Yuping Ye
Partition-based Nonrigid Registration for 3D Face Model
Jan 05, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a partition-based surface registration for 3D morphable model(3DMM). In the 3DMM, it often requires to warp a handcrafted template model into different captured models. The proposed method first utilizes the landmarks to partition the template model then scale each part and finally smooth the boundaries. This method is especially effective when the disparity between the template model and the target model is huge. The experiment result shows the method perform well than the traditional warp method and robust to the local minima.
A Food Package Recognition and Sorting System Based on Structured Light and Deep Learning
Sep 07, 2023



Abstract:Vision algorithm-based robotic arm grasping system is one of the robotic arm systems that can be applied to a wide range of scenarios. It uses algorithms to automatically identify the location of the target and guide the robotic arm to grasp it, which has more flexible features than the teachable robotic arm grasping system. However, for some food packages, their transparent packages or reflective materials bring challenges to the recognition of vision algorithms, and traditional vision algorithms cannot achieve high accuracy for these packages. In addition, in the process of robotic arm grasping, the positioning on the z-axis height still requires manual setting of parameters, which may cause errors. Based on the above two problems, we designed a sorting system for food packaging using deep learning algorithms and structured light 3D reconstruction technology. Using a pre-trained MASK R-CNN model to recognize the class of the object in the image and get its 2D coordinates, then using structured light 3D reconstruction technique to calculate its 3D coordinates, and finally after the coordinate system conversion to guide the robotic arm for grasping. After testing, it is shown that the method can fully automate the recognition and grasping of different kinds of food packages with high accuracy. Using this method, it can help food manufacturers to reduce production costs and improve production efficiency.
Benchmarks for Industrial Inspection Based on Structured Light
Jul 02, 2022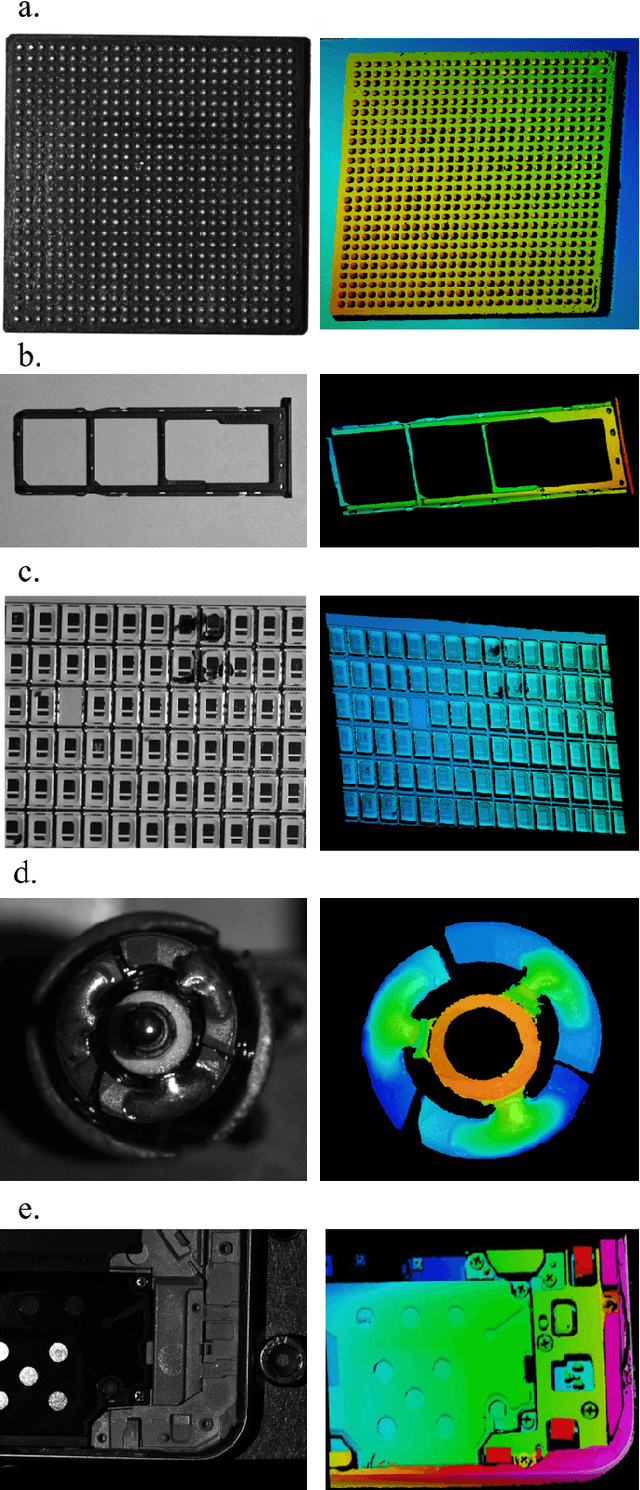
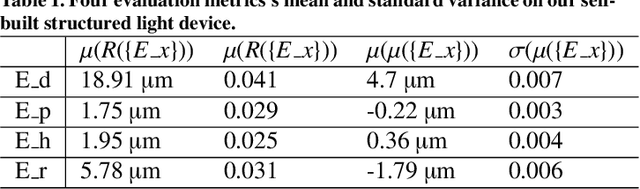
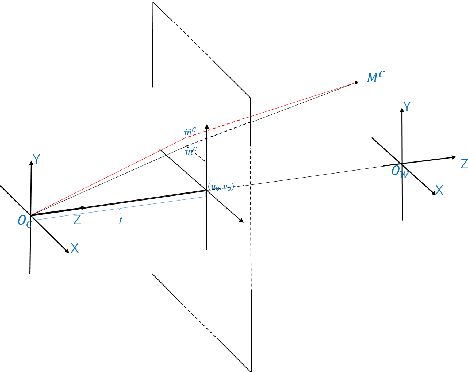
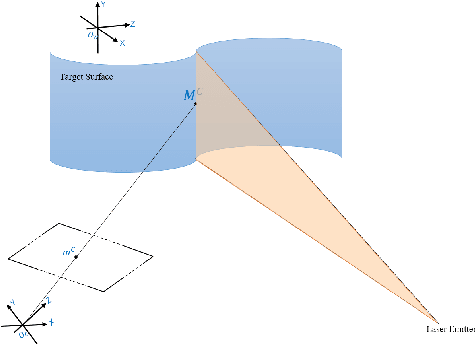
Abstract:Robustness and accuracy are two critical metrics for industrial inspection. In this paper, we propose benchmarks that can evaluate the structured light method's performance. Our evaluation metric was learning from a lot of inspection tasks from the factories. The metric we proposed consists of four detailed criteria such as flatness, length, height and sphericity. Then we can judge whether the structured light method/device can be applied to a specified inspection task by our evaluation metric quickly. A structured light device built for TypeC pin needles inspection performance is evaluated via our metrics in the final experimental section.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge