Zachary H. Levine
Quantum Measurement Division, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, Maryland 20899, USA
Physics-assisted Generative Adversarial Network for X-Ray Tomography
Apr 07, 2022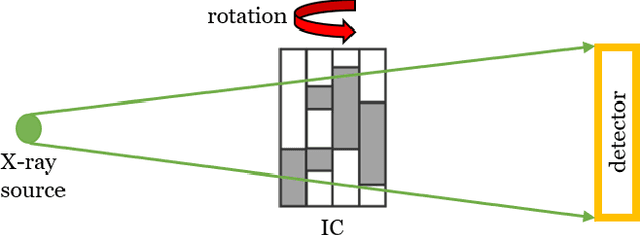
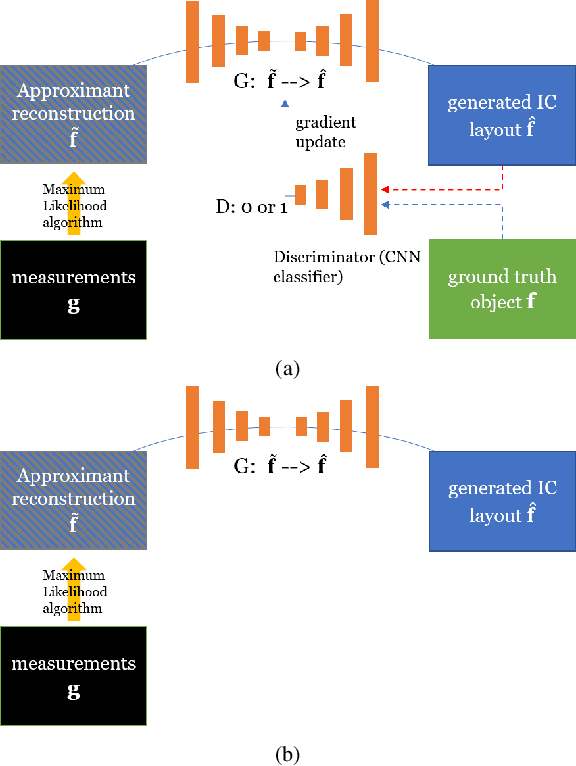
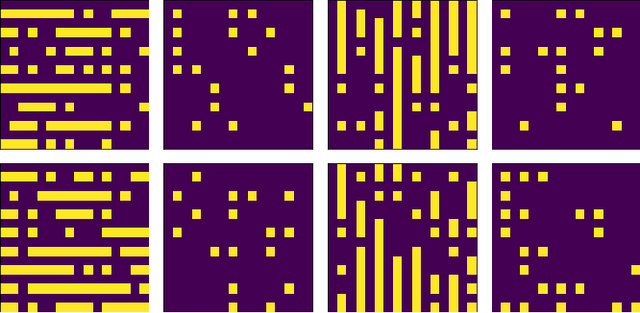
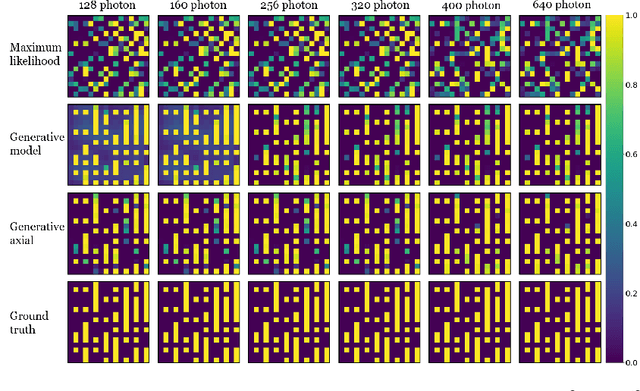
Abstract:X-ray tomography is capable of imaging the interior of objects in three dimensions non-invasively, with applications in biomedical imaging, materials science, electronic inspection, and other fields. The reconstruction process can be an ill-conditioned inverse problem, requiring regularization to obtain satisfactory reconstructions. Recently, deep learning has been adopted for tomographic reconstruction. Unlike iterative algorithms which require a distribution that is known a priori, deep reconstruction networks can learn a prior distribution through sampling the training distributions. In this work, we develop a Physics-assisted Generative Adversarial Network (PGAN), a two-step algorithm for tomographic reconstruction. In contrast to previous efforts, our PGAN utilizes maximum-likelihood estimates derived from the measurements to regularize the reconstruction with both known physics and the learned prior. Synthetic objects with spatial correlations are integrated circuits (IC) from a proposed model CircuitFaker. Compared with maximum-likelihood estimation, PGAN can reduce the photon requirement with limited projection angles to achieve a given error rate. We further attribute the improvement to the learned prior by reconstructing objects created without spatial correlations. The advantages of using a prior from deep learning in X-ray tomography may further enable low-photon nanoscale imaging.
Advantage of Machine Learning over Maximum Likelihood in Limited-Angle Low-Photon X-Ray Tomography
Nov 15, 2021



Abstract:Limited-angle X-ray tomography reconstruction is an ill-conditioned inverse problem in general. Especially when the projection angles are limited and the measurements are taken in a photon-limited condition, reconstructions from classical algorithms such as filtered backprojection may lose fidelity and acquire artifacts due to the missing-cone problem. To obtain satisfactory reconstruction results, prior assumptions, such as total variation minimization and nonlocal image similarity, are usually incorporated within the reconstruction algorithm. In this work, we introduce deep neural networks to determine and apply a prior distribution in the reconstruction process. Our neural networks learn the prior directly from synthetic training samples. The neural nets thus obtain a prior distribution that is specific to the class of objects we are interested in reconstructing. In particular, we used deep generative models with 3D convolutional layers and 3D attention layers which are trained on 3D synthetic integrated circuit (IC) data from a model dubbed CircuitFaker. We demonstrate that, when the projection angles and photon budgets are limited, the priors from our deep generative models can dramatically improve the IC reconstruction quality on synthetic data compared with maximum likelihood estimation. Training the deep generative models with synthetic IC data from CircuitFaker illustrates the capabilities of the learned prior from machine learning. We expect that if the process were reproduced with experimental data, the advantage of the machine learning would persist. The advantages of machine learning in limited angle X-ray tomography may further enable applications in low-photon nanoscale imaging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge