H. Xie
AI-Driven Three-Dimensional Reconstruction and Quantitative Analysis for Burn Injury Assessment
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Accurate, reproducible burn assessment is critical for treatment planning, healing monitoring, and medico-legal documentation, yet conventional visual inspection and 2D photography are subjective and limited for longitudinal comparison. This paper presents an AI-enabled burn assessment and management platform that integrates multi-view photogrammetry, 3D surface reconstruction, and deep learning-based segmentation within a structured clinical workflow. Using standard multi-angle images from consumer-grade cameras, the system reconstructs patient-specific 3D burn surfaces and maps burn regions onto anatomy to compute objective metrics in real-world units, including surface area, TBSA, depth-related geometric proxies, and volumetric change. Successive reconstructions are spatially aligned to quantify healing progression over time, enabling objective tracking of wound contraction and depth reduction. The platform also supports structured patient intake, guided image capture, 3D analysis and visualization, treatment recommendations, and automated report generation. Simulation-based evaluation demonstrates stable reconstructions, consistent metric computation, and clinically plausible longitudinal trends, supporting a scalable, non-invasive approach to objective, geometry-aware burn assessment and decision support in acute and outpatient care.
GlassNet: Label Decoupling-based Three-stream Neural Network for Robust Image Glass Detection
Aug 25, 2021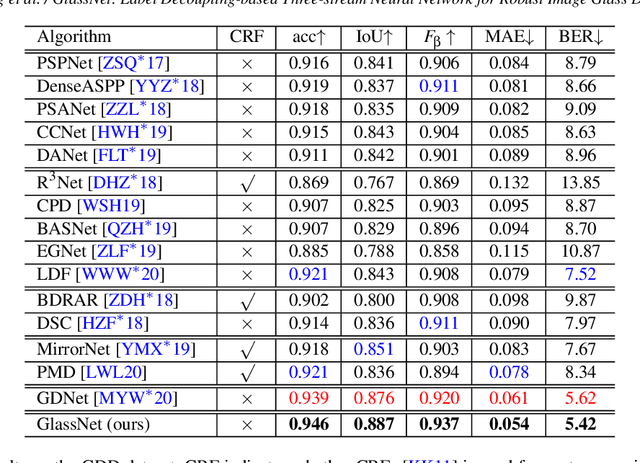
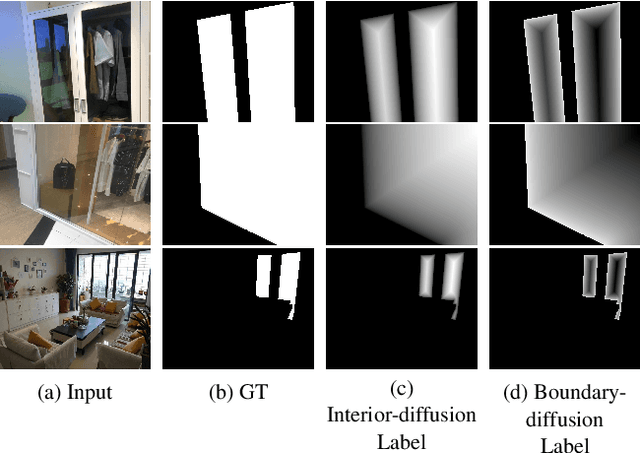
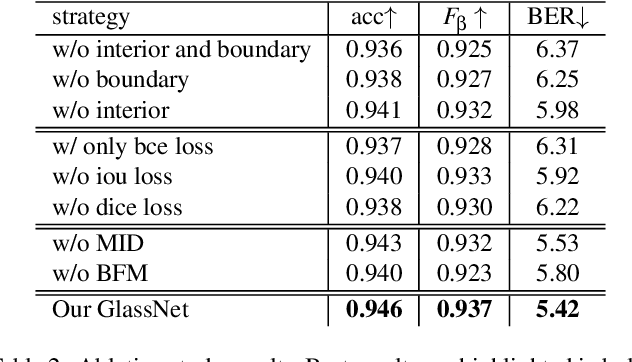

Abstract:Most of the existing object detection methods generate poor glass detection results, due to the fact that the transparent glass shares the same appearance with arbitrary objects behind it in an image. Different from traditional deep learning-based wisdoms that simply use the object boundary as auxiliary supervision, we exploit label decoupling to decompose the original labeled ground-truth (GT) map into an interior-diffusion map and a boundary-diffusion map. The GT map in collaboration with the two newly generated maps breaks the imbalanced distribution of the object boundary, leading to improved glass detection quality. We have three key contributions to solve the transparent glass detection problem: (1) We propose a three-stream neural network (call GlassNet for short) to fully absorb beneficial features in the three maps. (2) We design a multi-scale interactive dilation module to explore a wider range of contextual information. (3) We develop an attention-based boundary-aware feature Mosaic module to integrate multi-modal information. Extensive experiments on the benchmark dataset exhibit clear improvements of our method over SOTAs, in terms of both the overall glass detection accuracy and boundary clearness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge