Mask-TS Net: Mask Temperature Scaling Uncertainty Calibration for Polyp Segmentation
Paper and Code
May 09, 2024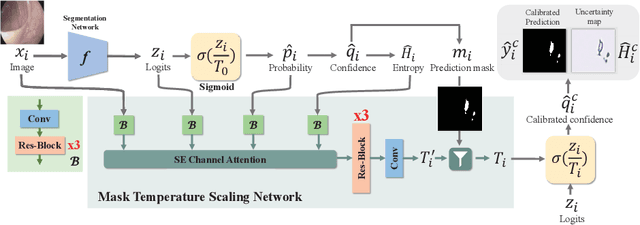
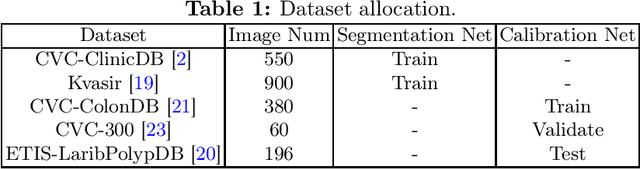
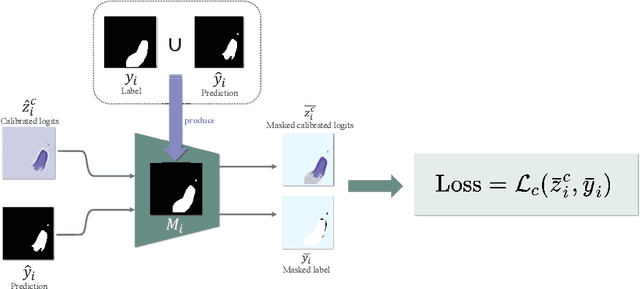
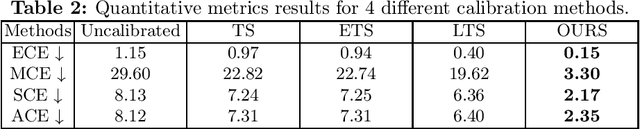
Lots of popular calibration methods in medical images focus on classification, but there are few comparable studies on semantic segmentation. In polyp segmentation of medical images, we find most diseased area occupies only a small portion of the entire image, resulting in previous models being not well-calibrated for lesion regions but well-calibrated for background, despite their seemingly better Expected Calibration Error (ECE) scores overall. Therefore, we proposed four-branches calibration network with Mask-Loss and Mask-TS strategies to more focus on the scaling of logits within potential lesion regions, which serves to mitigate the influence of background interference. In the experiments, we compare the existing calibration methods with the proposed Mask Temperature Scaling (Mask-TS). The results indicate that the proposed calibration network outperforms other methods both qualitatively and quantitatively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge