Yudian Zhang
ASTRA: Automated Synthesis of agentic Trajectories and Reinforcement Arenas
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as tool-augmented agents for multi-step decision making, yet training robust tool-using agents remains challenging. Existing methods still require manual intervention, depend on non-verifiable simulated environments, rely exclusively on either supervised fine-tuning (SFT) or reinforcement learning (RL), and struggle with stable long-horizon, multi-turn learning. To address these challenges, we introduce ASTRA, a fully automated end-to-end framework for training tool-augmented language model agents via scalable data synthesis and verifiable reinforcement learning. ASTRA integrates two complementary components. First, a pipeline that leverages the static topology of tool-call graphs synthesizes diverse, structurally grounded trajectories, instilling broad and transferable tool-use competence. Second, an environment synthesis framework that captures the rich, compositional topology of human semantic reasoning converts decomposed question-answer traces into independent, code-executable, and rule-verifiable environments, enabling deterministic multi-turn RL. Based on this method, we develop a unified training methodology that integrates SFT with online RL using trajectory-level rewards to balance task completion and interaction efficiency. Experiments on multiple agentic tool-use benchmarks demonstrate that ASTRA-trained models achieve state-of-the-art performance at comparable scales, approaching closed-source systems while preserving core reasoning ability. We release the full pipelines, environments, and trained models at https://github.com/LianjiaTech/astra.
ODC-SA Net: Orthogonal Direction Enhancement and Scale Aware Network for Polyp Segmentation
May 10, 2024Abstract:Accurate polyp segmentation is crucial for the early detection and prevention of colorectal cancer. However, the existing polyp detection methods sometimes ignore multi-directional features and drastic changes in scale. To address these challenges, we design an Orthogonal Direction Enhancement and Scale Aware Network (ODC-SA Net) for polyp segmentation. The Orthogonal Direction Convolutional (ODC) block can extract multi-directional features using transposed rectangular convolution kernels through forming an orthogonal feature vector basis, which solves the issue of random feature direction changes and reduces computational load. Additionally, the Multi-scale Fusion Attention (MSFA) mechanism is proposed to emphasize scale changes in both spatial and channel dimensions, enhancing the segmentation accuracy for polyps of varying sizes. Extraction with Re-attention Module (ERA) is used to re-combinane effective features, and Structures of Shallow Reverse Attention Mechanism (SRA) is used to enhance polyp edge with low level information. A large number of experiments conducted on public datasets have demonstrated that the performance of this model is superior to state-of-the-art methods.
Mask-TS Net: Mask Temperature Scaling Uncertainty Calibration for Polyp Segmentation
May 09, 2024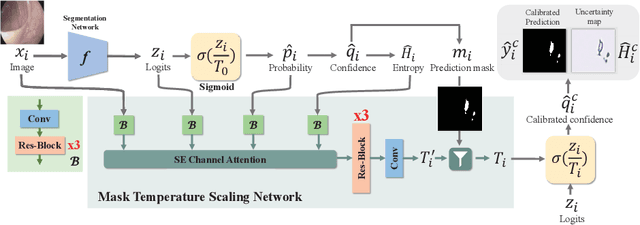
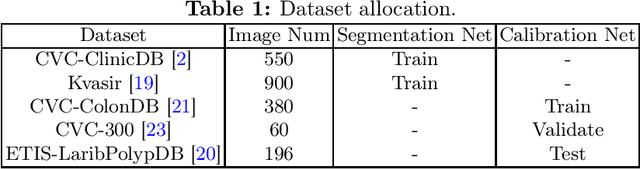
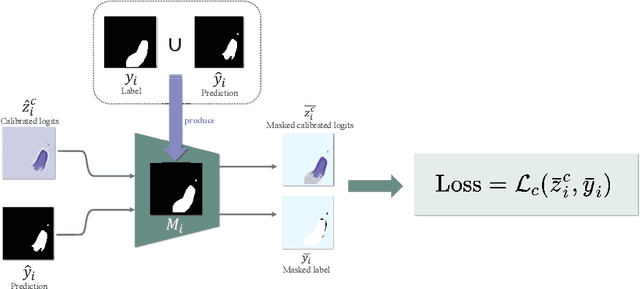
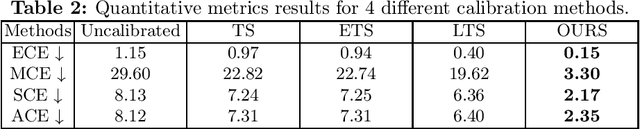
Abstract:Lots of popular calibration methods in medical images focus on classification, but there are few comparable studies on semantic segmentation. In polyp segmentation of medical images, we find most diseased area occupies only a small portion of the entire image, resulting in previous models being not well-calibrated for lesion regions but well-calibrated for background, despite their seemingly better Expected Calibration Error (ECE) scores overall. Therefore, we proposed four-branches calibration network with Mask-Loss and Mask-TS strategies to more focus on the scaling of logits within potential lesion regions, which serves to mitigate the influence of background interference. In the experiments, we compare the existing calibration methods with the proposed Mask Temperature Scaling (Mask-TS). The results indicate that the proposed calibration network outperforms other methods both qualitatively and quantitatively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge