Zhanqing Yu
Fault Location in Power Distribution Systems via Deep Graph Convolutional Networks
Dec 22, 2018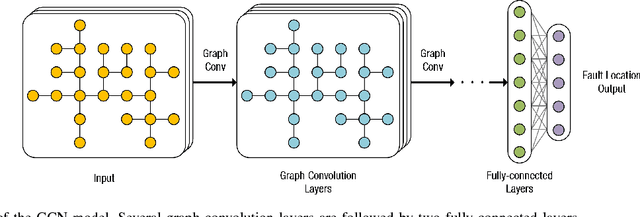
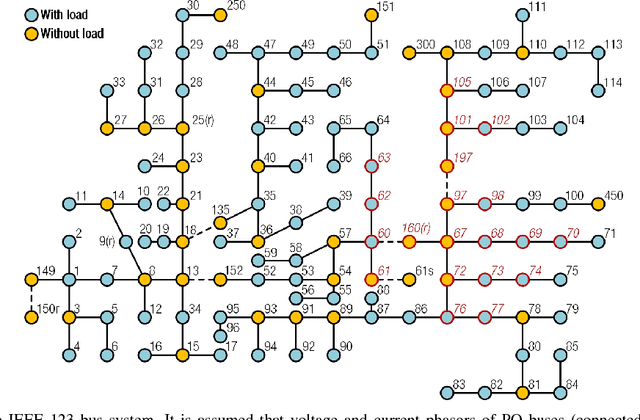
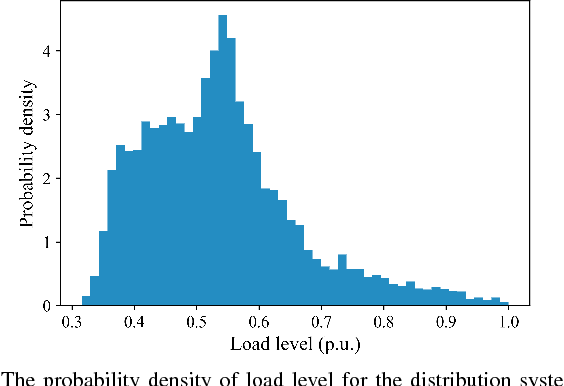
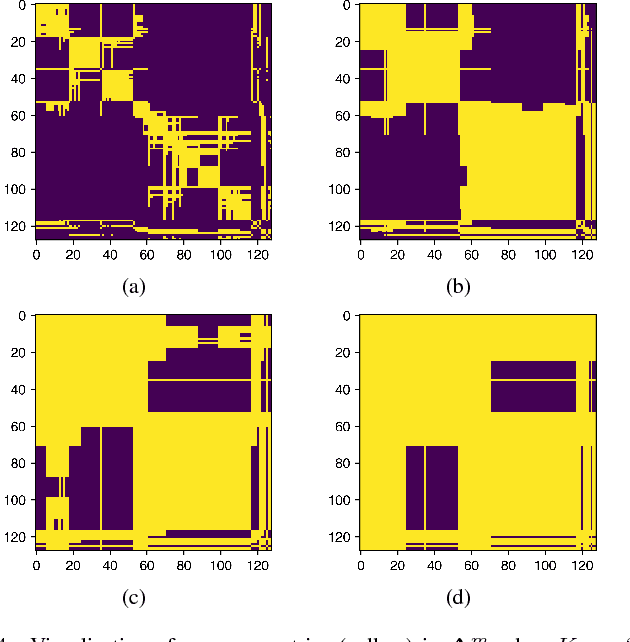
Abstract:This paper develops a novel graph convolutional network (GCN) framework for fault location in power distribution networks. The proposed approach integrates multiple measurements at different buses while takes system topology into account. The effectiveness of the GCN model is corroborated by the IEEE 123-bus benchmark system. Simulation results show that the GCN model significantly outperforms other widely-used machine learning schemes with very high fault location accuracy. In addition, the proposed approach is robust to measurement noise and errors, missing entries, as well as multiple connection possibilities. Finally, data visualization results of two competing neural networks are presented to explore the mechanism of GCN's superior performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge