Yuichi Kato
Anomaly Detection for Multivariate Time Series on Large-scale Fluid Handling Plant Using Two-stage Autoencoder
May 20, 2022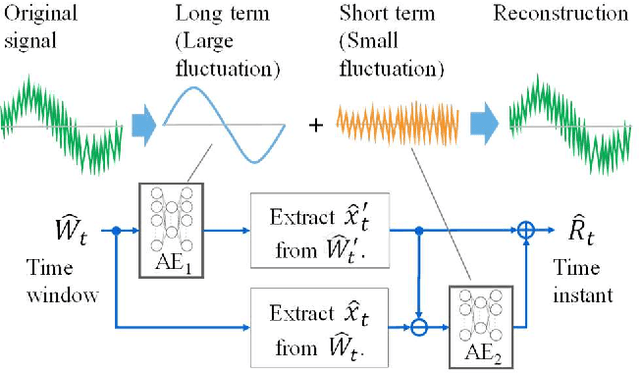
Abstract:This paper focuses on anomaly detection for multivariate time series data in large-scale fluid handling plants with dynamic components, such as power generation, water treatment, and chemical plants, where signals from various physical phenomena are observed simultaneously. In these plants, the need for anomaly detection techniques is increasing in order to reduce the cost of operation and maintenance, in view of a decline in the number of skilled engineers and a shortage of manpower. However, considering the complex behavior of high-dimensional signals and the demand for interpretability, the techniques constitute a major challenge. We introduce a Two-Stage AutoEncoder (TSAE) as an anomaly detection method suitable for such plants. This is a simple autoencoder architecture that makes anomaly detection more interpretable and more accurate, in which based on the premise that plant signals can be separated into two behaviors that have almost no correlation with each other, the signals are separated into long-term and short-term components in a stepwise manner, and the two components are trained independently to improve the inference capability for normal signals. Through experiments on two publicly available datasets of water treatment systems, we have confirmed the high detection performance, the validity of the premise, and that the model behavior was as intended, i.e., the technical effectiveness of TSAE.
* The 2nd Workshop on Large-scale Industrial Time Series Analysis at the 21st IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), 2021
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge