Yi-Hsin Li
Adaptive Segmentation-Based Initialization for Steered Mixture of Experts Image Regression
Sep 16, 2024



Abstract:Kernel image regression methods have shown to provide excellent efficiency in many image processing task, such as image and light-field compression, Gaussian Splatting, denoising and super-resolution. The estimation of parameters for these methods frequently employ gradient descent iterative optimization, which poses significant computational burden for many applications. In this paper, we introduce a novel adaptive segmentation-based initialization method targeted for optimizing Steered-Mixture-of Experts (SMoE) gating networks and Radial-Basis-Function (RBF) networks with steering kernels. The novel initialization method allocates kernels into pre-calculated image segments. The optimal number of kernels, kernel positions, and steering parameters are derived per segment in an iterative optimization and kernel sparsification procedure. The kernel information from "local" segments is then transferred into a "global" initialization, ready for use in iterative optimization of SMoE, RBF, and related kernel image regression methods. Results show that drastic objective and subjective quality improvements are achievable compared to widely used regular grid initialization, "state-of-the-art" K-Means initialization and previously introduced segmentation-based initialization methods, while also drastically improving the sparsity of the regression models. For same quality, the novel initialization results in models with around 50% reduction of kernels. In addition, a significant reduction of convergence time is achieved, with overall run-time savings of up to 50%. The segmentation-based initialization strategy itself admits heavy parallel computation; in theory, it may be divided into as many tasks as there are segments in the images. By accessing only four parallel GPUs, run-time savings of already 50% for initialization are achievable.
Steered Mixture of Experts Regression for Image Denoising with Multi-Model-Inference
Mar 30, 2023
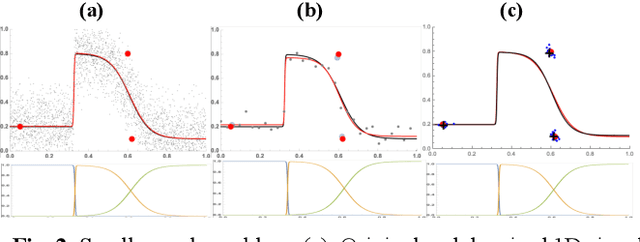
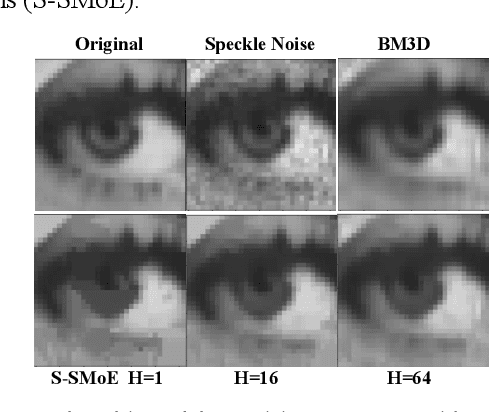
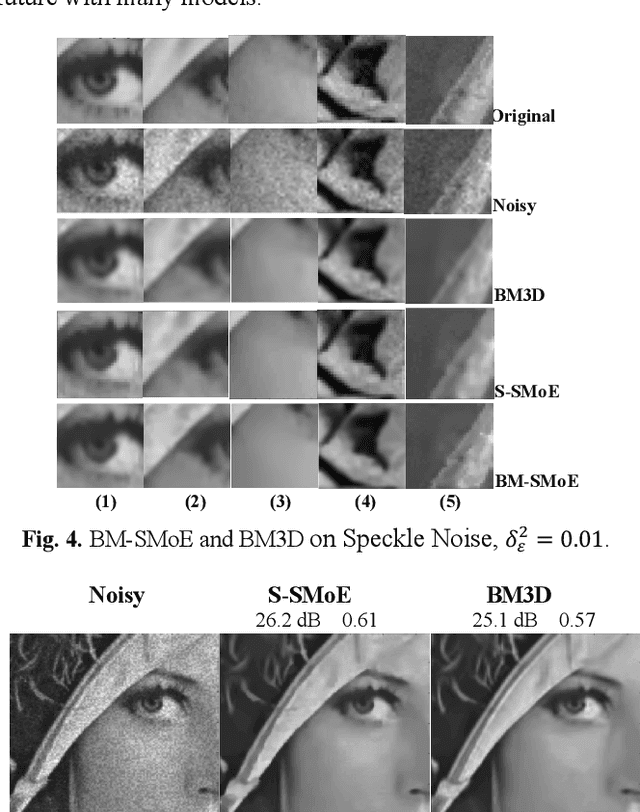
Abstract:In this paper we introduce a novel block-based regression strategy for image denoising based on edge-aware Steered-Mixture-of-Experts (SMoE) models. SMoEs provide very sparse image representations, able to model sharp edges as well as smooth transitions in images efficiently with few parameters. A multi-model inference strategy is developed that improves significantly the denoising capacity of single SMoE models. We show that the important edge reconstruction properties of SMoEs are well preserved, even when many models are fused under severe noise. We investigate model-inference from local neighborhood blocks as well as from distant blocks using block-matching as in BM3D. Our initial results indicate that SMoE multi-model regression can provide promising results compared to state-of-the-art BM3D with excellent edge quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge