Y. Guo
Beyond Pixels: A Training-Free, Text-to-Text Framework for Remote Sensing Image Retrieval
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Semantic retrieval of remote sensing (RS) images is a critical task fundamentally challenged by the \textquote{semantic gap}, the discrepancy between a model's low-level visual features and high-level human concepts. While large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) offer a promising path to bridge this gap, existing methods often rely on costly, domain-specific training, and there is a lack of benchmarks to evaluate the practical utility of VLM-generated text in a zero-shot retrieval context. To address this research gap, we introduce the Remote Sensing Rich Text (RSRT) dataset, a new benchmark featuring multiple structured captions per image. Based on this dataset, we propose a fully training-free, text-only retrieval reference called TRSLLaVA. Our methodology reformulates cross-modal retrieval as a text-to-text (T2T) matching problem, leveraging rich text descriptions as queries against a database of VLM-generated captions within a unified textual embedding space. This approach completely bypasses model training or fine-tuning. Experiments on the RSITMD and RSICD benchmarks show our training-free method is highly competitive with state-of-the-art supervised models. For instance, on RSITMD, our method achieves a mean Recall of 42.62\%, nearly doubling the 23.86\% of the standard zero-shot CLIP baseline and surpassing several top supervised models. This validates that high-quality semantic representation through structured text provides a powerful and cost-effective paradigm for remote sensing image retrieval.
GlassNet: Label Decoupling-based Three-stream Neural Network for Robust Image Glass Detection
Aug 25, 2021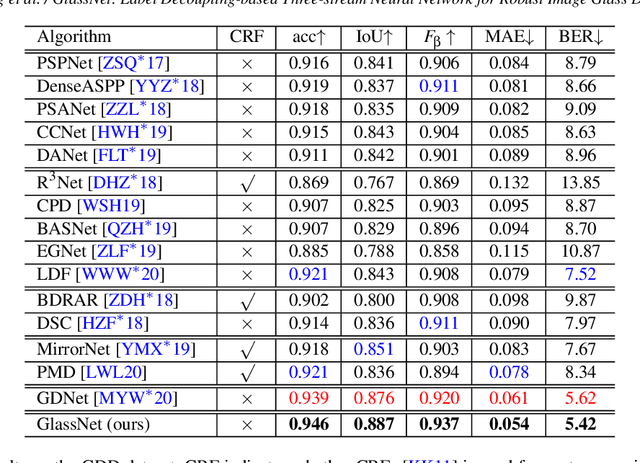
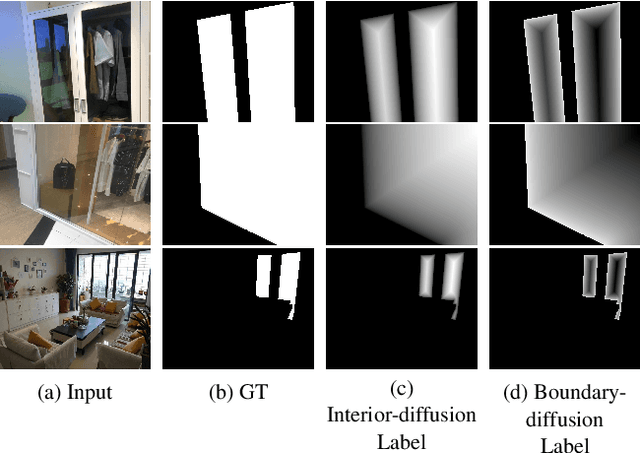
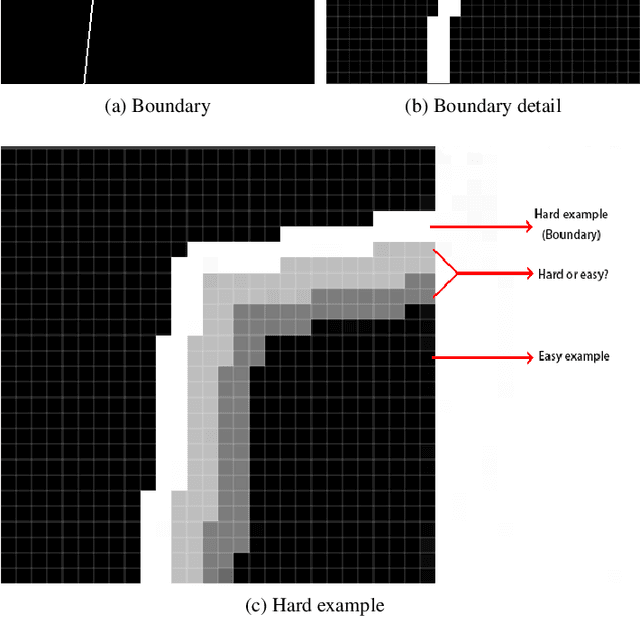
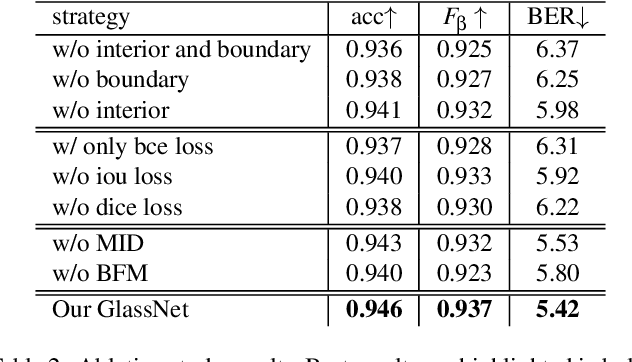

Abstract:Most of the existing object detection methods generate poor glass detection results, due to the fact that the transparent glass shares the same appearance with arbitrary objects behind it in an image. Different from traditional deep learning-based wisdoms that simply use the object boundary as auxiliary supervision, we exploit label decoupling to decompose the original labeled ground-truth (GT) map into an interior-diffusion map and a boundary-diffusion map. The GT map in collaboration with the two newly generated maps breaks the imbalanced distribution of the object boundary, leading to improved glass detection quality. We have three key contributions to solve the transparent glass detection problem: (1) We propose a three-stream neural network (call GlassNet for short) to fully absorb beneficial features in the three maps. (2) We design a multi-scale interactive dilation module to explore a wider range of contextual information. (3) We develop an attention-based boundary-aware feature Mosaic module to integrate multi-modal information. Extensive experiments on the benchmark dataset exhibit clear improvements of our method over SOTAs, in terms of both the overall glass detection accuracy and boundary clearness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge