Zejie Zhou
Modeling competitive evolution of multiple languages
Jul 16, 2019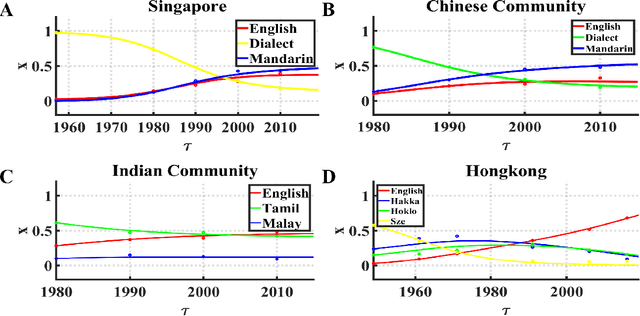
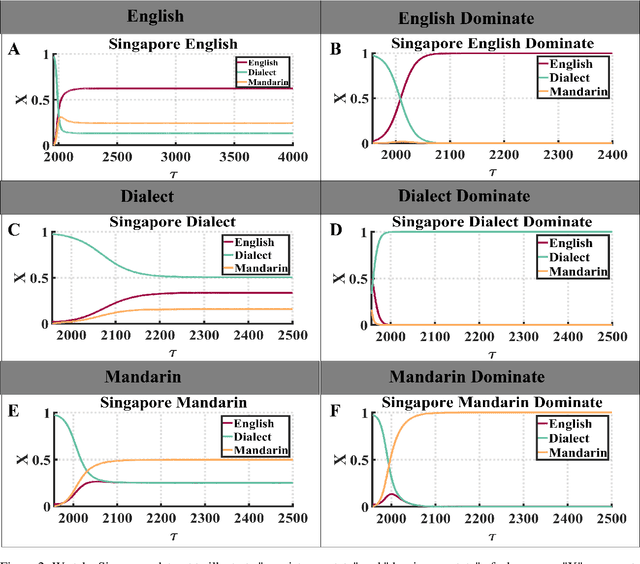
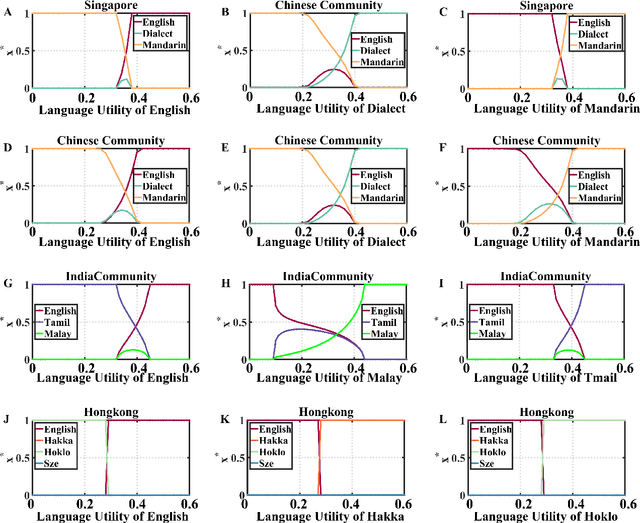
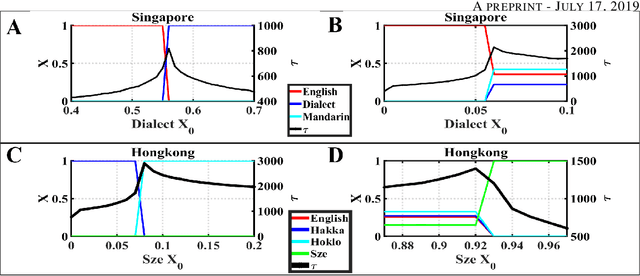
Abstract:Increasing evidence demonstrates that in many places language coexistence has become ubiquitous and essential for supporting language and cultural diversity and associated with its financial and economic benefits. The competitive evolution among multiple languages determines the evolution outcome, either coexistence, decline, or extinction. Here, we extend the Abrams-Strogatz model of language competition to multiple languages and then validate it by analyzing the behavioral transitions of language usage over the recent several decades in Singapore and Hong Kong. In each case, we estimate from data the model parameters that measure each language utility for its speakers and the strength of two biases, the majority preference for their language, and the minority aversion to it. The values of these two biases decide which language is the fastest growing in the competition and what would be the stable state of the system. We also study the system convergence time to stable states and discover the existence of tipping points with multiple attractors. Moreover, the critical slowdown of convergence to the stable fractions of language users appears near and peaks at the tipping points, signaling when the system approaches them. Our analysis furthers our understanding of multiple language evolution and the role of tipping points in behavioral transitions. These insights may help to protect languages from extinction and retain the language and cultural diversity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge