Xuqi Mao
MAPN: Enhancing Heterogeneous Sparse Graph Representation by Mamba-based Asynchronous Aggregation
Feb 23, 2025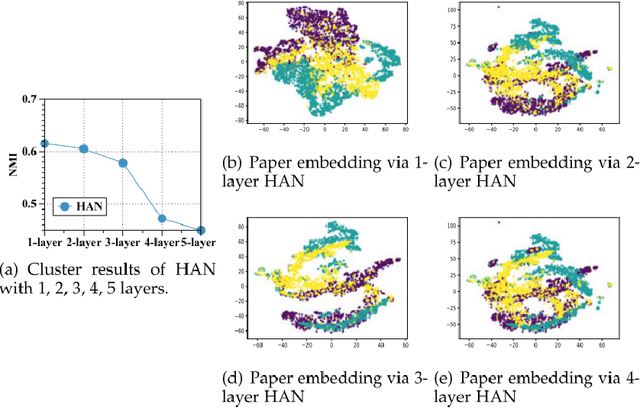
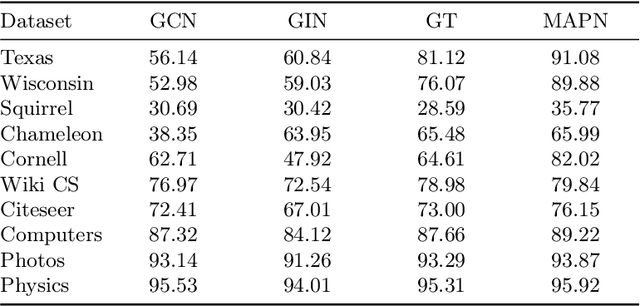
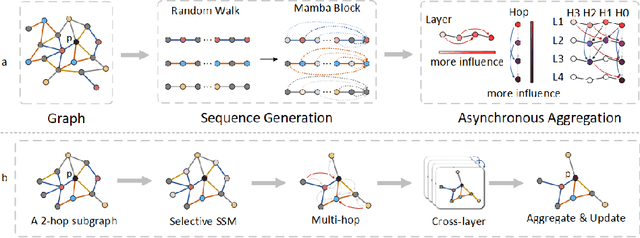
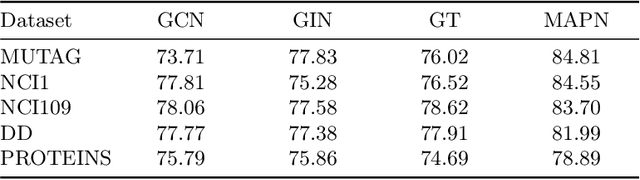
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have become the state of the art for various graph-related tasks and are particularly prominent in heterogeneous graphs (HetGs). However, several issues plague this paradigm: first, the difficulty in fully utilizing long-range information, known as over-squashing; second, the tendency for excessive message-passing layers to produce indistinguishable representations, referred to as over-smoothing; and finally, the inadequacy of conventional MPNNs to train effectively on large sparse graphs. To address these challenges in deep neural networks for large-scale heterogeneous graphs, this paper introduces the Mamba-based Asynchronous Propagation Network (MAPN), which enhances the representation of heterogeneous sparse graphs. MAPN consists of two primary components: node sequence generation and semantic information aggregation. Node sequences are initially generated based on meta-paths through random walks, which serve as the foundation for a spatial state model that extracts essential information from nodes at various distances. It then asynchronously aggregates semantic information across multiple hops and layers, effectively preserving unique node characteristics and mitigating issues related to deep network degradation. Extensive experiments across diverse datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of MAPN in graph embeddings for various downstream tasks underscoring its substantial benefits for graph representation in large sparse heterogeneous graphs.
FHGE: A Fast Heterogeneous Graph Embedding with Ad-hoc Meta-paths
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have emerged as the state of the art for a variety of graph-related tasks and have been widely used in Heterogeneous Graphs (HetGs), where meta-paths help encode specific semantics between various node types. Despite the revolutionary representation capabilities of existing heterogeneous GNNs (HGNNs) due to their focus on improving the effectiveness of heterogeneity capturing, the huge training costs hinder their practical deployment in real-world scenarios that frequently require handling ad-hoc queries with user-defined meta-paths. To address this, we propose FHGE, a Fast Heterogeneous Graph Embedding designed for efficient, retraining-free generation of meta-path-guided graph embeddings. The key design of the proposed framework is two-fold: segmentation and reconstruction modules. It employs Meta-Path Units (MPUs) to segment the graph into local and global components, enabling swift integration of node embeddings from relevant MPUs during reconstruction and allowing quick adaptation to specific meta-paths. In addition, a dual attention mechanism is applied to enhance semantics capturing. Extensive experiments across diverse datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of FHGE in generating meta-path-guided graph embeddings and downstream tasks, such as link prediction and node classification, highlighting its significant advantages for real-time graph analysis in ad-hoc queries.
HetFS: A Method for Fast Similarity Search with Ad-hoc Meta-paths on Heterogeneous Information Networks
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Numerous real-world information networks form Heterogeneous Information Networks (HINs) with diverse objects and relations represented as nodes and edges in heterogeneous graphs. Similarity between nodes quantifies how closely two nodes resemble each other, mainly depending on the similarity of the nodes they are connected to, recursively. Users may be interested in only specific types of connections in the similarity definition, represented as meta-paths, i.e., a sequence of node and edge types. Existing Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network (HGNN)-based similarity search methods may accommodate meta-paths, but require retraining for different meta-paths. Conversely, existing path-based similarity search methods may switch flexibly between meta-paths but often suffer from lower accuracy, as they rely solely on path information. This paper proposes HetFS, a Fast Similarity method for ad-hoc queries with user-given meta-paths on Heterogeneous information networks. HetFS provides similarity results based on path information that satisfies the meta-path restriction, as well as node content. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of HetFS in addressing ad-hoc queries, outperforming state-of-the-art HGNNs and path-based approaches, and showing strong performance in downstream applications, including link prediction, node classification, and clustering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge