Yinan Zhong
Zhejiang University
Catch You and I Can: Revealing Source Voiceprint Against Voice Conversion
Feb 24, 2023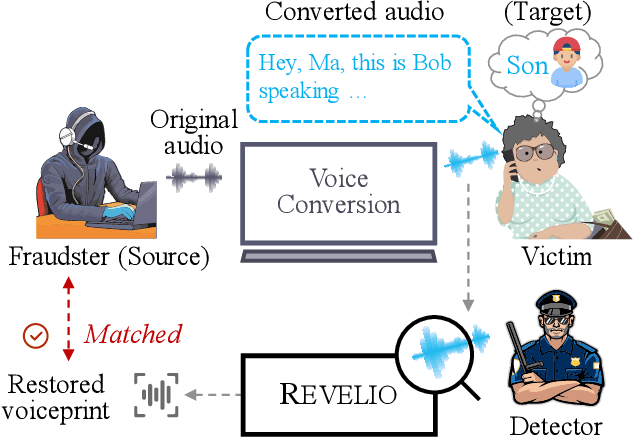
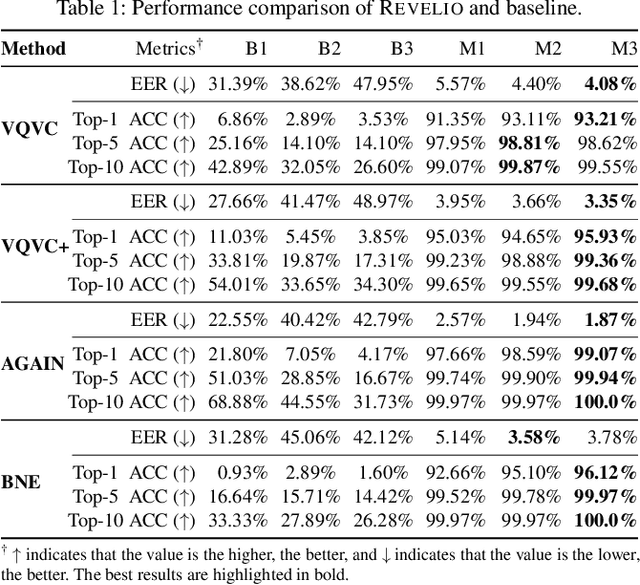
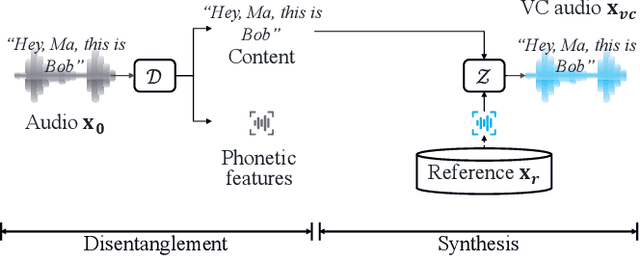
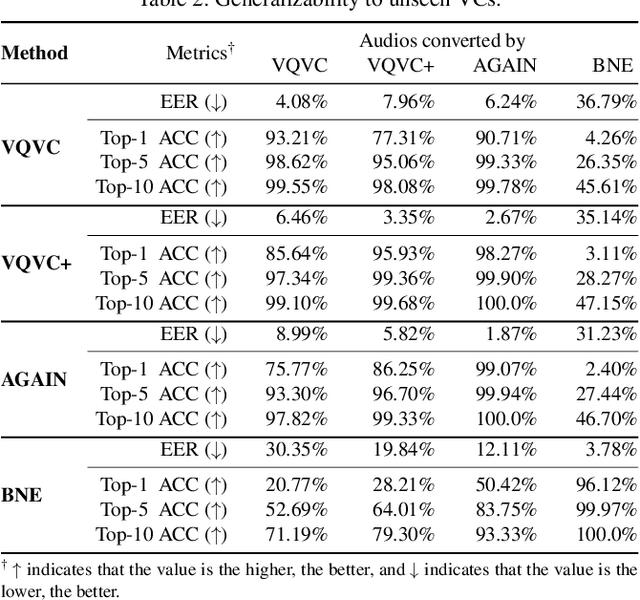
Abstract:Voice conversion (VC) techniques can be abused by malicious parties to transform their audios to sound like a target speaker, making it hard for a human being or a speaker verification/identification system to trace the source speaker. In this paper, we make the first attempt to restore the source voiceprint from audios synthesized by voice conversion methods with high credit. However, unveiling the features of the source speaker from a converted audio is challenging since the voice conversion operation intends to disentangle the original features and infuse the features of the target speaker. To fulfill our goal, we develop Revelio, a representation learning model, which learns to effectively extract the voiceprint of the source speaker from converted audio samples. We equip Revelio with a carefully-designed differential rectification algorithm to eliminate the influence of the target speaker by removing the representation component that is parallel to the voiceprint of the target speaker. We have conducted extensive experiments to evaluate the capability of Revelio in restoring voiceprint from audios converted by VQVC, VQVC+, AGAIN, and BNE. The experiments verify that Revelio is able to rebuild voiceprints that can be traced to the source speaker by speaker verification and identification systems. Revelio also exhibits robust performance under inter-gender conversion, unseen languages, and telephony networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge