Xutong Jin
NAT: Neural Acoustic Transfer for Interactive Scenes in Real Time
Jun 06, 2025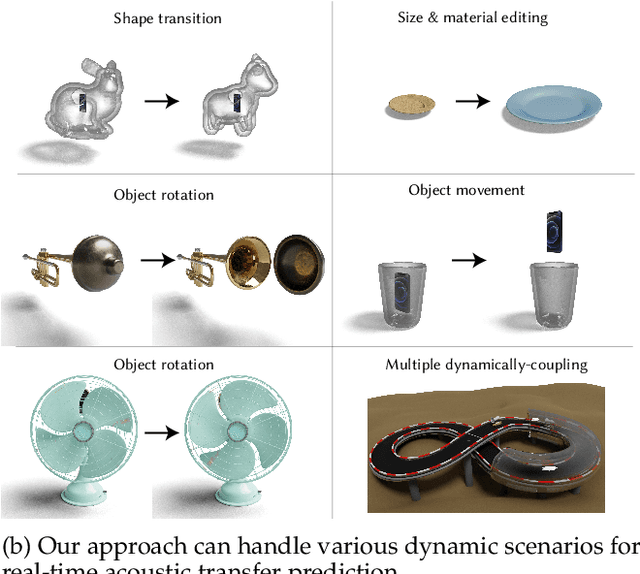
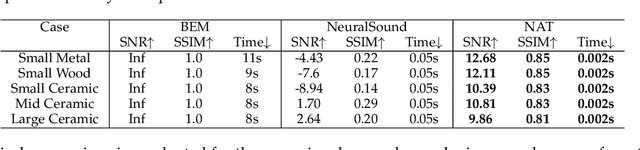
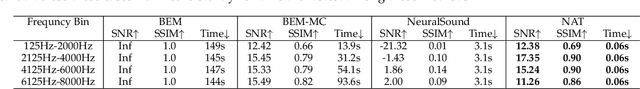
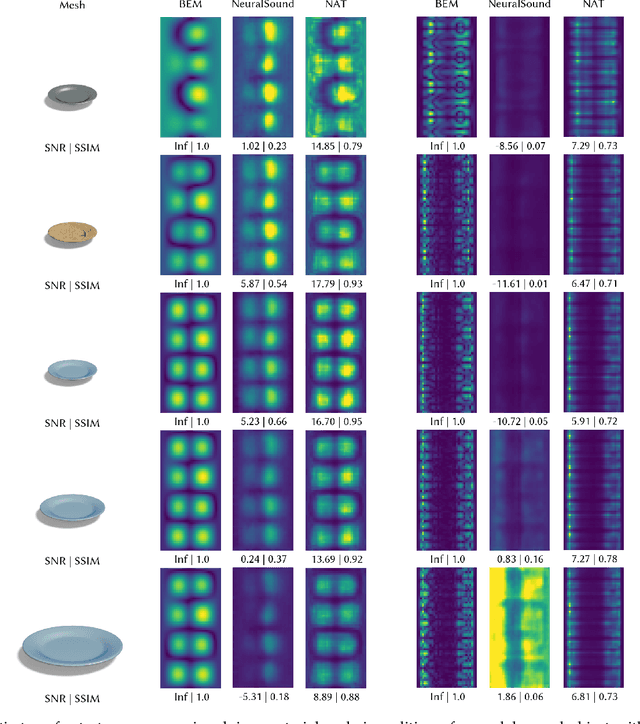
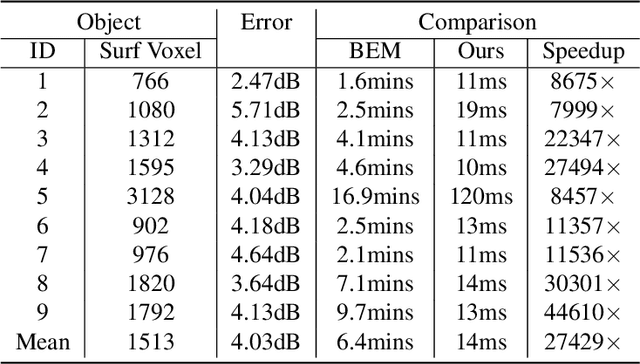
Abstract:Previous acoustic transfer methods rely on extensive precomputation and storage of data to enable real-time interaction and auditory feedback. However, these methods struggle with complex scenes, especially when dynamic changes in object position, material, and size significantly alter sound effects. These continuous variations lead to fluctuating acoustic transfer distributions, making it challenging to represent with basic data structures and render efficiently in real time. To address this challenge, we present Neural Acoustic Transfer, a novel approach that utilizes an implicit neural representation to encode precomputed acoustic transfer and its variations, allowing for real-time prediction of sound fields under varying conditions. To efficiently generate the training data required for the neural acoustic field, we developed a fast Monte-Carlo-based boundary element method (BEM) approximation for general scenarios with smooth Neumann conditions. Additionally, we implemented a GPU-accelerated version of standard BEM for scenarios requiring higher precision. These methods provide the necessary training data, enabling our neural network to accurately model the sound radiation space. We demonstrate our method's numerical accuracy and runtime efficiency (within several milliseconds for 30s audio) through comprehensive validation and comparisons in diverse acoustic transfer scenarios. Our approach allows for efficient and accurate modeling of sound behavior in dynamically changing environments, which can benefit a wide range of interactive applications such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and advanced audio production.
DeepEigen: Learning-based Modal Sound Synthesis with Acoustic Transfer Maps
Aug 17, 2021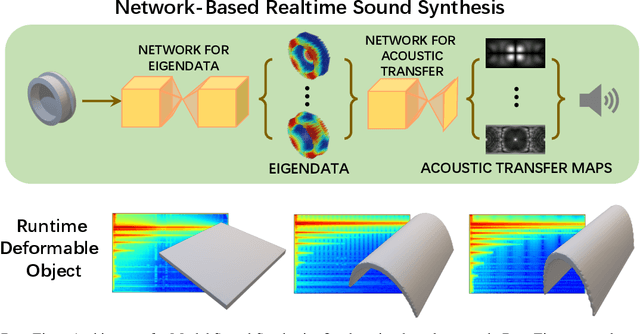
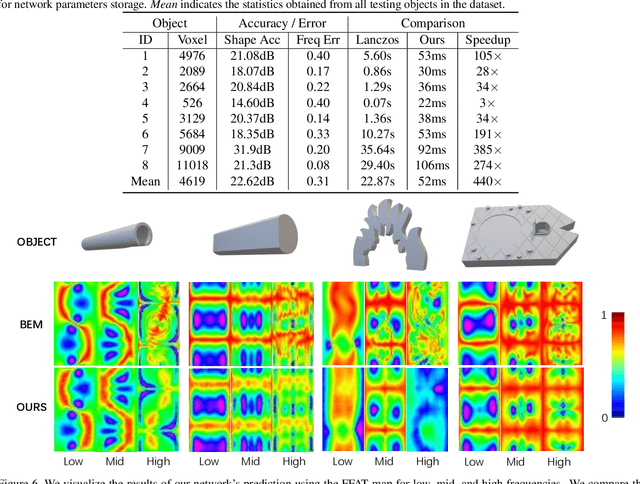
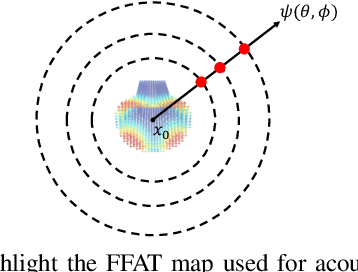
Abstract:We present a novel learning-based approach to compute the eigenmodes and acoustic transfer data for the sound synthesis of arbitrary solid objects. Our approach combines two network-based solutions to formulate a complete learning-based 3D modal sound model. This includes a 3D sparse convolution network as the eigendecomposition solver and an encoder-decoder network for the prediction of the Far-Field Acoustic Transfer maps (FFAT Maps). We use our approach to compute the vibration modes (eigenmodes) and FFAT maps for each mode (acoustic data) for arbitrary-shaped objects at interactive rates without any precomputed dataset for any new object. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and benefits of our approach. We compare its accuracy and efficiency with physically-based sound synthesis methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge