Yicheng Su
Consumer Image Quality Prediction using Recurrent Neural Networks for Spatial Pooling
Jun 02, 2021
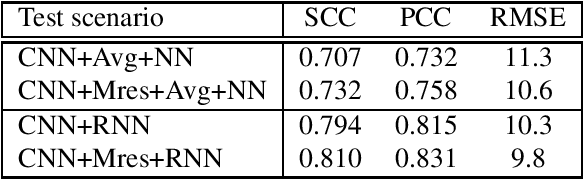


Abstract:Promising results for subjective image quality prediction have been achieved during the past few years by using convolutional neural networks (CNN). However, the use of CNNs for high resolution image quality assessment remains a challenge, since typical CNN architectures have been designed for small resolution input images. In this study, we propose an image quality model that attempts to mimic the attention mechanism of human visual system (HVS) by using a recurrent neural network (RNN) for spatial pooling of the features extracted from different spatial areas (patches) by a deep CNN-based feature extractor. The experimental study, conducted by using images with different resolutions from two recently published image quality datasets, indicates that the quality prediction accuracy of the proposed method is competitive against benchmark models representing the state-of-the-art, and the proposed method also performs consistently on different resolution versions of the same dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge