Yuan Tai
Bayesian Convolutional Neural Networks for Seven Basic Facial Expression Classifications
Jul 13, 2021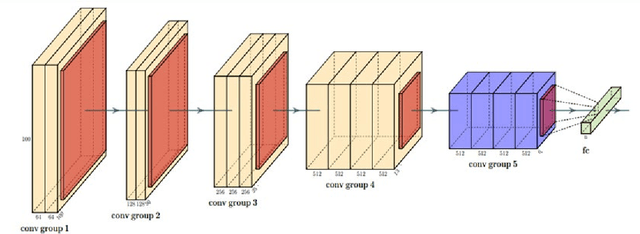
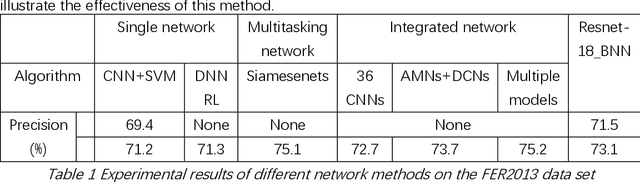
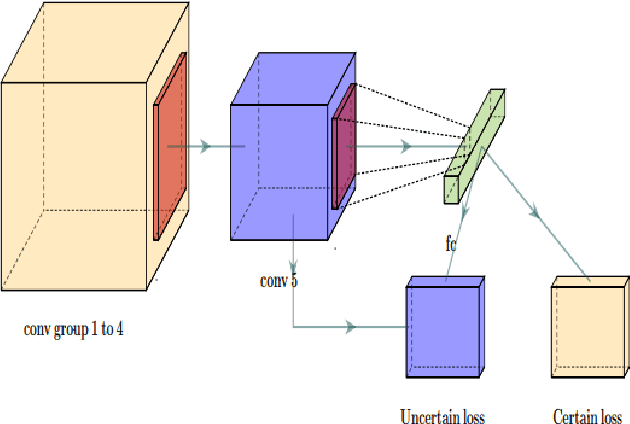
Abstract:The seven basic facial expression classifications are a basic way to express complex human emotions and are an important part of artificial intelligence research. Based on the traditional Bayesian neural network framework, the ResNet18_BNN network constructed in this paper has been improved in the following three aspects: (1) A new objective function is proposed, which is composed of the KL loss of uncertain parameters and the intersection of specific parameters. Entropy loss composition. (2) Aiming at a special objective function, a training scheme for alternately updating these two parameters is proposed. (3) Only model the parameters of the last convolution group. Through testing on the FER2013 test set, we achieved 71.5% and 73.1% accuracy in PublicTestSet and PrivateTestSet, respectively. Compared with traditional Bayesian neural networks, our method brings the highest classification accuracy gain.
Unsupervised Learning Framework of Interest Point Via Properties Optimization
Jul 26, 2019

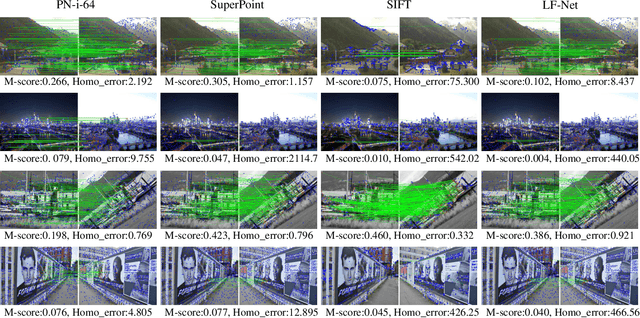

Abstract:This paper presents an entirely unsupervised interest point training framework by jointly learning detector and descriptor, which takes an image as input and outputs a probability and a description for every image point. The objective of the training framework is formulated as joint probability distribution of the properties of the extracted points. The essential properties are selected as sparsity, repeatability and discriminability which are formulated by the probabilities. To maximize the objective efficiently, latent variable is introduced to represent the probability of that a point satisfies the required properties. Therefore, original maximization can be optimized with Expectation Maximization algorithm (EM). Considering high computation cost of EM on large scale image set, we implement the optimization process with an efficient strategy as Mini-Batch approximation of EM (MBEM). In the experiments both detector and descriptor are instantiated with fully convolutional network which is named as Property Network (PN). The experiments demonstrate that PN outperforms state-of-the-art methods on a number of image matching benchmarks without need of retraining. PN also reveals that the proposed training framework has high flexibility to adapt to diverse types of scenes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge