Yangyang Zhao
Rescue Conversations from Dead-ends: Efficient Exploration for Task-oriented Dialogue Policy Optimization
May 05, 2023Abstract:Training a dialogue policy using deep reinforcement learning requires a lot of exploration of the environment. The amount of wasted invalid exploration makes their learning inefficient. In this paper, we find and define an important reason for the invalid exploration: dead-ends. When a conversation enters a dead-end state, regardless of the actions taken afterward, it will continue in a dead-end trajectory until the agent reaches a termination state or maximum turn. We propose a dead-end resurrection (DDR) algorithm that detects the initial dead-end state in a timely and efficient manner and provides a rescue action to guide and correct the exploration direction. To prevent dialogue policies from repeatedly making the same mistake, DDR also performs dialogue data augmentation by adding relevant experiences containing dead-end states. We first validate the dead-end detection reliability and then demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of the method by reporting experimental results on several dialogue datasets from different domains.
Automatic Curriculum Learning With Over-repetition Penalty for Dialogue Policy Learning
Dec 28, 2020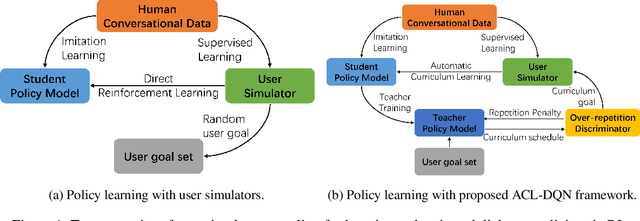
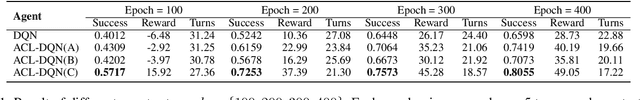
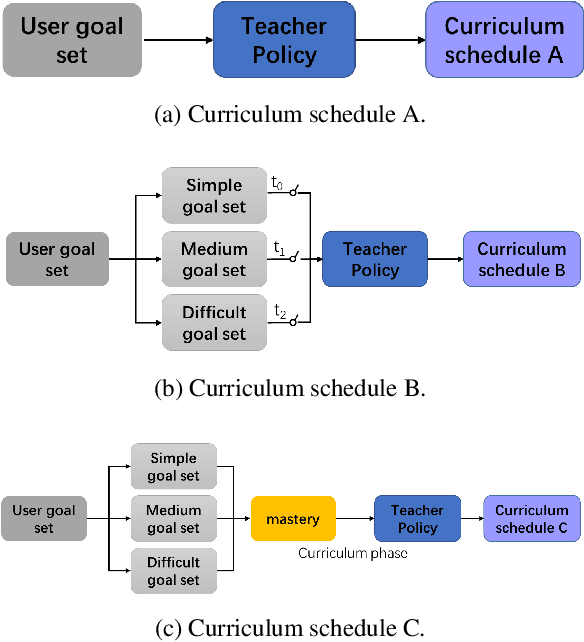
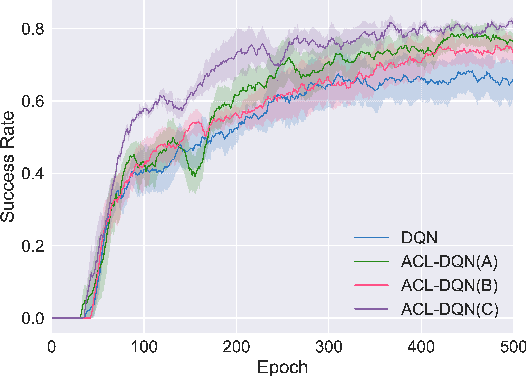
Abstract:Dialogue policy learning based on reinforcement learning is difficult to be applied to real users to train dialogue agents from scratch because of the high cost. User simulators, which choose random user goals for the dialogue agent to train on, have been considered as an affordable substitute for real users. However, this random sampling method ignores the law of human learning, making the learned dialogue policy inefficient and unstable. We propose a novel framework, Automatic Curriculum Learning-based Deep Q-Network (ACL-DQN), which replaces the traditional random sampling method with a teacher policy model to realize the dialogue policy for automatic curriculum learning. The teacher model arranges a meaningful ordered curriculum and automatically adjusts it by monitoring the learning progress of the dialogue agent and the over-repetition penalty without any requirement of prior knowledge. The learning progress of the dialogue agent reflects the relationship between the dialogue agent's ability and the sampled goals' difficulty for sample efficiency. The over-repetition penalty guarantees the sampled diversity. Experiments show that the ACL-DQN significantly improves the effectiveness and stability of dialogue tasks with a statistically significant margin. Furthermore, the framework can be further improved by equipping with different curriculum schedules, which demonstrates that the framework has strong generalizability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge