Yuefeng Shi
Exploiting Sentiment and Common Sense for Zero-shot Stance Detection
Aug 18, 2022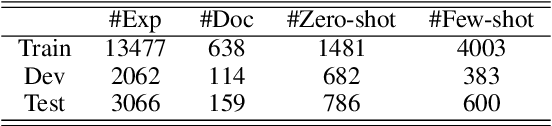
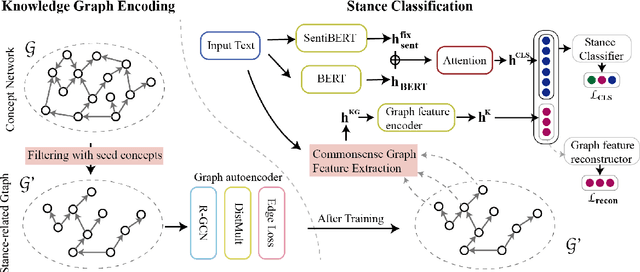

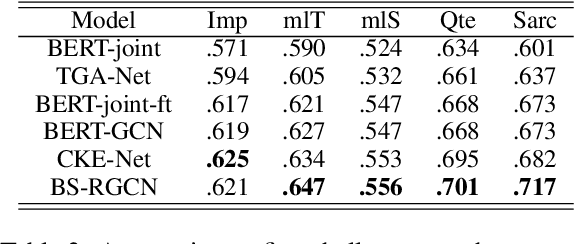
Abstract:The stance detection task aims to classify the stance toward given documents and topics. Since the topics can be implicit in documents and unseen in training data for zero-shot settings, we propose to boost the transferability of the stance detection model by using sentiment and commonsense knowledge, which are seldom considered in previous studies. Our model includes a graph autoencoder module to obtain commonsense knowledge and a stance detection module with sentiment and commonsense. Experimental results show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on the zero-shot and few-shot benchmark dataset--VAST. Meanwhile, ablation studies prove the significance of each module in our model. Analysis of the relations between sentiment, common sense, and stance indicates the effectiveness of sentiment and common sense.
A Pilot Study for Chinese SQL Semantic Parsing
Oct 16, 2019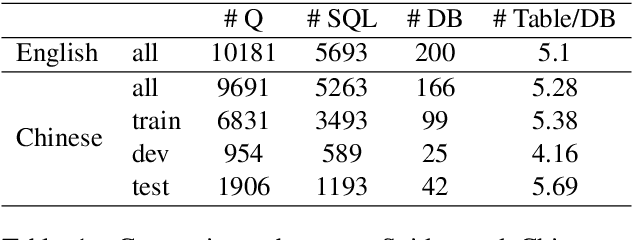


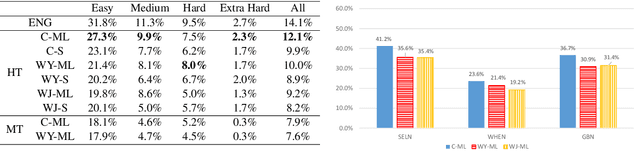
Abstract:The task of semantic parsing is highly useful for dialogue and question answering systems. Many datasets have been proposed to map natural language text into SQL, among which the recent Spider dataset provides cross-domain samples with multiple tables and complex queries. We build a Spider dataset for Chinese, which is currently a low-resource language in this task area. Interesting research questions arise from the uniqueness of the language, which requires word segmentation, and also from the fact that SQL keywords and columns of DB tables are typically written in English. We compare character- and word-based encoders for a semantic parser, and different embedding schemes. Results show that word-based semantic parser is subject to segmentation errors and cross-lingual word embeddings are useful for text-to-SQL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge