Yash Melkani
TrackSorter: A Transformer-based sorting algorithm for track finding in High Energy Physics
Jul 31, 2024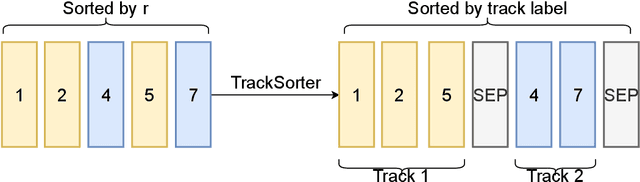
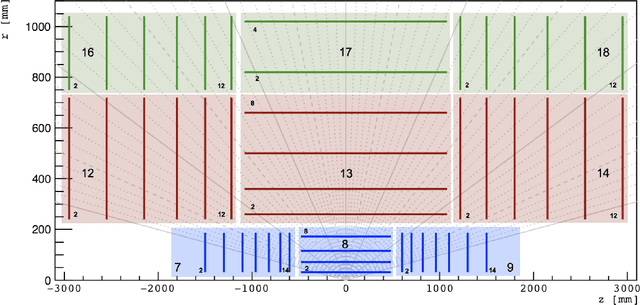
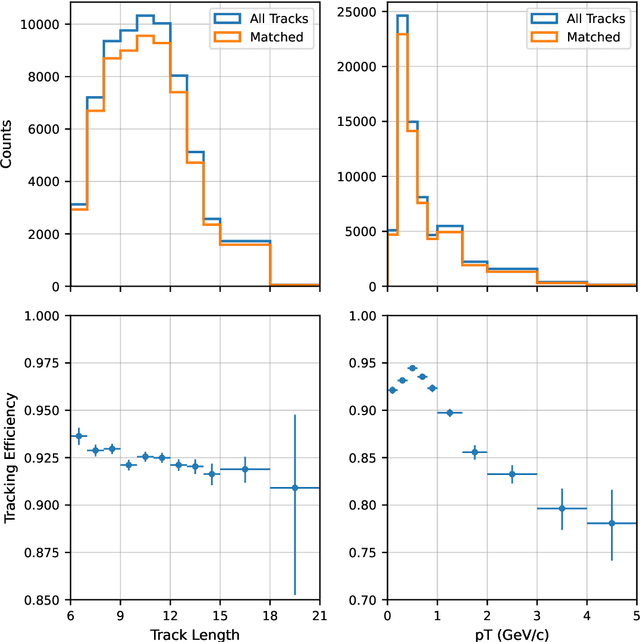
Abstract:Track finding in particle data is a challenging pattern recognition problem in High Energy Physics. It takes as inputs a point cloud of space points and labels them so that space points created by the same particle have the same label. The list of space points with the same label is a track candidate. We argue that this pattern recognition problem can be formulated as a sorting problem, of which the inputs are a list of space points sorted by their distances away from the collision points and the outputs are the space points sorted by their labels. In this paper, we propose the TrackSorter algorithm: a Transformer-based algorithm for pattern recognition in particle data. TrackSorter uses a simple tokenization scheme to convert space points into discrete tokens. It then uses the tokenized space points as inputs and sorts the input tokens into track candidates. TrackSorter is a novel end-to-end track finding algorithm that leverages Transformer-based models to solve pattern recognition problems. It is evaluated on the TrackML dataset and has good track finding performance.
A Language Model for Particle Tracking
Feb 14, 2024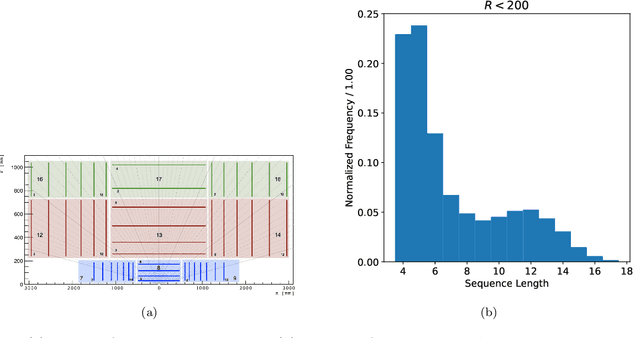

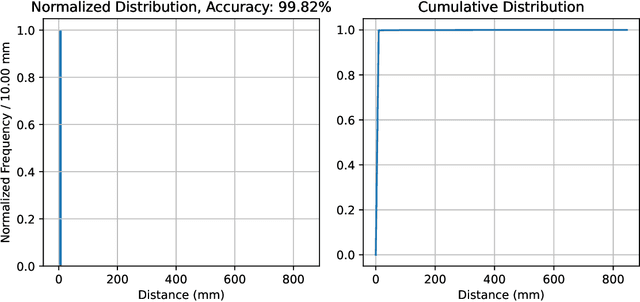
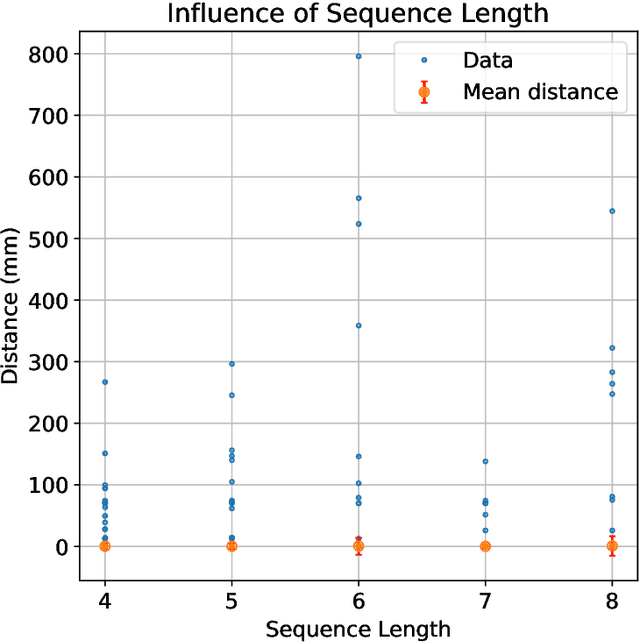
Abstract:Particle tracking is crucial for almost all physics analysis programs at the Large Hadron Collider. Deep learning models are pervasively used in particle tracking related tasks. However, the current practice is to design and train one deep learning model for one task with supervised learning techniques. The trained models work well for tasks they are trained on but show no or little generalization capabilities. We propose to unify these models with a language model. In this paper, we present a tokenized detector representation that allows us to train a BERT model for particle tracking. The trained BERT model, namely TrackingBERT, offers latent detector module embedding that can be used for other tasks. This work represents the first step towards developing a foundational model for particle detector understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge