Zenun Kastrati
Demographic-aware fine-grained classification of pediatric wrist fractures
Jul 18, 2025Abstract:Wrist pathologies are frequently observed, particularly among children who constitute the majority of fracture cases. However, diagnosing these conditions is time-consuming and requires specialized expertise. Computer vision presents a promising avenue, contingent upon the availability of extensive datasets, a notable challenge in medical imaging. Therefore, reliance solely on one modality, such as images, proves inadequate, especially in an era of diverse and plentiful data types. In this study, we employ a multifaceted approach to address the challenge of recognizing wrist pathologies using an extremely limited dataset. Initially, we approach the problem as a fine-grained recognition task, aiming to identify subtle X-ray pathologies that conventional CNNs overlook. Secondly, we enhance network performance by fusing patient metadata with X-ray images. Thirdly, rather than pre-training on a coarse-grained dataset like ImageNet, we utilize weights trained on a fine-grained dataset. While metadata integration has been used in other medical domains, this is a novel application for wrist pathologies. Our results show that a fine-grained strategy and metadata integration improve diagnostic accuracy by 2% with a limited dataset and by over 10% with a larger fracture-focused dataset.
Navigating limitations with precision: A fine-grained ensemble approach to wrist pathology recognition on a limited x-ray dataset
Dec 18, 2024

Abstract:The exploration of automated wrist fracture recognition has gained considerable research attention in recent years. In practical medical scenarios, physicians and surgeons may lack the specialized expertise required for accurate X-ray interpretation, highlighting the need for machine vision to enhance diagnostic accuracy. However, conventional recognition techniques face challenges in discerning subtle differences in X-rays when classifying wrist pathologies, as many of these pathologies, such as fractures, can be small and hard to distinguish. This study tackles wrist pathology recognition as a fine-grained visual recognition (FGVR) problem, utilizing a limited, custom-curated dataset that mirrors real-world medical constraints, relying solely on image-level annotations. We introduce a specialized FGVR-based ensemble approach to identify discriminative regions within X-rays. We employ an Explainable AI (XAI) technique called Grad-CAM to pinpoint these regions. Our ensemble approach outperformed many conventional SOTA and FGVR techniques, underscoring the effectiveness of our strategy in enhancing accuracy in wrist pathology recognition.
Learning from the few: Fine-grained approach to pediatric wrist pathology recognition on a limited dataset
Aug 24, 2024


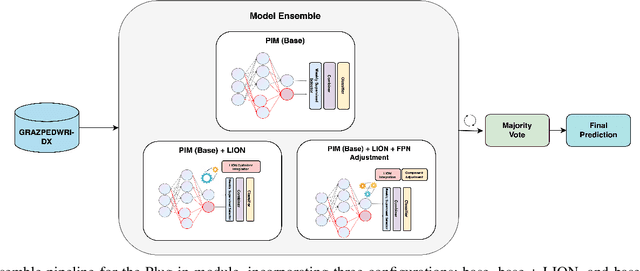
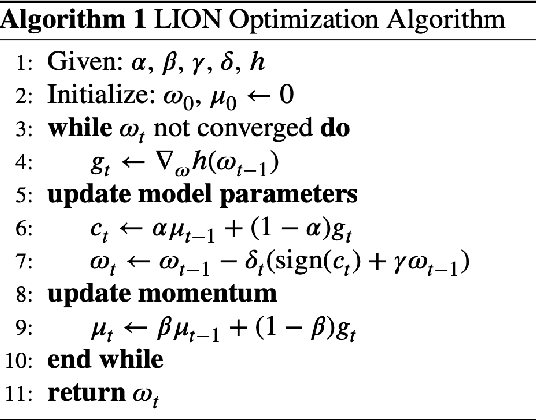
Abstract:Wrist pathologies, {particularly fractures common among children and adolescents}, present a critical diagnostic challenge. While X-ray imaging remains a prevalent diagnostic tool, the increasing misinterpretation rates highlight the need for more accurate analysis, especially considering the lack of specialized training among many surgeons and physicians. Recent advancements in deep convolutional neural networks offer promise in automating pathology detection in trauma X-rays. However, distinguishing subtle variations between {pediatric} wrist pathologies in X-rays remains challenging. Traditional manual annotation, though effective, is laborious, costly, and requires specialized expertise. {In this paper, we address the challenge of pediatric wrist pathology recognition with a fine-grained approach, aimed at automatically identifying discriminative regions in X-rays without manual intervention. We refine our fine-grained architecture through ablation analysis and the integration of LION.} Leveraging Grad-CAM, an explainable AI technique, we highlight these regions. Despite using limited data, reflective of real-world medical study constraints, our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art image recognition models on both augmented and original (challenging) test sets. {Our proposed refined architecture achieves an increase in accuracy of 1.06% and 1.25% compared to the baseline method, resulting in accuracies of 86% and 84%, respectively. Moreover, our approach demonstrates the highest fracture sensitivity of 97%, highlighting its potential to enhance wrist pathology recognition. The implementation code can be found at https://github.com/ammarlodhi255/fine-grained-approach-to-wrist-pathology-recognition
Enhancing Wrist Abnormality Detection with YOLO: Analysis of State-of-the-art Single-stage Detection Models
Jul 17, 2024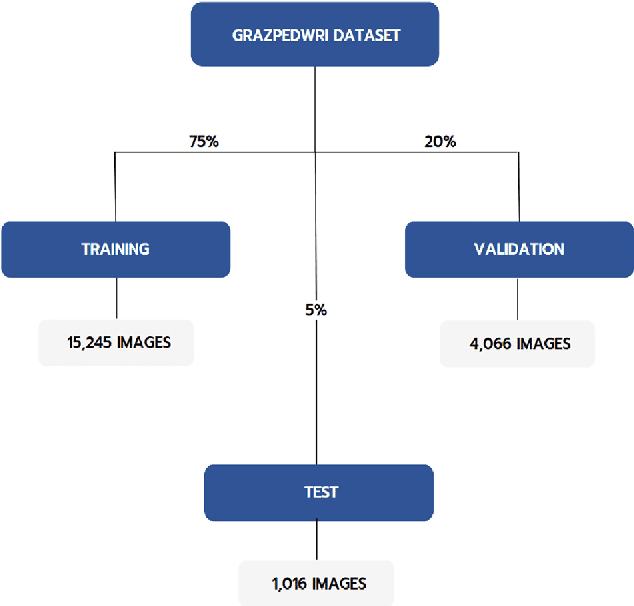
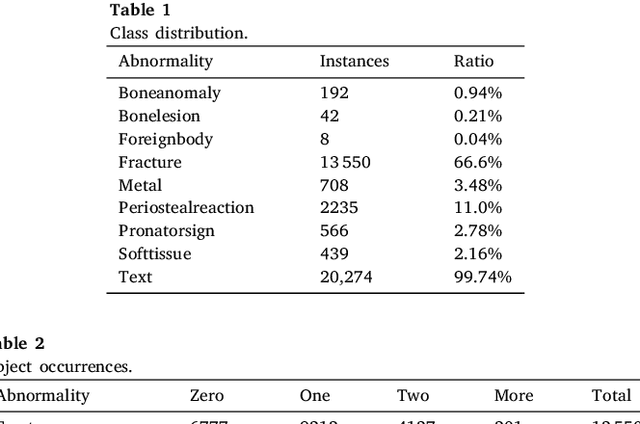
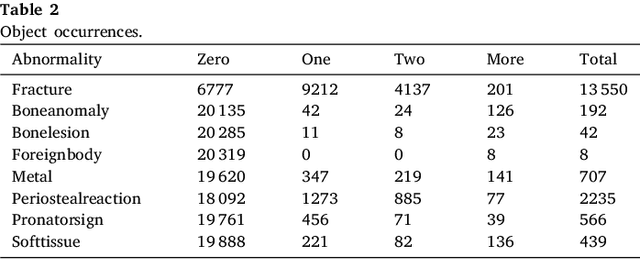
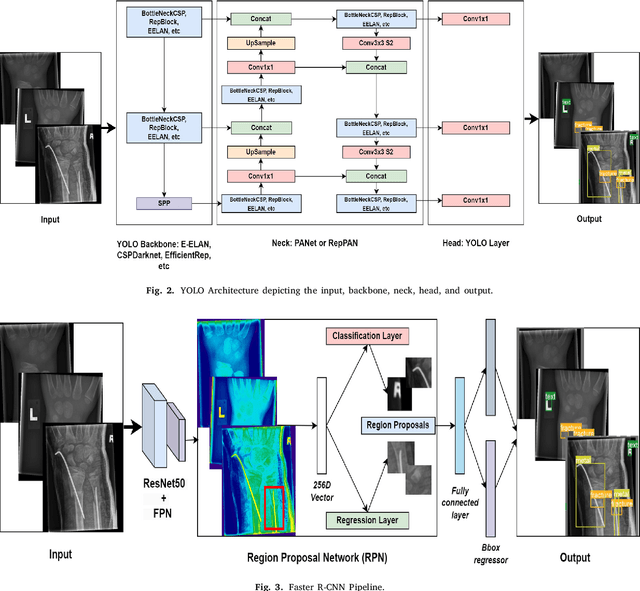
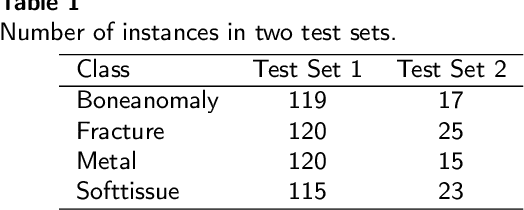
Abstract:Diagnosing and treating abnormalities in the wrist, specifically distal radius, and ulna fractures, is a crucial concern among children, adolescents, and young adults, with a higher incidence rate during puberty. However, the scarcity of radiologists and the lack of specialized training among medical professionals pose a significant risk to patient care. This problem is further exacerbated by the rising number of imaging studies and limited access to specialist reporting in certain regions. This highlights the need for innovative solutions to improve the diagnosis and treatment of wrist abnormalities. Automated wrist fracture detection using object detection has shown potential, but current studies mainly use two-stage detection methods with limited evidence for single-stage effectiveness. This study employs state-of-the-art single-stage deep neural network-based detection models YOLOv5, YOLOv6, YOLOv7, and YOLOv8 to detect wrist abnormalities. Through extensive experimentation, we found that these YOLO models outperform the commonly used two-stage detection algorithm, Faster R-CNN, in bone fracture detection. Additionally, compound-scaled variants of each YOLO model were compared, with YOLOv8x demonstrating a fracture detection mean average precision (mAP) of 0.95 and an overall mAP of 0.77 on the GRAZPEDWRI-DX pediatric wrist dataset, highlighting the potential of single-stage models for enhancing pediatric wrist imaging.
Cross-Cultural Polarity and Emotion Detection Using Sentiment Analysis and Deep Learning -- a Case Study on COVID-19
Aug 23, 2020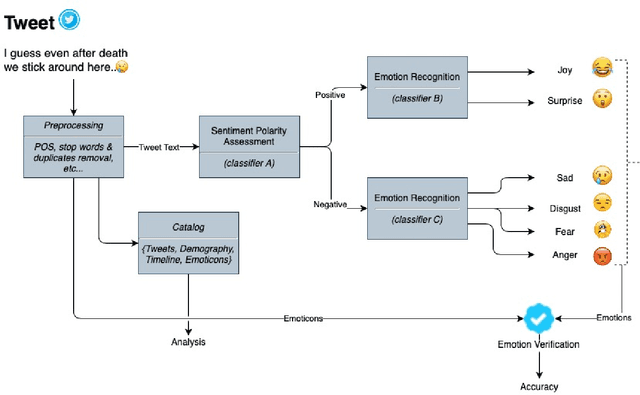
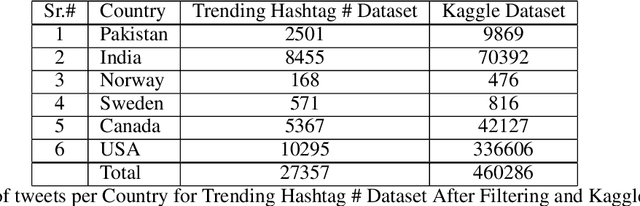
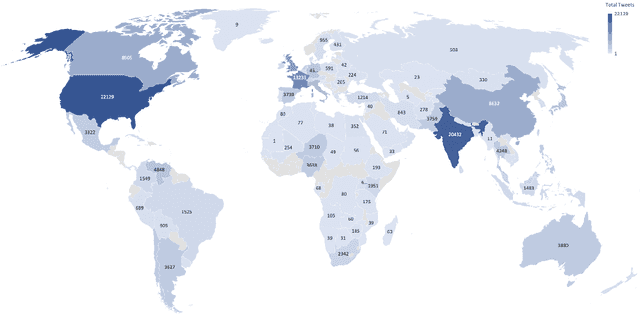
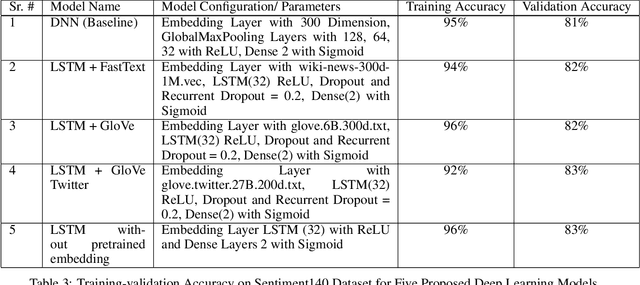
Abstract:How different cultures react and respond given a crisis is predominant in a society's norms and political will to combat the situation. Often the decisions made are necessitated by events, social pressure, or the need of the hour, which may not represent the will of the nation. While some are pleased with it, others might show resentment. Coronavirus (COVID-19) brought a mix of similar emotions from the nations towards the decisions taken by their respective governments. Social media was bombarded with posts containing both positive and negative sentiments on the COVID-19, pandemic, lockdown, hashtags past couple of months. Despite geographically close, many neighboring countries reacted differently to one another. For instance, Denmark and Sweden, which share many similarities, stood poles apart on the decision taken by their respective governments. Yet, their nation's support was mostly unanimous, unlike the South Asian neighboring countries where people showed a lot of anxiety and resentment. This study tends to detect and analyze sentiment polarity and emotions demonstrated during the initial phase of the pandemic and the lockdown period employing natural language processing (NLP) and deep learning techniques on Twitter posts. Deep long short-term memory (LSTM) models used for estimating the sentiment polarity and emotions from extracted tweets have been trained to achieve state-of-the-art accuracy on the sentiment140 dataset. The use of emoticons showed a unique and novel way of validating the supervised deep learning models on tweets extracted from Twitter.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge