Yong Chen Goh
Joint Models for Handling Non-Ignorable Missing Data using Bayesian Additive Regression Trees: Application to Leaf Photosynthetic Traits Data
Dec 19, 2024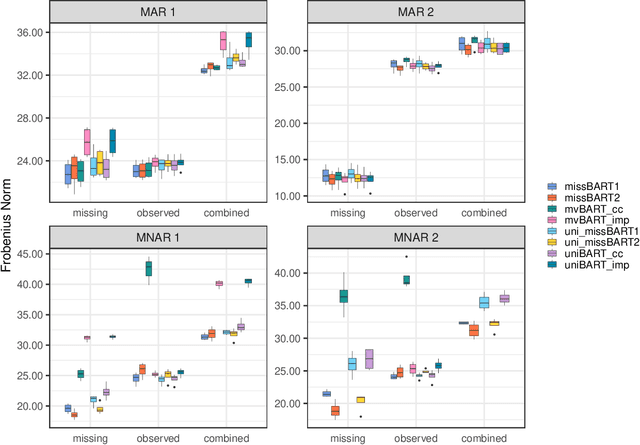
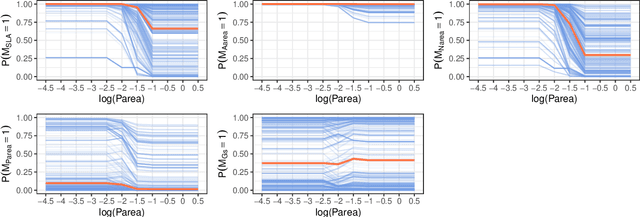
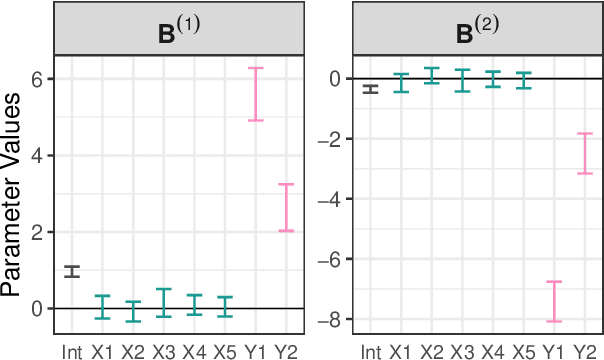
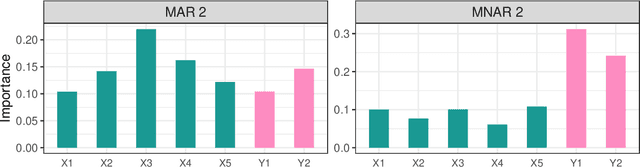
Abstract:Dealing with missing data poses significant challenges in predictive analysis, often leading to biased conclusions when oversimplified assumptions about the missing data process are made. In cases where the data are missing not at random (MNAR), jointly modeling the data and missing data indicators is essential. Motivated by a real data application with partially missing multivariate outcomes related to leaf photosynthetic traits and several environmental covariates, we propose two methods under a selection model framework for handling data with missingness in the response variables suitable for recovering various missingness mechanisms. Both approaches use a multivariate extension of Bayesian additive regression trees (BART) to flexibly model the outcomes. The first approach simultaneously uses a probit regression model to jointly model the missingness. In scenarios where the relationship between the missingness and the data is more complex or non-linear, we propose a second approach using a probit BART model to characterize the missing data process, thereby employing two BART models simultaneously. Both models also effectively handle ignorable covariate missingness. The efficacy of both models compared to existing missing data approaches is demonstrated through extensive simulations, in both univariate and multivariate settings, and through the aforementioned application to the leaf photosynthetic trait data.
Bayesian Causal Forests for Multivariate Outcomes: Application to Irish Data From an International Large Scale Education Assessment
Mar 08, 2023Abstract:Bayesian Causal Forests (BCF) is a causal inference machine learning model based on a highly flexible non-parametric regression and classification tool called Bayesian Additive Regression Trees (BART). Motivated by data from the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS), which includes data on student achievement in both mathematics and science, we present a multivariate extension of the BCF algorithm. With the help of simulation studies we show that our approach can accurately estimate causal effects for multiple outcomes subject to the same treatment. We also apply our model to Irish data from TIMSS 2019. Our findings reveal the positive effects of having access to a study desk at home (Mathematics ATE 95% CI: [0.20, 11.67]) while also highlighting the negative consequences of students often feeling hungry at school (Mathematics ATE 95% CI: [-11.15, -2.78] , Science ATE 95% CI: [-10.82,-1.72]) or often being absent (Mathematics ATE 95% CI: [-12.47, -1.55]).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge