Yvonne Y. Cheung
Sensitivity and Specificity Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Detection of Pneumoperitoneum on Chest Radiographs
Oct 17, 2020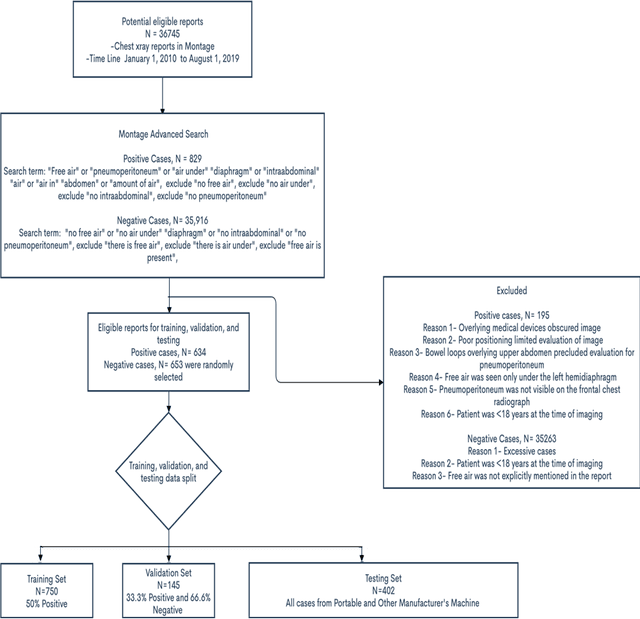
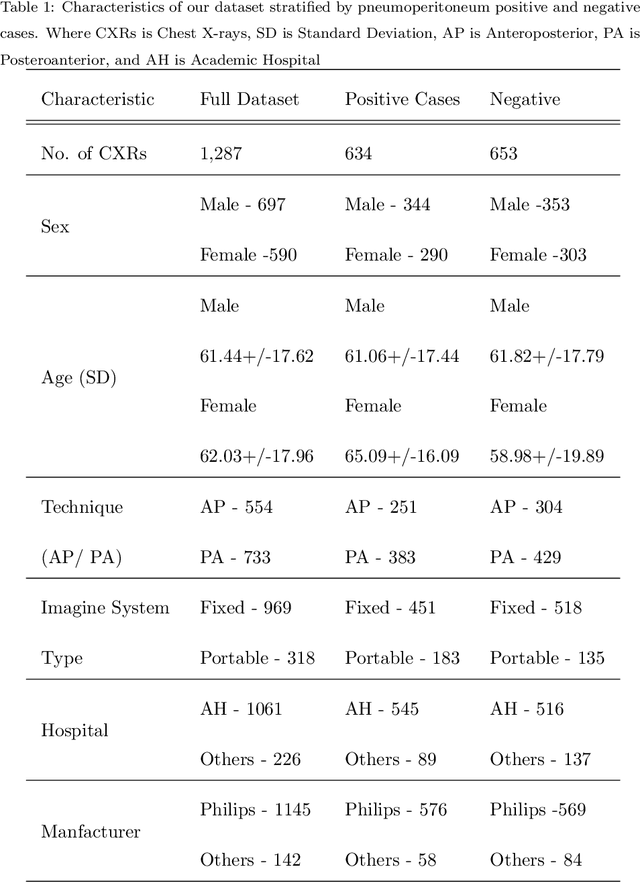
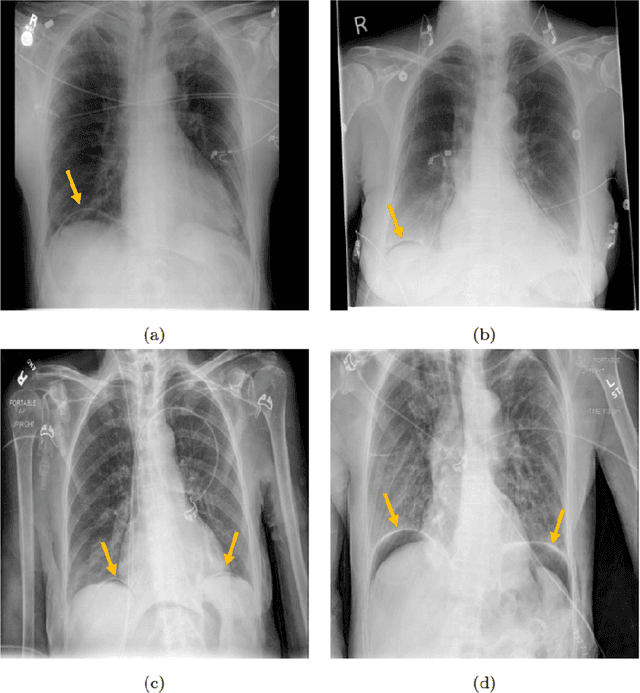
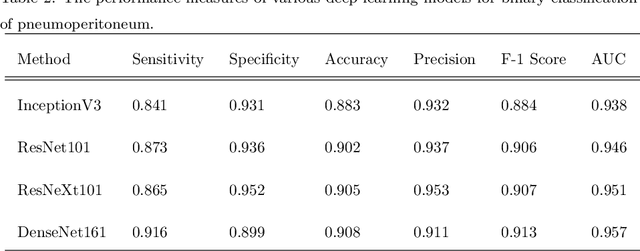
Abstract:Background: Deep learning has great potential to assist with detecting and triaging critical findings such as pneumoperitoneum on medical images. To be clinically useful, the performance of this technology still needs to be validated for generalizability across different types of imaging systems. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study included 1,287 chest X-ray images of patients who underwent initial chest radiography at 13 different hospitals between 2011 and 2019. The chest X-ray images were labelled independently by four radiologist experts as positive or negative for pneumoperitoneum. State-of-the-art deep learning models (ResNet101, InceptionV3, DenseNet161, and ResNeXt101) were trained on a subset of this dataset, and the automated classification performance was evaluated on the rest of the dataset by measuring the AUC, sensitivity, and specificity for each model. Furthermore, the generalizability of these deep learning models was assessed by stratifying the test dataset according to the type of the utilized imaging systems. Results: All deep learning models performed well for identifying radiographs with pneumoperitoneum, while DenseNet161 achieved the highest AUC of 95.7%, Specificity of 89.9%, and Sensitivity of 91.6%. DenseNet161 model was able to accurately classify radiographs from different imaging systems (Accuracy: 90.8%), while it was trained on images captured from a specific imaging system from a single institution. This result suggests the generalizability of our model for learning salient features in chest X-ray images to detect pneumoperitoneum, independent of the imaging system.
Self-Supervised Contextual Language Representation of Radiology Reports to Improve the Identification of Communication Urgency
Dec 05, 2019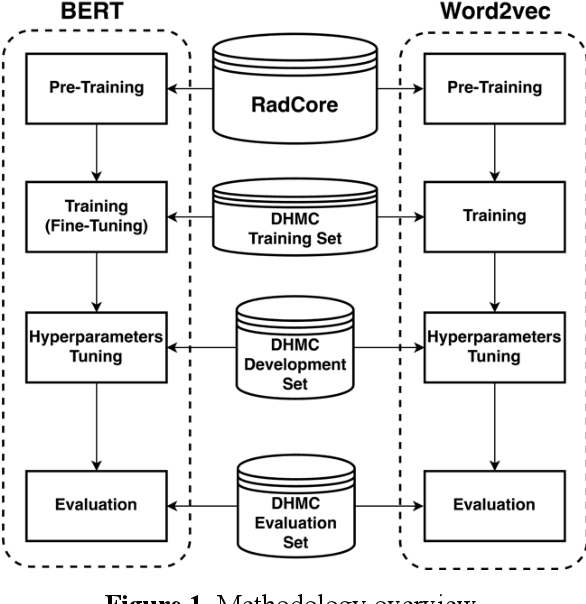
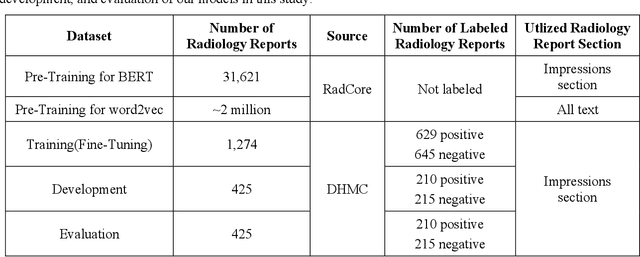
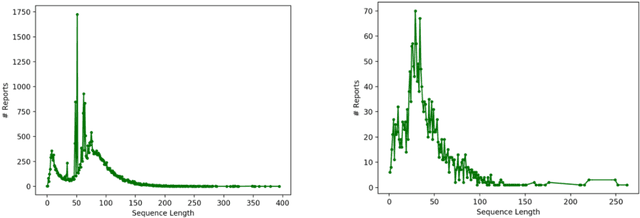
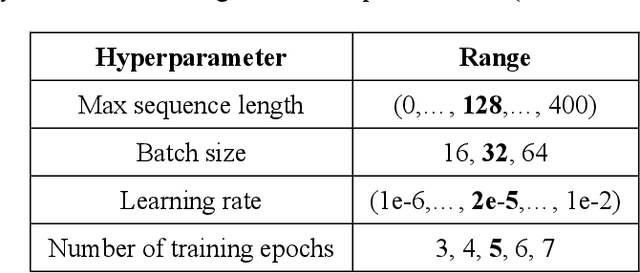
Abstract:Machine learning methods have recently achieved high-performance in biomedical text analysis. However, a major bottleneck in the widespread application of these methods is obtaining the required large amounts of annotated training data, which is resource intensive and time consuming. Recent progress in self-supervised learning has shown promise in leveraging large text corpora without explicit annotations. In this work, we built a self-supervised contextual language representation model using BERT, a deep bidirectional transformer architecture, to identify radiology reports requiring prompt communication to the referring physicians. We pre-trained the BERT model on a large unlabeled corpus of radiology reports and used the resulting contextual representations in a final text classifier for communication urgency. Our model achieved a precision of 97.0%, recall of 93.3%, and F-measure of 95.1% on an independent test set in identifying radiology reports for prompt communication, and significantly outperformed the previous state-of-the-art model based on word2vec representations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge