Zelin Zhu
RoS-Guard: Robust and Scalable Online Change Detection with Delay-Optimal Guarantees
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Online change detection (OCD) aims to rapidly identify change points in streaming data and is critical in applications such as power system monitoring, wireless network sensing, and financial anomaly detection. Existing OCD methods typically assume precise system knowledge, which is unrealistic due to estimation errors and environmental variations. Moreover, existing OCD methods often struggle with efficiency in large-scale systems. To overcome these challenges, we propose RoS-Guard, a robust and optimal OCD algorithm tailored for linear systems with uncertainty. Through a tight relaxation and reformulation of the OCD optimization problem, RoS-Guard employs neural unrolling to enable efficient parallel computation via GPU acceleration. The algorithm provides theoretical guarantees on performance, including expected false alarm rate and worst-case average detection delay. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of RoS-Guard and demonstrate significant computational speedup in large-scale system scenarios.
Triadic-OCD: Asynchronous Online Change Detection with Provable Robustness, Optimality, and Convergence
May 03, 2024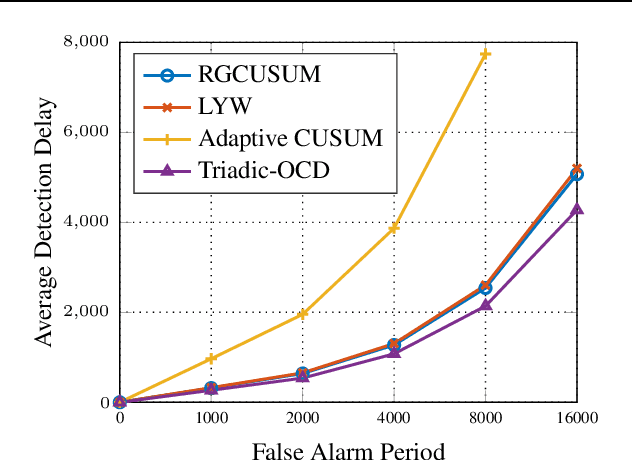
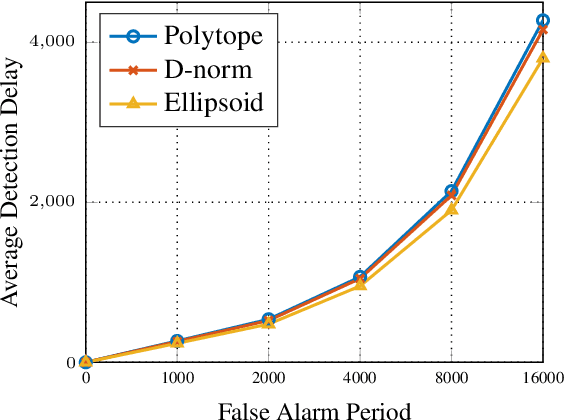
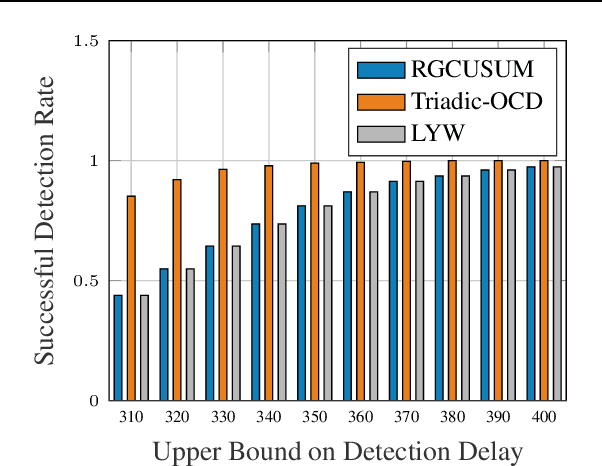
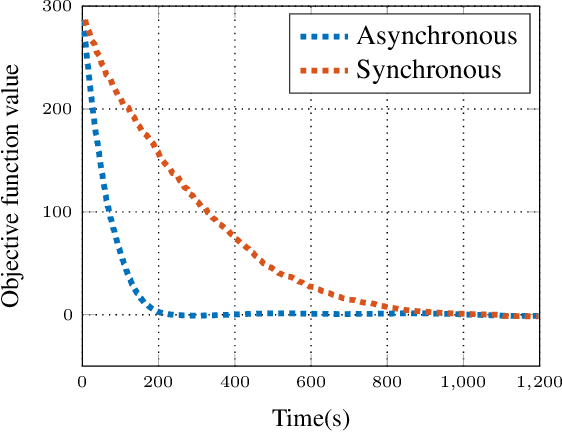
Abstract:The primary goal of online change detection (OCD) is to promptly identify changes in the data stream. OCD problem find a wide variety of applications in diverse areas, e.g., security detection in smart grids and intrusion detection in communication networks. Prior research usually assumes precise knowledge of the parameters linked to the data stream. Nevertheless, this presumption often proves unattainable in practical scenarios due to factors such as estimation errors, system updates, etc. This paper aims to take the first attempt to develop a triadic-OCD framework with certifiable robustness, provable optimality, and guaranteed convergence. In addition, the proposed triadic-OCD algorithm can be realized in a fully asynchronous distributed manner, easing the necessity of transmitting the data to a single server. This asynchronous mechanism also could mitigate the straggler issue that faced by traditional synchronous algorithm. We then analyze the non-asymptotic convergence property of triadic-OCD and derive its iteration complexity to achieve an $\epsilon$-optimal point. Finally, extensive experiments have been conducted to elucidate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Plane Spiral OAM Mode-Group Based MIMO Communications: An Experimental Study
Mar 11, 2021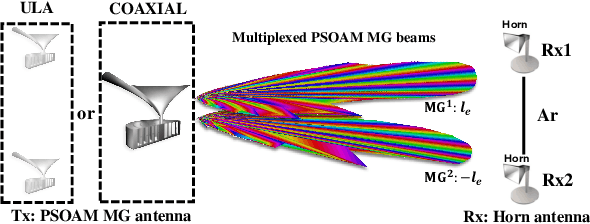
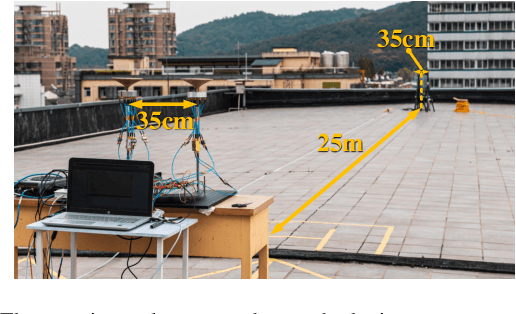
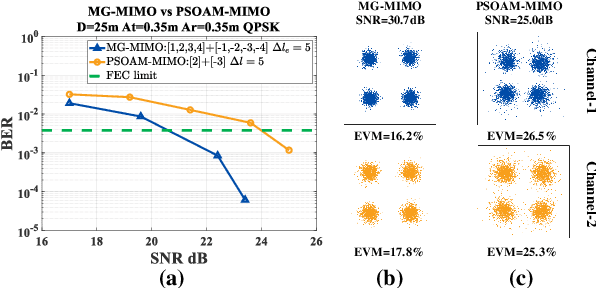
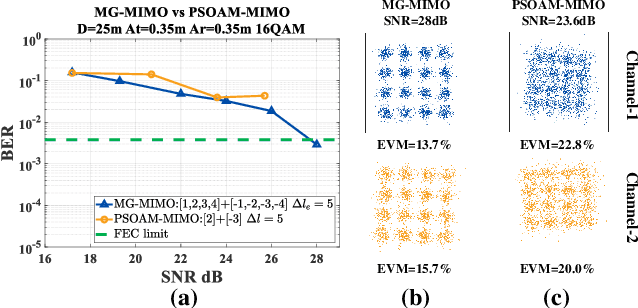
Abstract:Spatial division multiplexing using conventional orbital angular momentum (OAM) has become a well-known physical layer transmission method over the past decade. The mode-group (MG) superposed by specific single mode plane spiral OAM (PSOAM) waves has been proved to be a flexible beamforming method to achieve the azimuthal pattern diversity, which inherits the spiral phase distribution of conventional OAM wave. Thus, it possesses both the beam directionality and vorticity. In this paper, it's the first time to show and verify novel PSOAM MG based multiple-in-multiple-out (MIMO) communication link (MG-MIMO) experimentally in a line-of-sight (LoS) scenario. A compact multi-mode PSOAM antenna is demonstrated experimentally to generate multiple independent controllable PSOAM waves, which can be used for constructing MGs. After several proof-of-principle tests, it has been verified that the beam directionality gain of MG can improve the receiving signal-to-noise (SNR) level in an actual system, meanwhile, the vorticity can provide another degree of freedom (DoF) to reduce the spatial correlation of MIMO system. Furthermore, a tentative long-distance transmission experiment operated at 10.2 GHz has been performed successfully at a distance of 50 m with a single-way spectrum efficiency of 3.7 bits/s/Hz/stream. The proposed MG-MIMO may have potential in the long-distance LoS back-haul scenario.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge