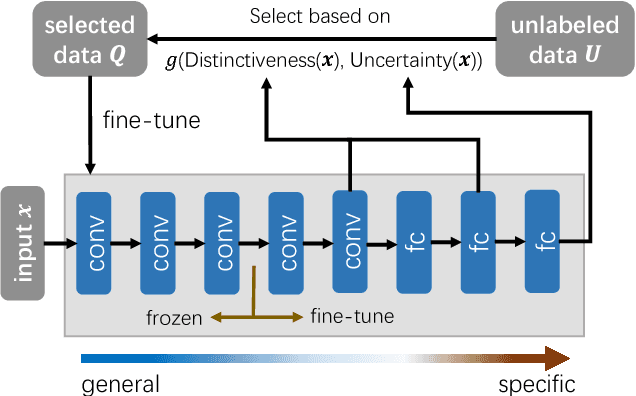
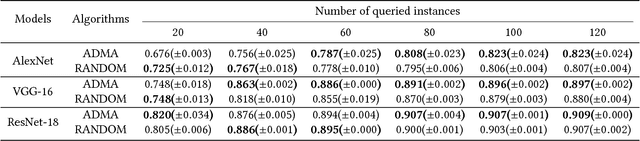
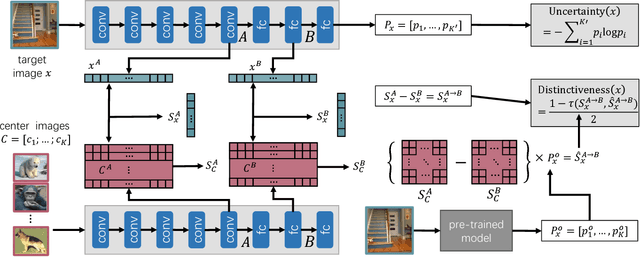
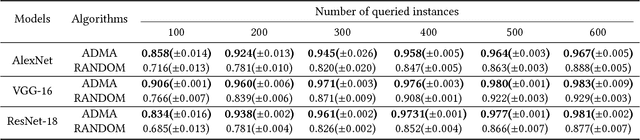
Abstract:Deep convolutional neural networks have achieved great success in various applications. However, training an effective DNN model for a specific task is rather challenging because it requires a prior knowledge or experience to design the network architecture, repeated trial-and-error process to tune the parameters, and a large set of labeled data to train the model. In this paper, we propose to overcome these challenges by actively adapting a pre-trained model to a new task with less labeled examples. Specifically, the pre-trained model is iteratively fine tuned based on the most useful examples. The examples are actively selected based on a novel criterion, which jointly estimates the potential contribution of an instance on optimizing the feature representation as well as improving the classification model for the target task. On one hand, the pre-trained model brings plentiful information from its original task, avoiding redesign of the network architecture or training from scratch; and on the other hand, the labeling cost can be significantly reduced by active label querying. Experiments on multiple datasets and different pre-trained models demonstrate that the proposed approach can achieve cost-effective training of DNNs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge