Yehonatan Fridman
ChangeChip: A Reference-Based Unsupervised Change Detection for PCB Defect Detection
Sep 13, 2021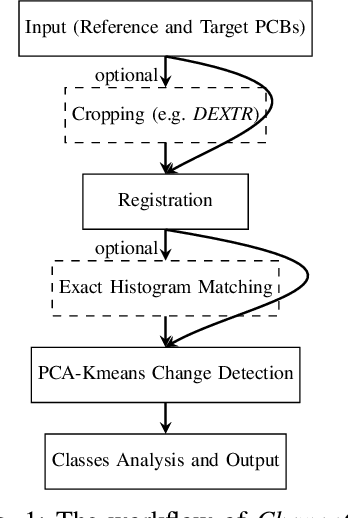

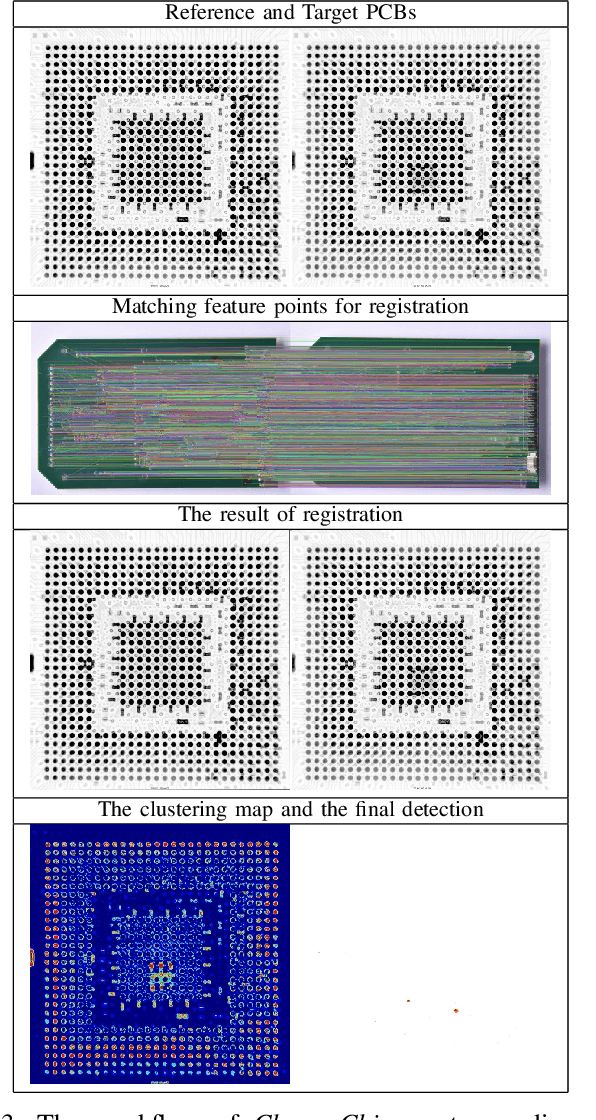

Abstract:The usage of electronic devices increases, and becomes predominant in most aspects of life. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is the most common industrial method for manufacturing electric devices in which electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a Printed Circuit Board (PCB). Although the expansion of electronic devices affects our lives in a productive way, failures or defects in the manufacturing procedure of those devices might also be counterproductive and even harmful in some cases. It is therefore desired and sometimes crucial to ensure zero-defect quality in electronic devices and their production. While traditional Image Processing (IP) techniques are not sufficient to produce a complete solution, other promising methods like Deep Learning (DL) might also be challenging for PCB inspection, mainly because such methods require big adequate datasets which are missing, not available or not updated in the rapidly growing field of PCBs. Thus, PCB inspection is conventionally performed manually by human experts. Unsupervised Learning (UL) methods may potentially be suitable for PCB inspection, having learning capabilities on the one hand, while not relying on large datasets on the other. In this paper, we introduce ChangeChip, an automated and integrated change detection system for defect detection in PCBs, from soldering defects to missing or misaligned electronic elements, based on Computer Vision (CV) and UL. We achieve good quality defect detection by applying an unsupervised change detection between images of a golden PCB (reference) and the inspected PCB under various setting. In this work, we also present CD-PCB, a synthesized labeled dataset of 20 pairs of PCB images for evaluation of defect detection algorithms.
Complete CVDL Methodology for Investigating Hydrodynamic Instabilities
Apr 26, 2020



Abstract:In fluid dynamics, one of the most important research fields is hydrodynamic instabilities and their evolution in different flow regimes. The investigation of said instabilities is concerned with the highly non-linear dynamics. Currently, three main methods are used for understanding of such phenomenon - namely analytical models, experiments and simulations - and all of them are primarily investigated and correlated using human expertise. In this work we claim and demonstrate that a major portion of this research effort could and should be analysed using recent breakthrough advancements in the field of Computer Vision with Deep Learning (CVDL, or Deep Computer-Vision). Specifically, we target and evaluate specific state-of-the-art techniques - such as Image Retrieval, Template Matching, Parameters Regression and Spatiotemporal Prediction - for the quantitative and qualitative benefits they provide. In order to do so we focus in this research on one of the most representative instabilities, the Rayleigh-Taylor one, simulate its behaviour and create an open-sourced state-of-the-art annotated database (RayleAI). Finally, we use adjusted experimental results and novel physical loss methodologies to validate the correspondence of the predicted results to actual physical reality to prove the models efficiency. The techniques which were developed and proved in this work can be served as essential tools for physicists in the field of hydrodynamics for investigating a variety of physical systems, and also could be used via Transfer Learning to other instabilities research. A part of the techniques can be easily applied on already exist simulation results. All models as well as the data-set that was created for this work, are publicly available at: https://github.com/scientific-computing-nrcn/SimulAI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge