Yoonwon Jung
Developing Social Robots with Empathetic Non-Verbal Cues Using Large Language Models
Aug 31, 2023Abstract:We propose augmenting the empathetic capacities of social robots by integrating non-verbal cues. Our primary contribution is the design and labeling of four types of empathetic non-verbal cues, abbreviated as SAFE: Speech, Action (gesture), Facial expression, and Emotion, in a social robot. These cues are generated using a Large Language Model (LLM). We developed an LLM-based conversational system for the robot and assessed its alignment with social cues as defined by human counselors. Preliminary results show distinct patterns in the robot's responses, such as a preference for calm and positive social emotions like 'joy' and 'lively', and frequent nodding gestures. Despite these tendencies, our approach has led to the development of a social robot capable of context-aware and more authentic interactions. Our work lays the groundwork for future studies on human-robot interactions, emphasizing the essential role of both verbal and non-verbal cues in creating social and empathetic robots.
Social Robots As Companions for Lonely Hearts: The Role of Anthropomorphism and Robot Appearances
Jun 05, 2023



Abstract:Loneliness is a distressing personal experience and a growing social issue. Social robots could alleviate the pain of loneliness, particularly for those who lack in-person interaction. This paper investigated how the effect of loneliness on anthropomorphizing social robots differs by robot appearances, and how it leads to the purchase intention of social robots. Participants viewed a video of one of the three robots(machine-like, animal-like, and human-like) moving and interacting with a human counterpart. The results revealed that when individuals were lonelier, the tendency to anthropomorphize human-like robots increased more than that of animal-like robots. The moderating effect remained significant after covariates were included. The increase in anthropomorphic tendency predicted the heightened purchase intent. The findings imply that human-like robots induce lonely individuals' desire to replenish the sense of connectedness from robots more than animal-like robots, and that anthropomorphic tendency reveals the potential of social robots as real-life companions of lonely individuals.
A Computational Approach to Measure Empathy and Theory-of-Mind from Written Texts
Aug 26, 2021

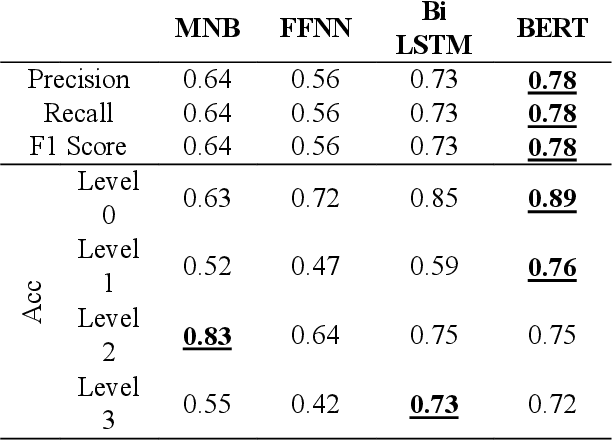

Abstract:Theory-of-mind (ToM), a human ability to infer the intentions and thoughts of others, is an essential part of empathetic experiences. We provide here the framework for using NLP models to measure ToM expressed in written texts. For this purpose, we introduce ToM-Diary, a crowdsourced 18,238 diaries with 74,014 Korean sentences annotated with different ToM levels. Each diary was annotated with ToM levels by trained psychology students and reviewed by selected psychology experts. The annotators first divided the diaries based on whether they mentioned other people: self-focused and other-focused. Examples of self-focused sentences are "I am feeling good". The other-focused sentences were further classified into different levels. These levels differ by whether the writer 1) mentions the presence of others without inferring their mental state(e.g., I saw a man walking down the street), 2) fails to take the perspective of others (e.g., I don't understand why they refuse to wear masks), or 3) successfully takes the perspective of others (It must have been hard for them to continue working). We tested whether state-of-the-art transformer-based models (e.g., BERT) could predict underlying ToM levels in sentences. We found that BERT more successfully detected self-focused sentences than other-focused ones. Sentences that successfully take the perspective of others (the highest ToM level) were the most difficult to predict. Our study suggests a promising direction for large-scale and computational approaches for identifying the ability of authors to empathize and take the perspective of others. The dataset is at [URL](https://github.com/humanfactorspsych/covid19-tom-empathy-diary)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge