Yi Zhuo
Displacement field calculation of large-scale structures using computer vision with physical constraints
Mar 31, 2023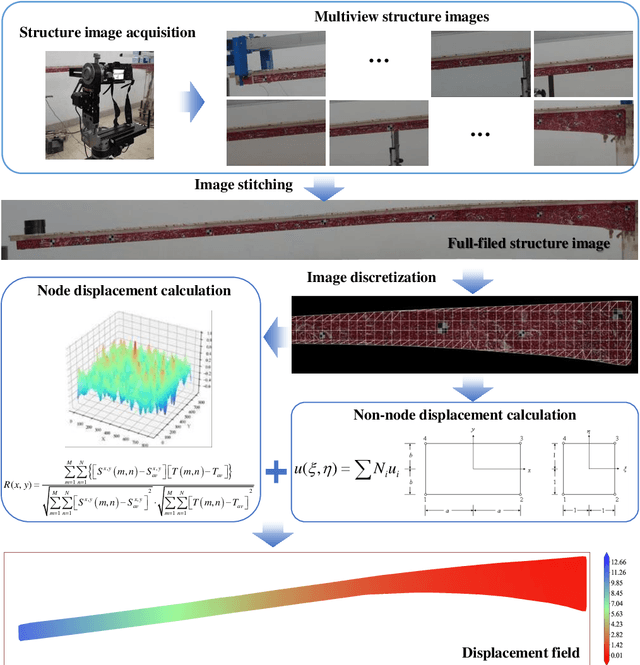

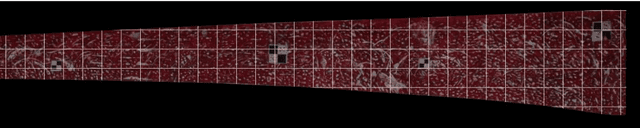
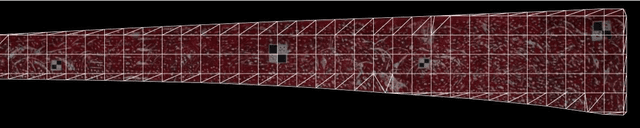
Abstract:Because of the advantages of easy deployment, low cost and non-contact, computer vision-based structural displacement acquisition technique has received wide attention and research in recent years. However, the displacement field acquisition of large-scale structures is a challenging topic due to the contradiction of camera field of view and resolution. This paper presents a large-scale structural displacement field calculation framework with integrated computer vision and physical constraints using only one camera. Firstly, the full-field image of the large-scale structure is obtained by processing the multi-view image using image stitching technique; secondly, the full-field image is meshed and the node displacements are calculated using an improved template matching method; and finally, the non-node displacements are described using shape functions considering physical constraints. The developed framework was validated using a scaled bridge model and evaluated by the proposed evaluation index for displacement field calculation accuracy. This paper can provide an effective way to obtain displacement fields of large-scale structures efficiently and cost-effectively.
Local track irregularity identification based on multi-sensor time-frequency features of high-speed railway bridge accelerations
Mar 28, 2023Abstract:Shortwave track diseases are generally reflected in the form of local track irregularity. Such diseases will greatly impact the train-track-bridge interaction (TTBI) dynamic system, seriously affecting train safety. Therefore, a method is proposed to detect and localize local track irregularities based on multis-sensor time-frequency features of high-speed railway bridge accelerations. Continuous wavelet transform (CWT) is used to analyze the multi-sensor accelerations of railway bridges. Moreover, time-frequency features based on the sum of wavelet coefficients are proposed, considering the influence of the distance from the measurement points to the local irregularity on the recognition accuracy. Then, the multi-domain features are utilized to recognize deteriorated railway locations. A simply-supported high-speed railway bridge traversed by a railway train is adopted as a numerical simulation. Comparative studies are conducted to investigate the influence of vehicle speeds and the location of local track irregularity on the algorithm. Numerical simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can detect and locate local track irregularity accurately and is robust to vehicle speeds.
Chloride Ion Erosion of Pre-Stressed Concrete Bridges in Cold Regions
Mar 28, 2023Abstract:The erosion of chloride ions in concrete bridges will accelerate the corrosion of reinforcement, which is an important reason for the decline of bridge durability. The erosion process of chloride ion, especially deicing salt solution in cold regions, is complex and has many influencing factors. It is very important to use accurate and effective methods to analyze the chloride ion erosion process in concrete. In this study, the pre-stressed concrete bridge retired in the cold region was taken as the research object, and the specimens from the whole bridge are obtained by the method of core drilling sampling. The concentration of chloride ion was measured at different depths of the specimens. The process of chloride ion erosion was simulated in two-dimensional space through COMSOL multi-physical field simulation, and compared with the measured results. The simulation method proposed in this paper has good reliability and accuracy.
Damage detection of high-speed railway box girder using train-induced dynamic responses
Mar 23, 2023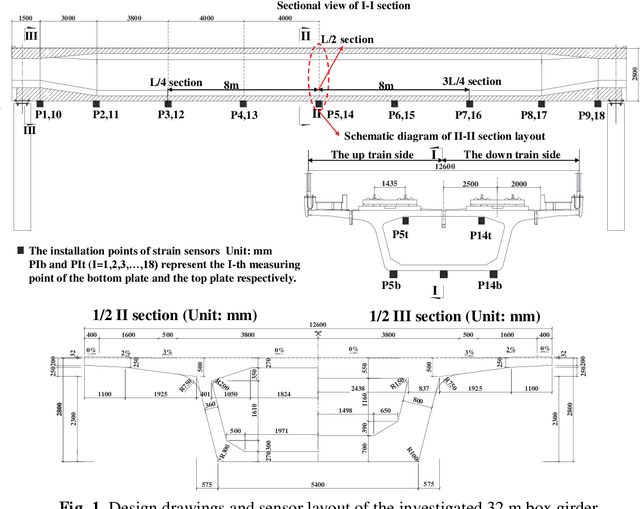
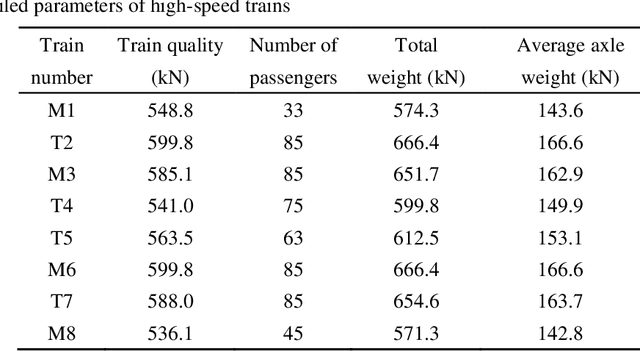
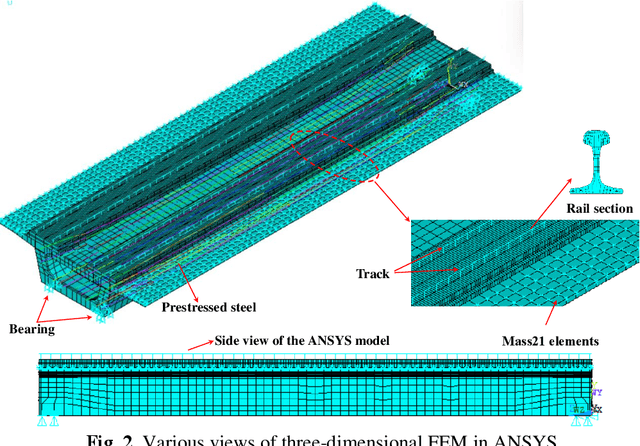

Abstract:This paper proposes a damage detection method based on the train-induced responses of high-speed railway box girder. Under the coupling effects of bending and torsion, the traditional damage detection method based on the Euler beam theory cannot be applied. In this research, the box girder section is divided into different components based on the plate element analysis method. The strain responses were preprocessed based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA) method to remove the influence of train operation variation. The residual error of autoregressive (AR) model was used as a potential index of damage features. The optimal order of the model was determined based on Bayesian information criterion (BIC) criterion. Finally, the confidence boundary (CB) of damage features (DF) constituting outliers can be estimated by Gaussian inverse cumulative distribution function (ICDF). The numerical simulation results show that the proposed method in this paper can effectively identify, locate and quantify the damage, which verifies the accuracy of the proposed method. The proposed method effectively identifies the early damage of all components on the key section by using four strain sensors, and it is helpful for developing effective maintenance strategies for high-speed railway box girder.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge